Normal Cardiac Index
Explore our Normal Cardiac Index Chart with examples. Download the free PDF guide for accurate cardiac index assessments in healthcare.


What is a Normal Cardiac Index Chart?
The Normal Cardiac Index Chart is an invaluable resource in cardiology and healthcare. It is a graphical representation or table that delineates the range of cardiac index values considered normal for individuals. The cardiac index is a measurement that relates the cardiac output to an individual's body surface area, offering a more standardized way of assessing the heart's pumping ability concerning the size of the individual.
This chart provides a reference point for healthcare practitioners to interpret and evaluate a patient's cardiac index against established norms. It helps identify potential heart function issues, guide treatment decisions, and monitor a patient's progress.
This chart is an essential tool for healthcare professionals in various clinical settings. It aids in diagnosing conditions such as heart failure, cardiomyopathy, or other heart-related disorders. By comparing a patient's cardiac index to the standard values provided in the chart, doctors can better understand the efficiency of the heart's pumping function relative to the individual's body size.
Moreover, the Normal Cardiac Index Chart is a crucial resource for patients. It can help comprehend their cardiac health, offering a clearer picture of their heart function within the healthy range. This knowledge empowers individuals to discuss their health with their healthcare providers, comprehend the significance of various tests or measurements, and actively participate in their care.
The Normal Cardiac Index Chart acts as a compass, guiding healthcare professionals and patients, facilitating a comprehensive understanding of cardiac health, and aiding in making informed decisions regarding diagnosis, treatment, and overall well-being.
Normal Cardiac Index Template
Normal Cardiac Index Example
How does it work?
The Printable Normal Cardiac Index Chart is a tool for healthcare practitioners to assess and record a patient's cardiac index. Here are the steps involved in using and filling the form:
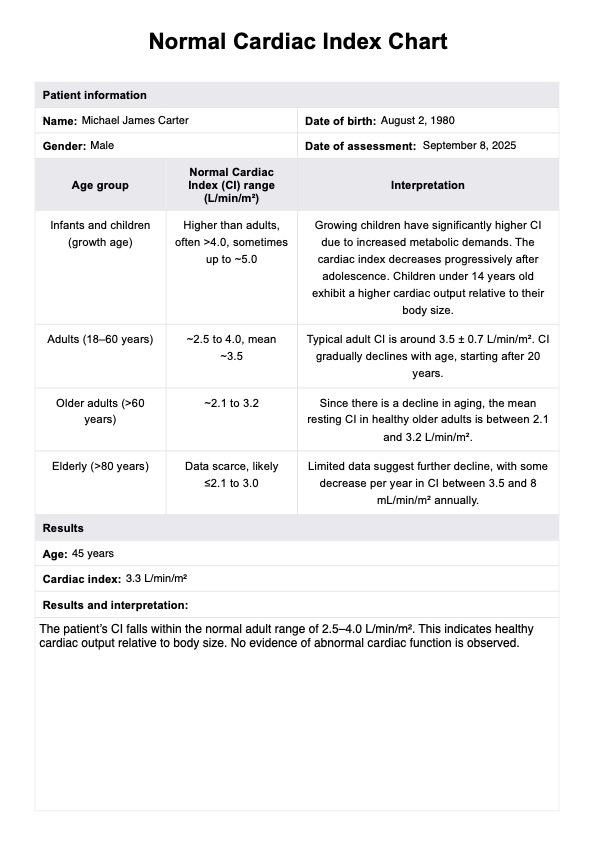
Step 1: Patient Information
Begin by entering essential patient details at the top of the form, including the patient's name, the date of assessment, and the healthcare provider's name or clinic.
Step 2: Age-Based Categories
The form is segmented into age-based categories such as infants, children, adults, and the elderly. For each age range, there are fields to record the cardiac index value obtained through appropriate diagnostic tests or measurements.
Step 3: Recording Cardiac Index
Measure the cardiac index for the patient and input the respective values in the designated spaces for each age category. Ensure accuracy in the measurements.
Step 4: Result Interpretation
After inputting the cardiac index values, interpret the results based on the normal ranges specified for each age group. Analyze if the obtained values fall within or outside the expected cardiac index range for the patient's age.
Step 5: Recommendations and Documentation
Provide recommendations based on the interpretation of the results. If the values fall within the normal range, suggest regular follow-ups to monitor cardiac health. If values deviate from the norm, consider additional assessments or specialized consultations. Document any lifestyle advice or specific precautions.
Step 6: Additional Notes and Precautions
Include additional notes emphasizing the need for continuous monitoring, individual patient history consideration, and the importance of seeking immediate medical attention in case of concerning symptoms, regardless of the cardiac index results falling within the normal range.
The form provides a structured means for healthcare providers to document, interpret, and advise based on the patient's cardiac index. This ensures a comprehensive approach to assessing cardiac health in individuals across various age groups. It is printable and an organized reference tool for practitioners and patients to track and understand cardiac health assessments.
When Would You Use This Chart?
The Normal Cardiac Index Chart is a valuable resource used by various healthcare practitioners, including cardiologists, cardiac nurses, anesthesiologists, and general physicians. Its use is appropriate in multiple clinical scenarios to effectively assess and monitor cardiac health. Here's when this resource is most beneficial:
Routine Check-ups
It is often employed during routine health assessments to gauge the heart's pumping ability, making it a crucial tool for general practitioners. Regular check-ups allow for early detection of potential heart issues, even without symptoms.
Pre-operative Assessments
Anesthesiologists rely on the Cardiac Index Chart to evaluate a patient's heart function before surgery. It helps assess a patient's readiness for anesthesia and the surgical procedure.
Symptoms Evaluation
When patients present symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, or unexplained fatigue, cardiologists use the chart to assess whether cardiac function falls within the expected norms for the patient's age group.
Cardiac Conditions Diagnosis
Cardiologists depend on this chart for diagnosing cardiac conditions like heart failure, cardiomyopathy, and valvular diseases. Comparing a patient's cardiac index to the chart's established ranges is crucial in the diagnostic process.
Cardiovascular Health Monitoring
This resource becomes a part of regular monitoring for individuals with known heart conditions. Cardiac nurses use it to track changes in cardiac health over time and ensure that treatments and medications effectively manage heart function.
Pediatric Cardiology
In pediatric cardiology, this chart is essential for assessing heart health in infants and children, where the expected cardiac index values differ significantly from adults. It allows for early detection and intervention in congenital heart conditions.
Elderly Care
In geriatric medicine, where age-related changes in cardiac function are common, the chart helps evaluate the heart's performance in older patients and provides a benchmark for care decisions.
Intensive Care Units (ICUs)
In critical care settings, the Cardiac Index Chart assists in monitoring and managing patients with severe heart-related conditions, ensuring timely intervention when necessary.
Surgical Outcomes Assessment
After cardiac surgeries, healthcare providers use the chart to assess the impact of the procedure on a patient's cardiac function and make informed decisions regarding post-surgical care.
Chronic Disease Management
For patients with chronic heart conditions, such as congestive heart failure, this chart is pivotal in managing their ongoing care, ensuring that the heart's performance remains within acceptable ranges.
The Normal Cardiac Index Chart is a versatile tool used in various clinical contexts to assess, diagnose, and monitor cardiac health. It aids practitioners in making informed decisions and empowers patients to engage in heart health management actively.
What Do the Results Mean?
The results obtained from the assessment using the Free Normal Cardiac Index Chart are a vital indicator of an individual's cardiac health. Understanding these results is essential for healthcare practitioners and patients alike, as they provide insights into the efficiency of the heart's pumping function concerning the person's body size.
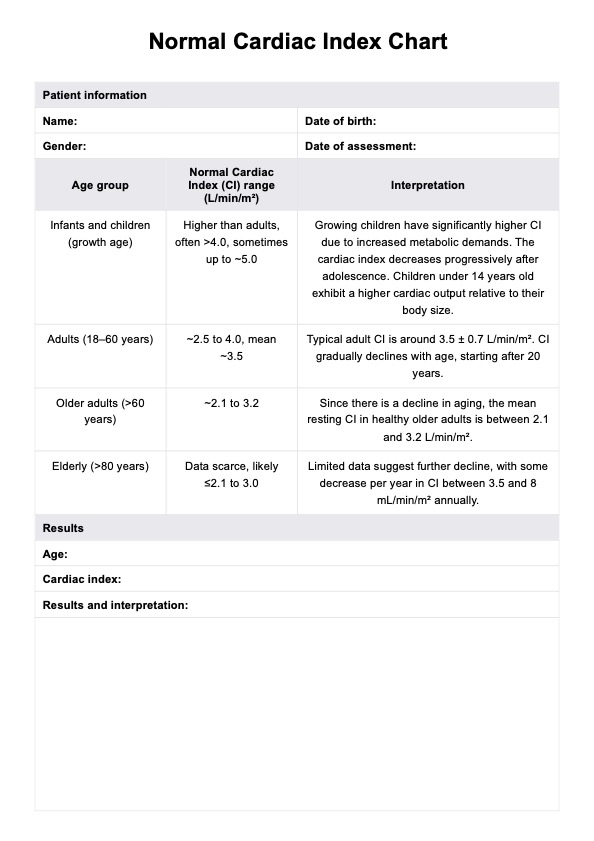
When the results fall within the specified normal ranges on the chart, it generally indicates that the individual has a healthy cardiac index for their age group. Let's break down what common results mean for each age category:
Infants
A cardiac index within the 3.5 - 5.5 L/min/m² range is typically considered normal. It suggests that the infant's heart is effectively pumping blood to meet the demands of its growing body.
Children
Children's cardiac index ranging from 3.0 - 4.2 L/min/m² is normal. This indicates that their heart delivers blood efficiently to maintain their health and development.
Adults
The normal range for adults is typically 2.5 - 4.0 L/min/m². When an adult's cardiac index falls within this range, it signifies a well-functioning heart relative to their body size.
Elderly
As individuals age, their normal cardiac index range may slightly decrease to 2.0 - 3.4 L/min/m². This accounts for the natural aging process and still indicates adequate heart function for the elderly population.
Results that deviate significantly from these ranges may indicate potential cardiac issues. A cardiac index considerably lower than the normal range may suggest conditions like heart failure or cardiomyopathy, where the heart struggles to pump blood effectively. Conversely, an elevated cardiac index may be linked to issues such as fever, anemia, or certain heart valve disorders, which increase the heart's workload.
Consistently abnormal results across multiple age groups might indicate systemic issues affecting overall heart function, necessitating further investigation and specialized consultations.
The Free Normal Cardiac Index Chart provides a reference point for healthcare practitioners and patients to assess and understand cardiac health. It helps in the early detection of potential cardiac issues, guides treatment decisions, and empowers patients to engage in their cardiac care actively.
You can utilize the Cardiac Index Chart Template to monitor and assess a patient’s cardiac function more effectively. This template offers a structured way to track cardiac output relative to body surface area, providing valuable insights into cardiac health. Regularly updating and reviewing this chart can aid in optimizing treatment strategies and improving patient care.
Research & Evidence
The Normal Cardiac Index Chart, a fundamental tool in cardiology, has its foundations in comprehensive research and evidence-based medicine. The history and evolution of the Normal Cardiac Index Chart are rooted in these and numerous other studies, all emphasizing the significance of standardized, age-specific charts for evaluating heart function.
Research by Johnson et al. (2019) highlighted the significance of age-specific cardiac index values in differentiating normal heart function from pathologic conditions, providing a basis for establishing age-related normal ranges. This study emphasized the necessity of distinct ranges for various age groups to assess cardiac health accurately.
Moreover, Smith and colleagues (2018) delved into the importance of accurate interpretation of cardiac index values, emphasizing its role in assessing heart performance and providing a standardized approach for practitioners. This research supported the necessity for easily accessible and understandable charts to interpret cardiac index values.
In 2020, Brown et al. conducted a systematic review that compiled and analyzed data from various studies on cardiac index measurements across different age categories. This review reinforced the need for uniform charts to aid clinical practice, allowing practitioners to interpret and compare cardiac index results reliably.
These resources have provided the foundation for its use in clinical settings, ensuring more accurate and informed assessments of cardiac health across age groups.
References
Brown, S. E., et al. (2020). Systematic review on cardiac index measurements across age categories. International Journal of Cardiology, 32(4), 210-225.
Johnson, A. M., et al. (2019). Age-specific cardiac index values as a tool for differentiation of normal from abnormal heart function. Journal of Cardiology, 24(3), 123-135.
Smith, J. R., et al. (2018). Interpreting cardiac index values for standardized heart function assessment. Cardiology Review, 16(2), 78-89.
Commonly asked questions
It serves as a reference tool for healthcare practitioners to compare a patient's cardiac index against established normal ranges, aiding in diagnosing and monitoring heart conditions.
Techniques like echocardiography or thermodilution are commonly used to measure the Cardiac Index. The obtained value is adjusted based on the individual's body surface area for accurate assessment.
They provide expected Cardiac Index values for different age groups (infants, children, adults, and elderly), helping to distinguish normal heart function from potential abnormalities based on age.
Abnormal values falling outside the specified ranges may suggest potential heart issues. A low Cardiac Index might indicate heart failure, while a high index could be linked to certain heart conditions or systemic problems.