Cardiac Index Chart
Track and interpret key cardiac metrics with our Cardiac Index Chart. Download now for precise cardiovascular assessments.


What Is a Cardiac Index Chart?
The Cardiac Index Chart is a specialized tool that provides valuable insights into the health of a patient's heart. By graphically representing a patient's cardiac output about their body surface area, this chart offers a dynamic snapshot of the efficiency of the heart's pumping mechanism.
This enables healthcare practitioners to make informed decisions about cardiovascular assessments and assess cardiac function in critical care settings or when monitoring patients with cardiovascular conditions.
One of the key benefits of the Cardiac Index Chart is that it normalizes cardiac output to the patient's body surface area. This makes it possible to evaluate cardiac performance across individuals of varying sizes, making the chart a valuable resource for healthcare practitioners.
By presenting data clearly and comprehensibly, the Cardiac Index Chart enables quick analysis and informed decision-making, which can be crucial in emergencies.
The Carepatron platform has been designed to make it easy for healthcare practitioners to access and interpret the Cardiac Index Chart. The user-friendly interface ensures that even those not specialized in cardiovascular assessments can use this valuable resource.
Whether you're a seasoned cardiologist or a general practitioner, the Carepatron platform empowers you to make data-driven decisions, contributing to more effective patient care.
Cardiac Index Chart Template
Cardiac Index Chart Example
How Does It Work?
Exploring the Cardiac Index Chart's functionality involves a systematic process thoughtfully designed for simplicity and accuracy, even when using a template. Here's a brief guide to navigating the template:
Accessing the Form
Commence the Cardiac Index Chart assessment by acquiring a meticulously prepared printed copy of the dedicated template. Ensure the template encompasses all necessary sections, laying the foundation for a comprehensive evaluation.
Providing Patient Details
Delve into the assessment by meticulously filling in the provided spaces dedicated to patient information. Capture essential details such as the patient's name, age, and pertinent medical history, ensuring a holistic and personalized patient profile.
Specifying Body Surface Area (BSA)
Navigate to the section expressly designated for entering critical metrics. Input the patient's body surface area with precision—an indispensable step for accurate normalization of cardiac output data.
Entering Cardiac Output Values
Record the patient's cardiac output measurements within the assigned spaces, typically denoted in liters per minute (L/min). This step quantifies the heart's efficiency, laying the groundwork for nuanced analysis.
Verifying Units and Parameters
Ensure the utmost precision by meticulously confirming the accuracy of units and parameters specified on the printed template. This verification process is crucial to guarantee a meticulous Cardiac Index calculation.
Reviewing and Interpreting Results
Conclude the assessment by engaging in a comprehensive examination of the generated chart. Extract nuanced insights into the patient's cardiac performance, fostering an informed decision-making process within the clinical context.
When Would You Use This Chart?
The Cardiac Index Chart proves to be an invaluable resource for healthcare practitioners, particularly in scenarios where precise cardiovascular assessments are paramount. Here are vital instances when leveraging this resource is crucial:
- Cardiovascular Health Monitoring: Healthcare practitioners, including cardiologists and cardiovascular specialists, frequently utilize the Cardiac Index Chart to monitor patients with known heart conditions. It serves as a dynamic tool to assess changes in cardiac output over time, allowing for a nuanced understanding of the patient's cardiovascular health.
- Critical Care Settings: The chart becomes a lifeline for healthcare professionals in intensive care units (ICUs) and critical care environments. It aids in real-time assessment of cardiac performance, guiding interventions for patients in acute conditions and ensuring optimal hemodynamic management.
- Surgical Planning and Post-Operative Care: Cardiac surgeons and anesthesiologists utilize the chart as a preoperative assessment tool. It helps understand the patient's baseline cardiac function and guides decisions during surgery. Postoperatively, it facilitates monitoring for any fluctuations in cardiac output, informing tailored recovery plans.
- Chronic Disease Management: For practitioners managing chronic diseases such as heart failure, the Cardiac Index Chart is an indispensable resource. Regular use allows for the early detection of deteriorating cardiac function, enabling proactive adjustments to medication and treatment plans to optimize patient outcomes.
- Critical Pediatric Care: In pediatric cardiology, the chart finds application in assessing and monitoring the cardiovascular health of young patients. Its use is vital in guiding interventions and treatment strategies for children with congenital heart conditions.
What Do the Results Mean?
Understanding the results derived from the Cardiac Index Chart is vital for healthcare practitioners to make informed decisions about patient care. Here's an insight into common results and their implications:
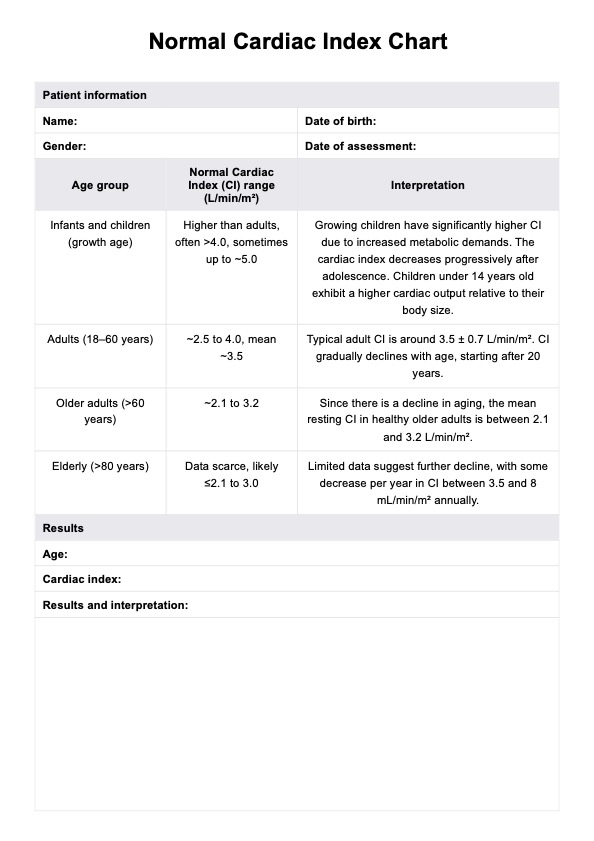
- Normal Range: In a healthy individual, the Cardiac Index typically falls within a standard range, indicating that the heart effectively meets the body's metabolic demands. A Cardiac Index within this range is generally a positive indicator of cardiovascular health.
- High Cardiac Index: An elevated Cardiac Index may suggest a hyperdynamic state where the heart pumps blood more vigorously than usual. This can be seen in conditions such as sepsis, hyperthyroidism, or early stages of shock. While it may initially compensate for reduced blood flow, prolonged high values indicate an underlying issue requiring attention.
- Low Cardiac Index: A lower-than-normal Cardiac Index may indicate reduced cardiac output, potentially pointing to conditions like heart failure, cardiogenic shock, or severe dehydration. In such cases, interventions may be necessary to enhance cardiac function and improve overall hemodynamics.
- Fluctuating Values: Occasional fluctuations in the Cardiac Index could be expected, especially in response to activity levels or stress changes. However, persistent and significant variations may warrant further investigation to identify and address the root cause.
- Post-Operative Changes: In the context of surgical interventions, a temporary decrease in the Cardiac Index may be expected due to the physiological response to anesthesia or the surgical procedure. Post-operative monitoring is crucial to ensure a gradual return to the normal range as the patient recovers.
Access to a Free Cardiac Index Chart allows practitioners to assess and interpret these results comprehensively. It is a dynamic tool to track trends over time, facilitating early detection of abnormalities and timely interventions for optimized patient outcomes.
Research & Evidence
The Cardiac Index Chart, a cornerstone in cardiovascular medicine, draws strength from a rich history steeped in thorough research and clinical evidence. It emerged in the mid-20th century, and understanding the limitations in assessing cardiac output without factoring in body size variations led to the creation of the Cardiac Index. This normalized measure accurately portrays cardiac performance across diverse patient populations (Cecconi et al., 2019).
Numerous studies in various clinical contexts affirm the utility of the Cardiac Index. Researchers have delved into its effectiveness in heart failure monitoring, critical care scenarios, and interventions within surgical and pediatric cardiology realms (Chen et al., 2021). Notably, the Cardiac Index consistently provides valuable insights into hemodynamic status, facilitating practitioners in making well-informed decisions (Guo et al., 2019).
Beyond this, the evidence supporting the Cardiac Index Chart extends to its role in guiding fluid resuscitation strategies, optimizing cardiovascular performance in septic patients, and contributing to nuanced management in critically ill individuals (Yartsev). Evolving with technological advancements, the seamless integration of the Cardiac Index Chart into digital platforms enhances its accessibility and usability in modern healthcare practices (Michałowska & Śmiałek, 2023).
References
Cecconi, M., Elliott, V., & Caliandro, F. (2019, January 17). Low Cardiac output. Cancer Therapy Advisor. https://www.cancertherapyadvisor.com/home/decision-support-in-medicine/critical-care-medicine/low-cardiac-output/
Chen, W., Zhang, Z., Tao, L., Xu, Q., Wei, X., & Chen, M. (2021). Afterload-related cardiac performance identifies cardiac impairment and associates with outcome in patients with septic shock: a retrospective cohort study. Journal of Intensive Care, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40560-021-00549-5
Guo, Z., Yin, M., Kong, J., Wang, B., Dai, K., Zuo, T., Yu, G., & Bao, Y. (2019). Relationship analysis of central venous-to-arterial carbon dioxide difference and cardiac index for septic shock. Scientific Reports, 9(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-45252-6
Michałowska, J., & Śmiałek, D. (2023, July 21). Cardiac Index Calculator. https://www.omnicalculator.com/health/cardiac-index
Yartsev, A. (n.d.). Derived values from cardiac output measurement devices. Deranged Physiology. https://derangedphysiology.com/main/cicm-primary-exam/required-reading/cardiovascular-system/Chapter%20812/derived-values-cardiac-output-measurement-devices
Commonly asked questions
Healthcare professionals, including cardiologists, cardiovascular specialists, anesthesiologists, and critical care practitioners, typically request Cardiac Index Charts.
Cardiac Index Charts are used in various clinical scenarios, such as routine cardiovascular monitoring, critical care settings, surgical planning, post-operative care, and chronic disease management.
Healthcare practitioners use Cardiac Index Charts to assess and normalize cardiac output data, providing insights into cardiovascular performance. The charts aid in informed decision-making, especially in adjusting treatment plans or interventions.
The time to complete a Cardiac Index Chart depends on the patient's complexity and the specific clinical context. Typically, the process is efficient and seamlessly integrated into the healthcare practitioner's workflow for timely assessments.