An HSCRP blood test measures the level of high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in the blood, which is a marker of inflammation. It's used to assess the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
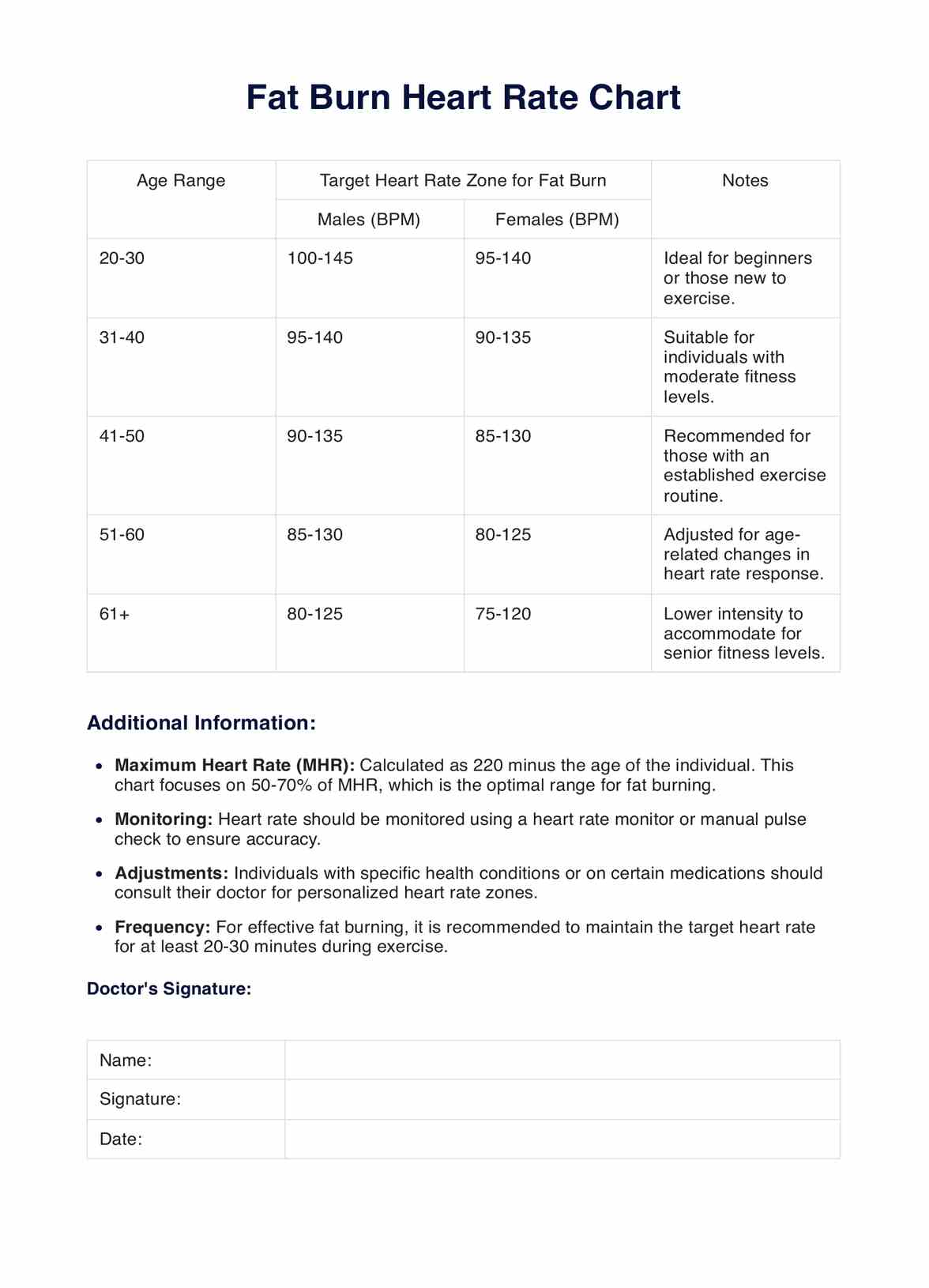
Fat Burn Heart Rate Chart
Explore our comprehensive guide on HSCRP Blood Tests with a free PDF download for healthcare professionals. Learn about its uses, interpretation, and more.
Use Template
Fat Burn Heart Rate Chart Template
Commonly asked questions
The frequency of the HSCRP blood test depends on individual risk factors and medical history. It's best to consult with a healthcare provider for personalized advice.
Yes, lifestyle changes such as a balanced diet, regular exercise, and avoiding smoking can help lower HSCRP levels and reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











