Heart Attack
Use our Heart Attack Test template to streamline diagnosis with ECG, Troponin tests, and echocardiogram. Ensure accurate heart attack detection and treatment.


What is an acute myocardial infarction test?
An acute myocardial infarction test, commonly known as the Heart Attack Test, is a series of diagnostic evaluations used to determine if an individual has experienced a myocardial infarction (MI). When a heart attack occurs, the blood flow to a part of the heart muscle becomes severely reduced or completely blocked, typically due to plaque buildup in the coronary arteries. This blockage leads to damage or death of heart muscle tissue, necessitating prompt diagnosis and treatment to minimize lasting harm.
High blood pressure and existing conditions such as coronary artery disease are significant risk factors for heart attacks. Recognizing symptoms of a heart attack, particularly chest pain, warrants immediate medical evaluation. Unlike certain medical conditions that can be diagnosed with a single test, diagnosing a heart attack requires multiple assessments, each designed to provide different types of information about the heart’s health and function. Additionally, a family history of heart disease can significantly influence the likelihood of a heart attack and necessitate more frequent and comprehensive medical evaluations and screenings.
The most common Heart Attack Tests include clinical assessments, blood tests for cardiac enzymes, electrocardiograms (ECG/EKG), echocardiograms, and imaging studies like coronary angiography and cardiac computed tomography (Mayo Clinic, 2023).
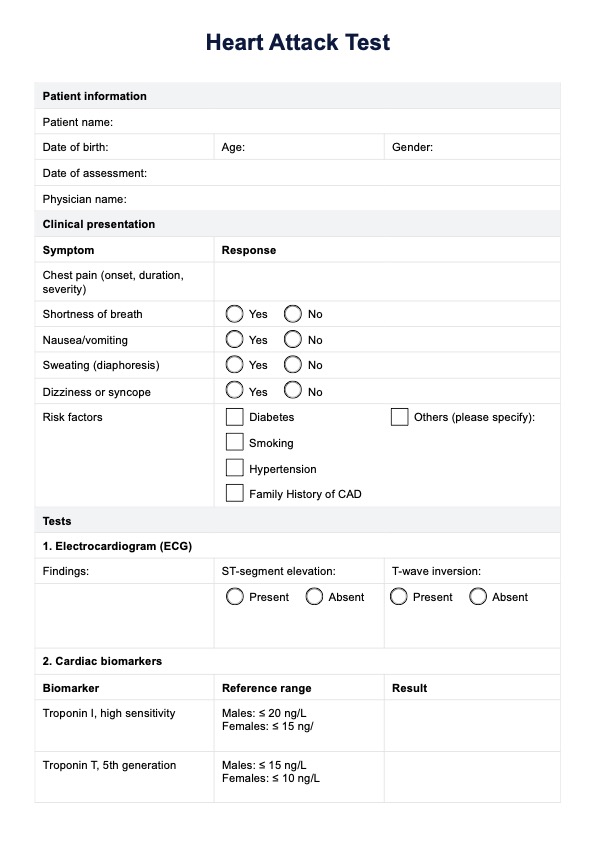
Heart Attack Template
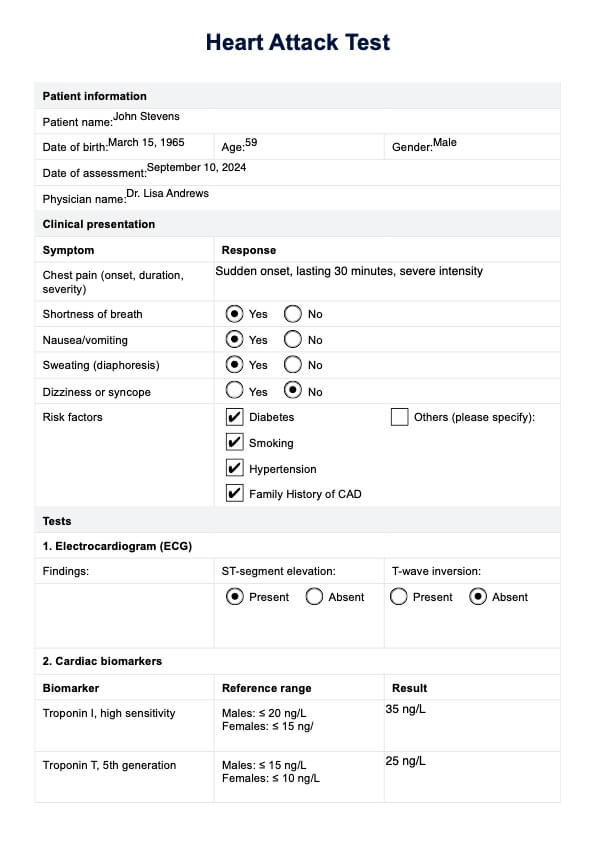
Heart Attack Example
Key diagnostic tools in heart attack testing
Diagnosing a heart attack requires multiple tests that provide essential information about the heart’s function and potential damage. Each test serves a specific purpose in identifying the cause and extent of myocardial injury, and the combination of results helps healthcare providers create an effective treatment plan. Here are the key diagnostic tools typically used in heart attack testing, focusing on why specific tests are prioritized.
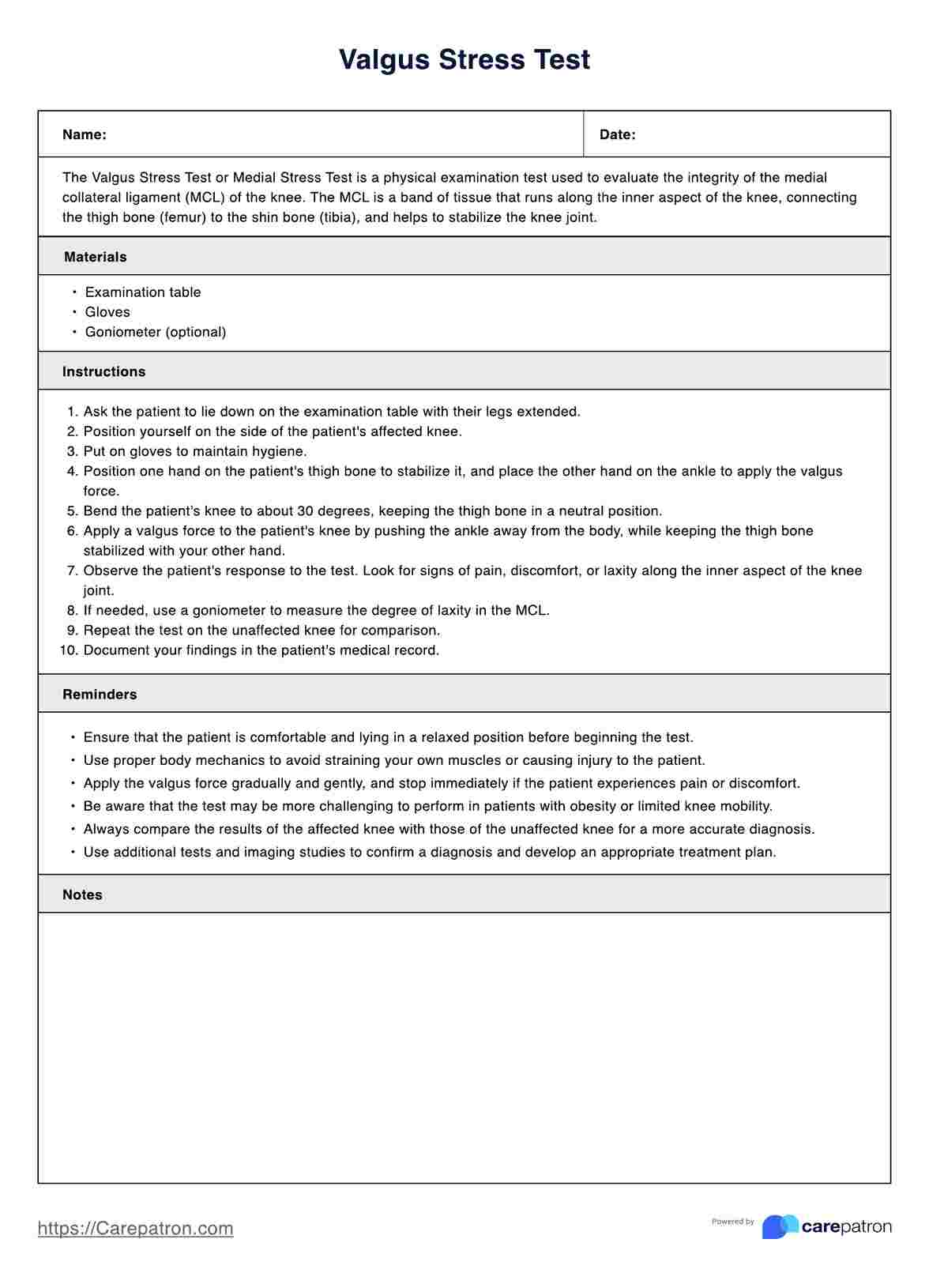
1. Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is often the first test conducted when a heart attack is suspected. This test records the electrical signals from blood vessels that travel through the heart (National Institutes of Health, 2022). Analyzing the heart's electrical activity can reveal abnormal heart rhythms, such as arrhythmias and heart structure changes.
Specifically, it can show ST-segment elevation, a hallmark sign of an ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). It can also detect non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) through T-wave inversions or abnormal Q-waves, indicating damage to the heart muscle.
Why it's essential: The ECG is a non-invasive, rapid test that provides critical information about the presence of a heart attack, particularly STEMI or NSTEMI. It helps determine whether immediate intervention, such as reperfusion therapy, is necessary.
2. Blood tests for cardiac biomarkers (Troponin I and Troponin T)
When heart muscle cells are damaged, they release specific proteins, known as cardiac biomarkers, into the bloodstream. The most sensitive and specific markers for myocardial injury are Troponin I and Troponin T (Mayo Clinic Laboratories, 2020a; Mayo Clinic Laboratories, 2020b). Elevated levels of these biomarkers are strong indicators of heart muscle damage and are the gold standard for diagnosing a heart attack.
Troponin levels rise within hours of heart muscle damage and remain elevated for several days, providing an extended window for detection.
Why it's essential: Troponin I and Troponin T are more sensitive and specific than other biomarkers like CK-MB for diagnosing myocardial infarction. They are instrumental in detecting NSTEMI, where ECG changes may not be as prominent.
3. Echocardiogram
An echocardiogram uses sound waves (ultrasound) to create images of the heart's structure and function. It can assess how well the heart pumps, detect wall motion abnormalities, and determine the severity of any heart attack symptoms and muscle damage. The echocardiogram is especially valuable in assessing ejection fraction, which measures how much blood the heart pumps with each beat. This information is crucial for determining the heart’s overall function and the extent of damage caused by the heart attack.
Why it's essential: The echocardiogram is noninvasive and provides detailed information about the heart’s structure and function. It helps identify complications like heart failure or wall motion abnormalities. It is beneficial in cases where the ECG and biomarkers alone do not provide a complete picture of the heart's condition.
How does our Heart Attack Test template work?
Our Heart Attack Test Template is designed to guide healthcare professionals through the essential diagnostic steps for assessing whether a patient has experienced a heart attack. By streamlining the documentation process, the template ensures that crucial information is recorded systematically, allowing for accurate diagnosis and efficient patient care. Here's how to use the template in three simple steps:
Step 1: Download and prepare the template
Begin by downloading the Heart Attack Test Template from the Carepatron platform. Ensure you have all necessary materials, including access to an ECG machine, blood testing capabilities for Troponin I and Troponin T, and access to echocardiogram equipment. Having the template ready will streamline the documentation process and allow you to record essential details during the assessment.
Step 2: Conduct the tests and record the results
Follow the template's structured sections for the patient’s clinical presentation and each diagnostic test. For example, the ECG section can document ST-segment elevation or T-wave inversion findings. Record Troponin I and Troponin T levels in the cardiac biomarkers section and compare them to reference ranges. Similarly, complete the echocardiogram section by documenting ejection fraction and any observed wall motion abnormalities. This ensures that each crucial aspect of heart attack testing is thoroughly documented.
Step 3: Summarize the overall result
Once all test results have been recorded, use the overall result section to determine future heart attack diagnoses. This section includes four checkboxes for the primary heart attack outcomes: STEMI, NSTEMI, unstable angina, and other non-cardiac cause. Based on the test results, select the appropriate diagnosis and provide a brief reason (e.g., "ST-segment elevation on ECG and elevated troponin levels indicate a STEMI"). This summary offers a concise conclusion for the patient's condition and helps guide further treatment decisions.
Benefits of using our template
Our Heart Attack Test template offers several key benefits for healthcare providers, ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and thoroughness in diagnosing heart attacks. Here are three main advantages:
Streamlined documentation process
The template simplifies the process of recording essential data during heart attack assessments, ensuring that no critical information is missed. It organizes the heart health diagnostic process, from clinical presentation to test results, allowing healthcare professionals to gather and document all relevant information efficiently.
Accurate diagnosis and prompt treatment
By focusing on the three most essential tests — ECG, Troponin I and T levels, and the echocardiogram — our template helps healthcare providers quickly and accurately diagnose heart attacks. Heart attacks happen when a piece of plaque breaks off, forming a blood clot obstructing blood flow to the heart, which these three tests measure. Early detection of STEMI or NSTEMI allows for faster intervention, crucial in reducing long-term heart damage risk factors and improving patient outcomes. Participation in cardiac rehab programs, which focus on exercise, nutrition, and emotional support, can improve heart health and reduce the risk of future heart attacks.
Enhanced communication and collaboration
The structured format of the template facilitates clear communication among healthcare providers, ensuring that everyone involved in the patient's care is on the same page. This promotes collaboration between the medical team and helps guide treatment decisions, improving the overall quality of care delivered to the patient.
References
Mayo Clinic. (2023, October 9). Heart attack - diagnosis and treatment. Mayo Clinic. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/heart-attack/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20373112
Mayo Clinic Laboratories. (2020a). HSTNI - overview: Troponin I, high sensitivity, plasma. https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/overview/614422
Mayo Clinic Laboratories. (2020b). TRPS - overview: Troponin T, 5th generation, plasma. https://www.mayocliniclabs.com/test-catalog/overview/65832
National Institutes of Health. (2022). Heart attack - diagnosis. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/heart-attack/diagnosis
Commonly asked questions
The template includes the Electrocardiogram (ECG), Troponin I and T blood tests, and the echocardiogram. These three tests are essential for diagnosing a heart attack and providing critical information about heart rhythm, muscle damage, and overall heart function.
Research has shown that Troponin I and T are more specific and sensitive markers for myocardial injury compared to CK-MB, which is now considered obsolete for diagnosing heart attacks. Troponin levels remain elevated longer after a heart attack and provide a more reliable indication of cardiac muscle damage.
No, this template is specifically designed to assess and diagnose heart attacks, particularly STEMI, NSTEMI, and unstable angina. While it provides valuable insights into myocardial infarctions, it is not intended to diagnose other cardiac conditions or symptoms like blood clots in arteries, heart failure, or arrhythmias.