Blood Test for Heart Attack
Learn about the importance of blood tests for detecting heart attacks and download Carepatron's free PDF example for reference. Find crucial information to help you understand the process.


What is a heart attack?
A heart attack, medically known as a myocardial infarction (MI), occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart muscle is blocked for a prolonged period, typically due to the formation of blood clots in the coronary arteries. These arteries are responsible for supplying oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle. The blockage deprives the heart muscle of oxygen and nutrients, leading to tissue damage or death if left untreated.
Heart attacks are primarily caused by coronary artery disease (CAD). In this condition, the blood vessels that supply the heart become narrowed or blocked by plaque buildup, consisting of cholesterol, fat, and other substances. High blood pressure, smoking, obesity, diabetes, and a sedentary lifestyle are significant risk factors for CAD and, consequently, heart attacks.
Timely heart attack diagnosis is crucial for initiating prompt treatment and minimizing damage to the heart muscle. Blood tests, specifically cardiac markers such as cardiac troponin, play a vital role in diagnosing a heart attack. These markers are released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged, providing valuable information to healthcare professionals.
Blood Test for Heart Attack Template
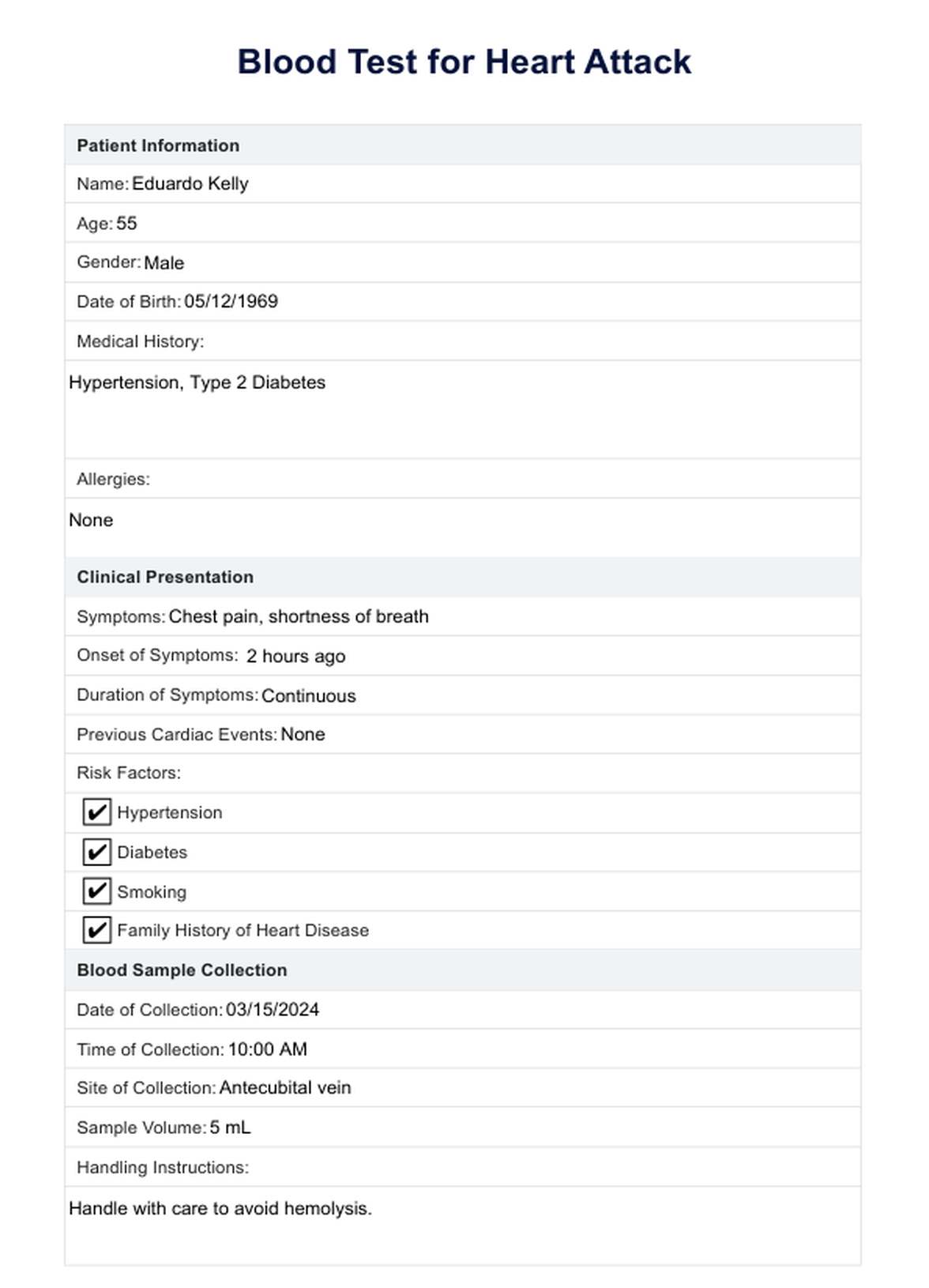
Blood Test for Heart Attack Example
Symptoms
The hallmark symptom of a heart attack is chest pain or discomfort, often described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain that may radiate to the arms, neck, jaw, or back. However, not all heart attacks present with chest pain, and symptoms can vary widely among individuals.
Recognizing the symptoms of a heart attack is crucial for seeking immediate medical attention and potentially saving lives. While chest pain is the most common symptom, heart attacks can manifest differently in each individual.
Here are the common symptoms to be aware of:
- Chest pain or discomfort: Often described as pressure, squeezing, fullness, or pain in the center or left side of the chest. The discomfort may last for a few minutes or come and go.
- Pain or discomfort in other areas of the upper body: This may include discomfort in one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
- Shortness of breath: Feeling breathless or having difficulty breathing may occur with or without chest discomfort.
- Nausea, indigestion, or vomiting: Some individuals may experience nausea, indigestion, heartburn, or vomiting, which can be mistaken for gastrointestinal issues.
- Dizziness or lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy, lightheaded, or faint may occur during a heart attack, often accompanied by other symptoms.
- Sweating: Profuse sweating, often described as cold and clammy, may occur during a heart attack.
- Fatigue: Feeling unusually tired or weary, even with minimal exertion, can be a heart attack symptom.
- Anxiety: A sense of impending doom or anxiety may accompany a heart attack, especially in women.
How to diagnose a heart attack
Diagnosing a heart attack involves a series of steps and tests to confirm the presence of cardiac damage and determine the extent of the condition. Medical professionals rely on various diagnostic tools and procedures to accurately diagnose a heart attack and initiate appropriate treatment.
Below are the key steps in diagnosing a heart attack:
Initial assessment
In the initial assessment, medical professionals gather crucial information about the patient's medical history, including any previous heart conditions, risk factors, and symptoms. A thorough physical examination follows this step to assess vital signs, listen for abnormal heart sounds, and check for signs of distress.
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a non-invasive test that measures the heart's electrical activity. It is often one of the first tests performed upon arrival at the hospital or emergency room. Abnormalities in the ECG, such as ST-segment elevation or depression, can indicate a heart attack.
Blood tests
Blood tests play a crucial role in diagnosing a heart attack. Cardiac indicators, including cardiac troponin, are measured to assess damage to the heart muscle. Elevated levels of cardiac markers indicate heart muscle injury and help evaluate the severity of the heart attack. A blood sample is taken and analyzed to measure these biomarkers accurately.
Imaging tests
Imaging tests, such as echocardiography (echo) or cardiac MRI, may be performed to visualize the heart's structure and function. These tests help assess the extent of damage to the heart muscle and identify any underlying heart conditions, such as cardiovascular disease or structural abnormalities.
Coronary angiography
Coronary angiography is a procedure used to evaluate blood flow in the coronary arteries. Contrast dye is injected into the arteries, and X-ray images (angiograms) are taken to visualize any blockages or narrowing. If significant blockages are found, further interventions such as coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) or angioplasty with stent placement may be necessary.
Differential diagnosis
In some cases, conditions like acute coronary syndrome (ACS), myocarditis, or pulmonary embolism may mimic heart attack symptoms. Medical professionals carefully consider the patient's symptoms, test results, and risk factors to rule out alternative diagnoses and ensure accurate treatment.
Blood tests used to diagnose a heart attack
When it comes to diagnosing a heart attack, blood tests play a pivotal role in providing valuable insights into cardiac health and identifying potential issues. These tests help healthcare professionals assess the risk of heart disease, evaluate heart function, and confirm the presence of a heart attack.
Here are the key blood tests used in diagnosing a heart attack:
Cardiac troponin test
Cardiac troponin test is one of the primary blood tests used to diagnose a heart attack. Troponin is a protein released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged, making it a highly sensitive and specific marker for cardiac injury. Elevated levels of cardiac troponin in a blood sample indicate heart muscle damage, confirming the diagnosis of a heart attack.
Lipid profile
A lipid profile is a blood test that measures cholesterol levels in the blood, including low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, and triglycerides. High LDL cholesterol, triglycerides, and low HDL cholesterol levels are significant risk factors for heart disease. They may contribute to blood clots and plaque buildup in the arteries.
Blood glucose test
Monitoring blood glucose levels is essential for assessing the risk of heart disease, especially in individuals with diabetes. High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of heart attack and stroke. A blood glucose test measures the amount of glucose in the blood and helps evaluate overall heart health and the risk of heart disease complications.
Complete blood count (CBC)
A complete blood count (CBC) is a routine blood test that provides valuable information about various blood components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Abnormalities in the CBC, such as anemia or abnormal white blood cell counts, may indicate underlying health conditions that can affect heart health and increase the risk of heart disease and complications.
Basic metabolic panel (BMP) or comprehensive metabolic panel (CMP)
These blood tests assess kidney function, electrolyte levels, and other metabolic markers that can impact heart health. Abnormalities in the BMP or CMP, such as abnormal kidney function or electrolyte imbalances, may indicate an increased risk of heart disease, heart failure, or other cardiovascular complications.
Blood pressure measurement
While not a blood test per se, blood pressure measurement is essential to assessing heart health. High blood pressure (hypertension) is a significant risk factor for heart disease, stroke, and other cardiovascular conditions. Regular monitoring of blood pressure helps identify individuals at risk and allows for early intervention to reduce the risk of heart attack and other complications.
How to use this template
Understanding how to effectively utilize this blood test for heart attack template is essential for accurately diagnosing and managing cardiovascular conditions. Follow these steps to maximize the utility of this template:
Collecting blood samples
Gather blood samples from the patient suspected of experiencing a heart attack. Ensure proper collection techniques and adherence to clinical practice guidelines to maintain sample integrity and accuracy of test results.
Conducting troponin test
Perform a troponin test on the collected blood samples. The troponin testis a critical component of diagnosing a heart attack, as elevated troponin levels indicate cardiac muscle damage, confirming the presence of a heart attack.
Interpreting test results
Carefully analyze the test results to determine the presence and severity of a heart attack. Elevated troponin test levelsand other clinical indicators may indicate a heart attack and guide subsequent treatment decisions.
Consider other tests
In addition to the troponin test, other tests should be performed based on the patient's clinical presentation and risk factors. These may include electrocardiograms (ECG), echocardiograms, and imaging studies to evaluate heart health further and identify potential complications.
Consult clinical practice guidelines
Refer to established clinical practice guidelines for diagnosing and managing heart attacks to ensure adherence to best practices and optimize patient outcomes. These guidelines provide evidence-based recommendations for diagnostic testing and treatment strategies.
Commonly asked questions
Yes, a blood test can detect a heart attack by measuring levels of cardiac biomarkers such as troponin released into the bloodstream during myocardial damage.
Tests commonly used to predict a heart attack include lipid profiles, blood glucose tests, and imaging studies such as cardiac computed tomography (CT) scans or coronary angiography.
Cardiac biomarkers commonly used to diagnose a heart attack include troponin, creatine kinase (CK-MB), myoglobin, and B-type natriuretic peptide (BNP). These biomarkers are released into the bloodstream when the heart muscle is damaged.