Cardiovascular Assessment
Explore comprehensive cardiovascular nursing assessments vital for monitoring heart health with this curated guide and free template!


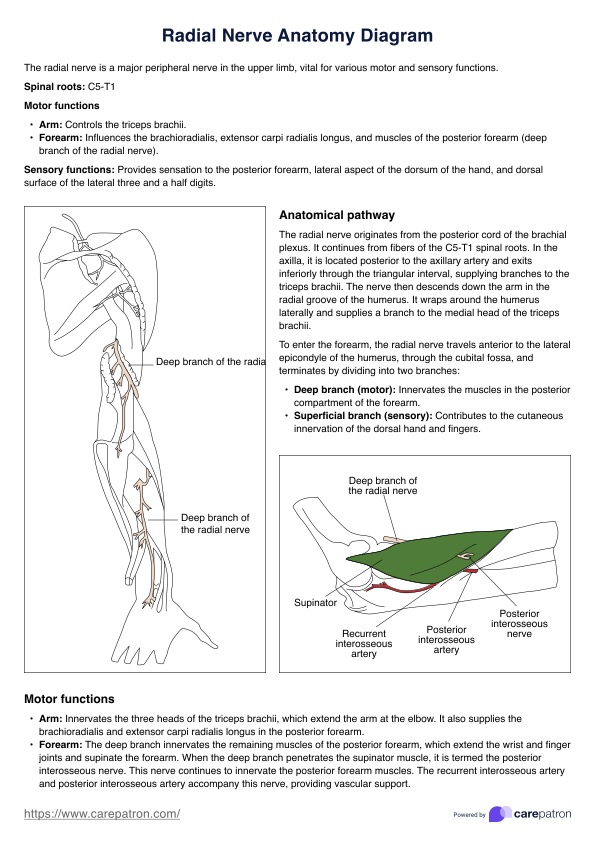
Brief overview of the cardiovascular system
The cardiovascular system, comprised of the heart and blood vessels, circulates blood to deliver oxygen and nutrients throughout the body. The heart pumps blood while arteries, veins, and capillaries facilitate this circulation. This system supplies tissues with nutrients, removes waste, and maintains bodily functions.
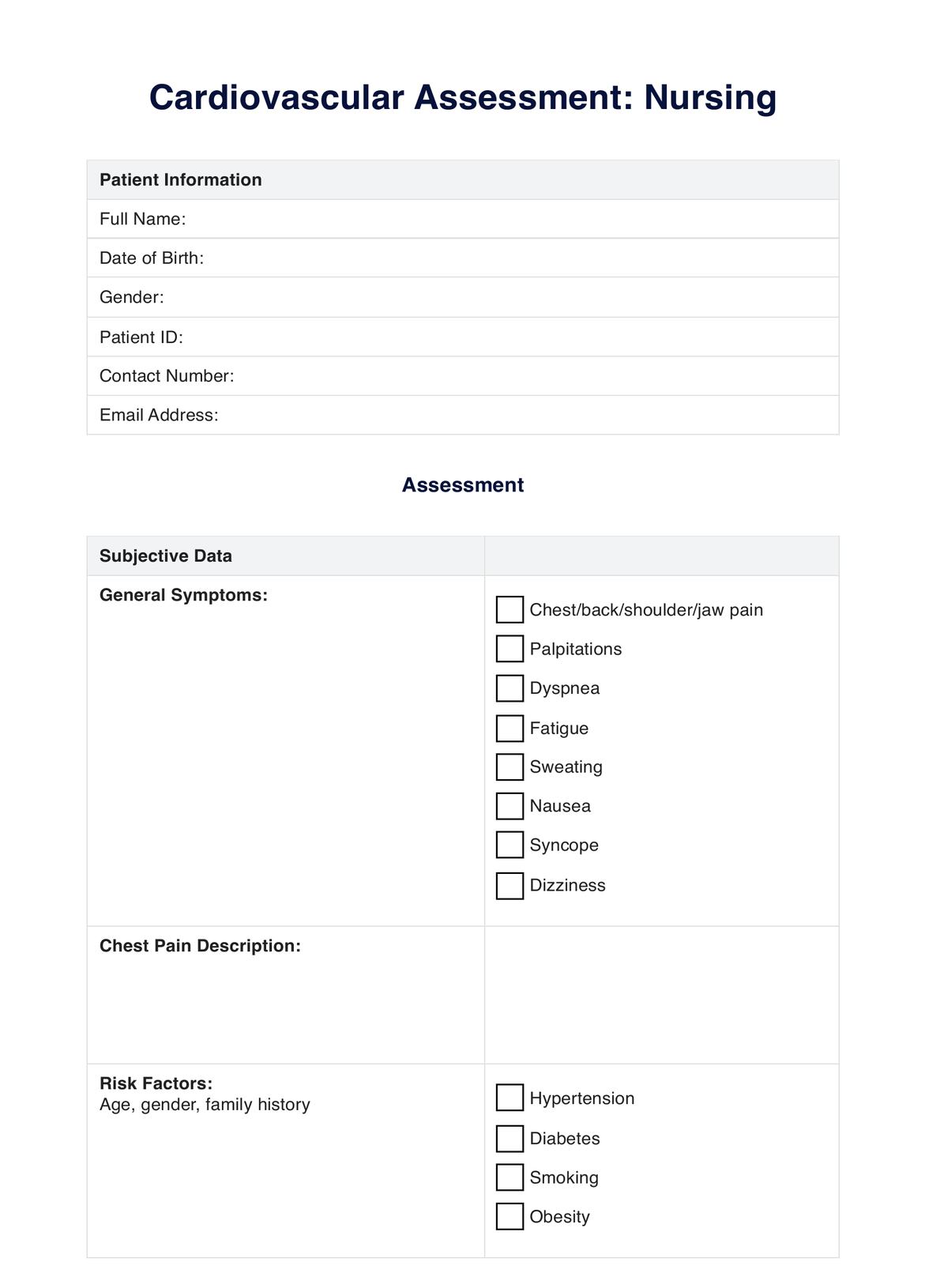
Cardiovascular Assessment Template
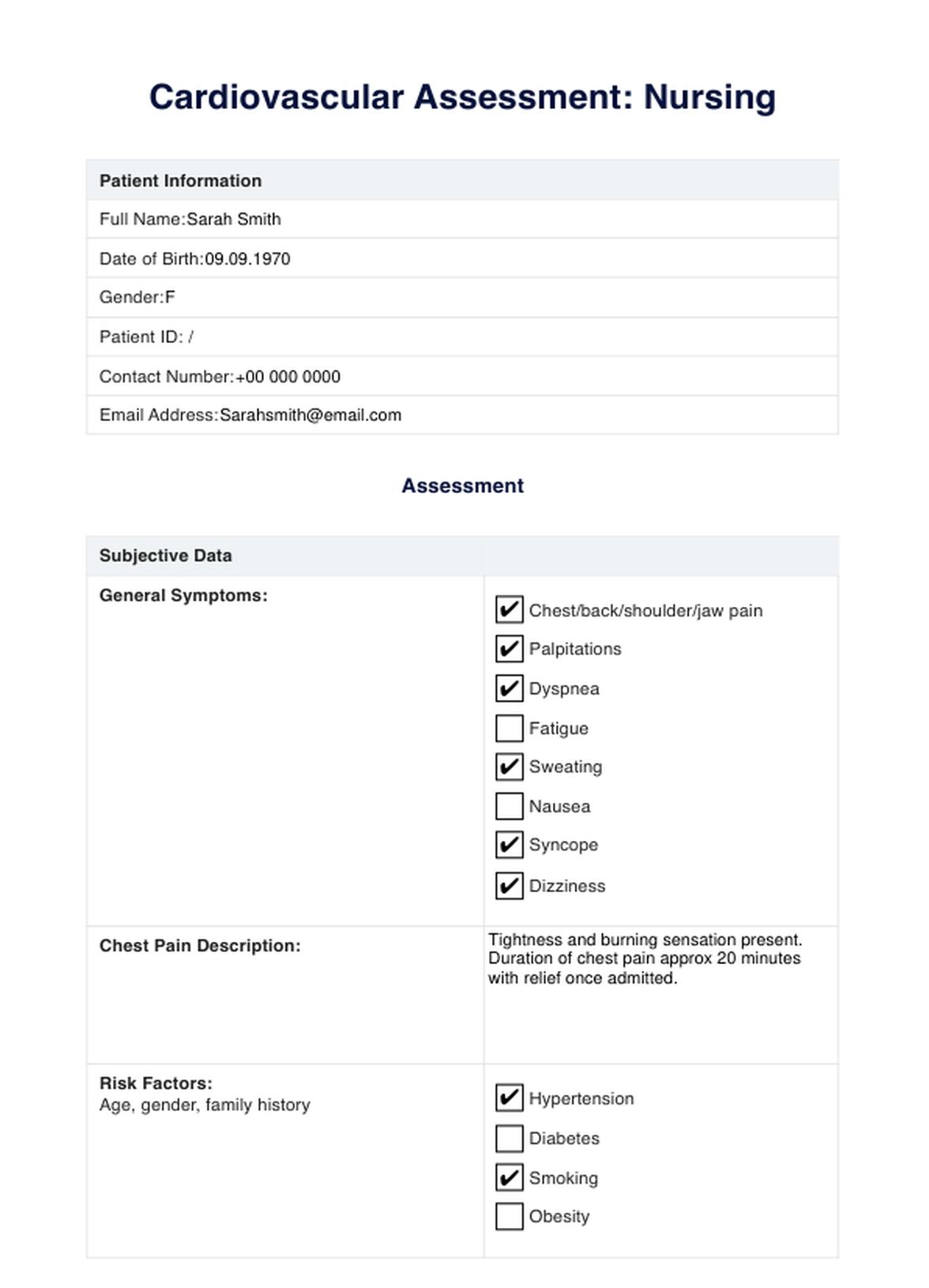
Cardiovascular Assessment Example
What is a nursing Cardiovascular Assessment?
A nursing cardiovascular assessment involves thoroughly evaluating a patient's cardiovascular system to determine its function and identify any potential issues or abnormalities. This assessment encompasses various components to understand the patient's heart health and circulatory status comprehensively.
One crucial aspect is assessing the patient's history of vascular disease, which involves gathering information about their past medical conditions, family history of cardiovascular diseases, lifestyle habits, and any current symptoms related to heart health. This helps understand potential risk factors or pre-existing conditions that might impact the cardiovascular system.
Physical examination plays a pivotal role, including assessing vital signs like blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm. Auscultation of the heart sounds using a stethoscope allows nurses to detect murmurs, irregularities, or abnormal heart sounds. Palpation of pulses in different body areas aids in assessing peripheral circulation and identifying potential abnormalities.
Assessing the patient for signs and symptoms of cardiovascular issues, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, edema, or fatigue, is essential. Observing for cyanosis (bluish discoloration) in extremities can indicate poor circulation. A key aspect of this assessment is the evaluation of the patient's cardiovascular disease risk factors, such as smoking, obesity, high blood pressure, diabetes, and cholesterol levels, which helps in risk stratification and determining preventive measures or interventions.
A nursing cardiovascular assessment also involves utilizing diagnostic tests or procedures, such as electrocardiograms (ECGs/EKGs), echocardiograms, or stress tests, as indicated by the patient's condition or symptoms. These tests provide valuable insights into the heart's electrical activity, structure, and function.
The value of a comprehensive cardiovascular assessment lies in the early detection of cardiovascular issues or risk factors, enabling timely interventions, lifestyle modifications, or referrals to specialists. It serves as a baseline for monitoring a patient's cardiac health, facilitating personalized care plans, and promoting optimal cardiovascular well-being.
How does it work?
Step One: Gather your resources
Afib Nursing Care Plans are a valuable resource and essential to keep on hand. Make sure that you have a copy of the free printable PDF when the need arises by either clicking the “Download Template” or “Use Template” button or by searching “AFib Nursing Care Plan” on Carepatron’s template library’s search bar on the website or app.
Step Two: Collate essential information
Once the patient has been diagnosed and assessed for cardiovascular injury, utilizing the cardiovascular assessment template to ensure all goals of care are met is seamless and easily accessible to relevant parties via Carepatron's centralized workspace.
Assessment, symptom management, and interventions can be collated within the single care plan and safely stored on a single database. The care plan allows for individualized treatment options. It acts as a scaffolding to ensure goals of care are met, and the next steps are recorded for future reference or distribution to other healthcare specialists who are part of the patient's care team.
Step Three: Store the chart securely
After reviewing the Cardiovascular assessment and creating a viable and individualized plan for the patient, you need to secure the plan so that access is only granted to relevant parties.
Ensure this through Carepatrons HIPAA-compliant free patient records software. Here, all relevant medical records can be safely stored and collated for ease and security.
When would you use this template?
A cardiovascular nursing assessment is utilized in various healthcare settings and situations:
Routine health checkups
During regular checkups or wellness visits, healthcare providers, including nurses, perform cardiovascular assessments to monitor heart health, especially in patients with known risk factors like hypertension, diabetes, or a family history of heart disease.
Pre-operative evaluations
Before surgeries or invasive procedures, healthcare professionals conduct cardiovascular assessments to ensure the patient's heart is stable and can withstand the stress of the procedure.
Emergencies
In emergency departments, nurses perform rapid cardiovascular assessments to evaluate patients presenting with chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac issues.
Hospital admissions
Upon admission to hospitals, patients undergo cardiovascular assessments to establish a baseline of their cardiac health. This physical assessment is particularly important for individuals with chronic conditions or those admitted for conditions affecting the cardiovascular system.
Chronic disease management
For patients with chronic cardiovascular conditions like heart failure, hypertension, or arrhythmias, regular nursing assessments are conducted to monitor disease progression, assess treatment effectiveness, and prevent exacerbations.
Post-operative care
Nursing assessments are crucial after cardiac surgeries or procedures to monitor the patient's recovery, detect complications, manage pain, and prevent issues like infections or thrombosis.
Rehabilitation Settings
In cardiac rehabilitation programs, nurses perform ongoing assessments to track patients' progress, assess their exercise tolerance, and guide them in managing their cardiovascular health.
Nursing cardiovascular assessment and intervention
In cardiovascular nursing, assessments and interventions are pivotal in evaluating heart health, identifying issues, and implementing strategies for optimal care:
Assessment
- Vital signs monitoring: Monitoring blood pressure, heart rate, and rhythm aids in detecting abnormalities like hypertension, arrhythmias, or signs of cardiovascular compromise. Early identification allows timely interventions to prevent complications such as stroke or heart failure.
- Auscultation and heart sound: Listening to heart sounds helps detect murmurs, abnormal rhythms, or valve issues. Early identification guides interventions, including referrals for further cardiac evaluations or medications to manage conditions like valvular disorders.
- Peripheral vascular evaluation (pulses and edema): Assessing peripheral pulses and checking for edema helps evaluate circulation and detect peripheral vascular diseases. This aids in identifying vascular insufficiencies and planning interventions to improve circulation and prevent complications like deep vein thrombosis.
Intervention
- Medication administration and monitoring: Administering medications for blood pressure control, antiarrhythmics, or anticoagulants requires vigilant monitoring. Regular assessments help monitor drug efficacy, adverse effects, and patient response, optimizing treatment outcomes and reducing risks.
- Lifestyle modifications: Educating patients about healthy lifestyle habits (diet, exercise, smoking cessation) is crucial. Such interventions reduce risk factors (like obesity and high cholesterol) and contribute to long-term cardiovascular health, preventing atherosclerosis or coronary artery disease.
- Patient education and compliance: Educating patients about their condition, medications, and the importance of adherence empowers them in self-management. Understanding their role in managing cardiovascular health enhances compliance with treatment plans, leading to better outcomes.
- Emergency response and CPR skills: Proficiency in immediate response to cardiac emergencies and CPR is critical. Quick intervention during cardiac events improves survival rates, reducing the risk of irreversible damage or death.
Research & evidence
One of the leading causes of death in the developed world, acute myocardial infarction, originates from a decreased supply of oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, culminating in cardiac ischemia. Accounting for over one million deaths in the U.S. annually, this irreversible damage to the heart requires careful and consistent monitoring (Nascimento et al., 2018).
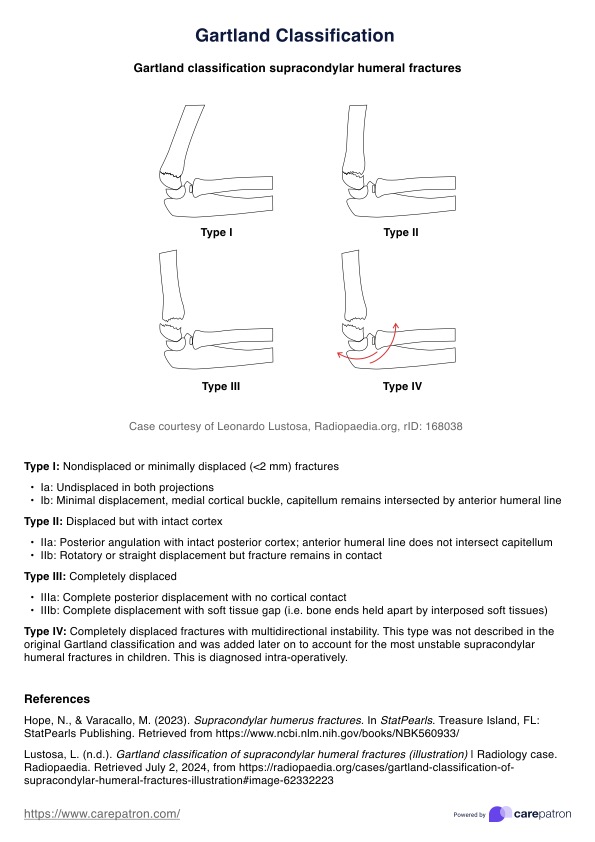
Delving into risk factors, fatal occurrences in approximately 70% of AMI cases are attributed to atherosclerotic plaque occlusion, making atherosclerosis the predominant driver of this cardiac event's onset. In efforts to prevent AMI, considerable focus is directed toward mitigating risk factors associated with atherosclerotic disease.
The basis of these preventive efforts revolves around managing modifiable risk factors, which wield substantial influence, accounting for 90% of men and 94% of women experiencing myocardial infarctions. These modifiable factors encompass an array of lifestyle and health elements, including cigarette smoking, exercise patterns, hypertension, obesity, cholesterol levels, low-density lipoprotein, and triglycerides. (Berg et al., 2018; Deng et al., 2018).
A significant influence on an individual's susceptibility to atherosclerotic disease and subsequent AMI events lies in age, sex, and family medical history. (Deng et al., 2018). Recognizing the interplay between modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors is imperative in creating comprehensive strategies and nursing care plans for MI prevention and management, acknowledging both the avenues for intervention and the inherent limitations in altering certain predisposing factors.
References
Berg, D. D., Wiviott, S. D., Braunwald, E., Guo, J., Im, K., Kashani, A., Gibson, C. M., Cannon, C. P., Morrow, D. A., Bhatt, D. L., Mega, J. L., O’Donoghue, M. L., Antman, E. M., Newby, L. K., Sabatine, M. S., & Giugliano, R. P. (2018). Modes and timing of death in 66 252 patients with non-ST-segment elevation acute coronary syndromes enrolled in 14 TIMI trials. European Heart Journal, 39(42), 3810–3820. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehy556
Deng, D., Liu, L., Xu, G., Gan, J., Shen, Y., Shi, Y., Zhu, R., & Lin, Y. (2018). Epidemiology and Serum Metabolic Characteristics of Acute Myocardial Infarction Patients in Chest Pain Centers. Iranian Journal of Public Health, 47(7), 1017–1029. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30182001/
Nascimento, B. R., Brant, L. C. C., Marino, B. C. A., Passaglia, L. G., & Ribeiro, A. L. P. (2018). Implementing myocardial infarction systems of care in low/middle-income countries. Heart, 105(1), 20–26. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2018-313398
Commonly asked questions
Monitoring blood pressure is crucial as it helps assess the force exerted by blood against arterial walls. Abnormalities in blood pressure, like hypertension or hypotension, can indicate cardiovascular issues such as heart disease, stroke risk, or vascular complications. Regular monitoring of blood flow aids in early detection and intervention to manage these conditions effectively.
Nurses listen for heart murmurs, abnormal rhythms, or additional sounds like gallops or clicks during auscultation. These can indicate valve problems, arrhythmias, or structural issues within the heart. Detecting these abnormalities early guides further investigations or treatment, preventing potential complications and promoting cardiac health.
Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet, regular exercise, smoking cessation, and stress management, significantly impact cardiovascular health. Nurses play a pivotal role in educating patients about these modifications. Supporting and guiding patients in adopting healthier habits reduces risk factors, improves heart health, and contributes to preventing cardiovascular diseases.