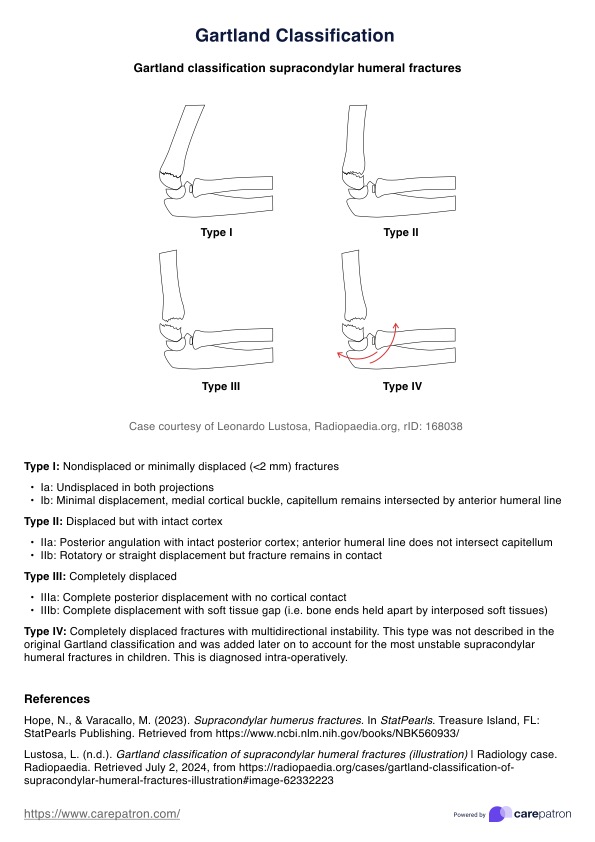
Anemia Nursing Care Plan
Download our Anemia Nursing Care Plan Template to streamline how you provide care for patients with anemia.


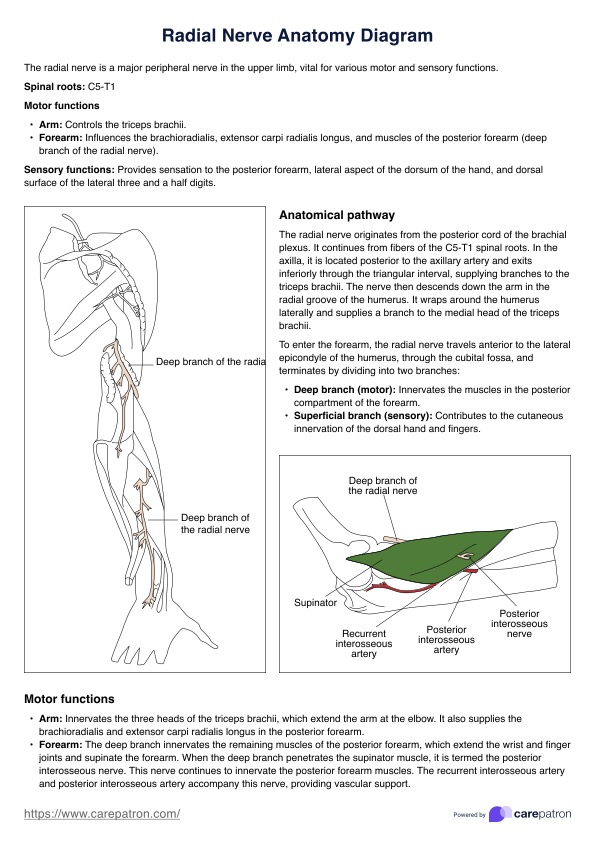
What is anemia?
Anemia is a common blood disorder characterized by decreased red blood cells or hemoglobin levels. This condition impairs the blood's ability to transport oxygen effectively throughout the body, leading to various symptoms and health complications.
Anemia occurs when the body doesn't have enough red blood cells to transport oxygen effectively to tissues. This decreased oxygen-carrying capacity can result from various factors, including nutritional deficiencies, chronic diseases, and genetic disorders. The most common type is iron deficiency anemia, but other forms like vitamin B12 deficiency (pernicious anemia), folate deficiency, and hemolytic anemia also exist. Other complications, such as sickle cell disease, can also put patients at risk for severe anemia.
Anemia Nursing Care Plan Template
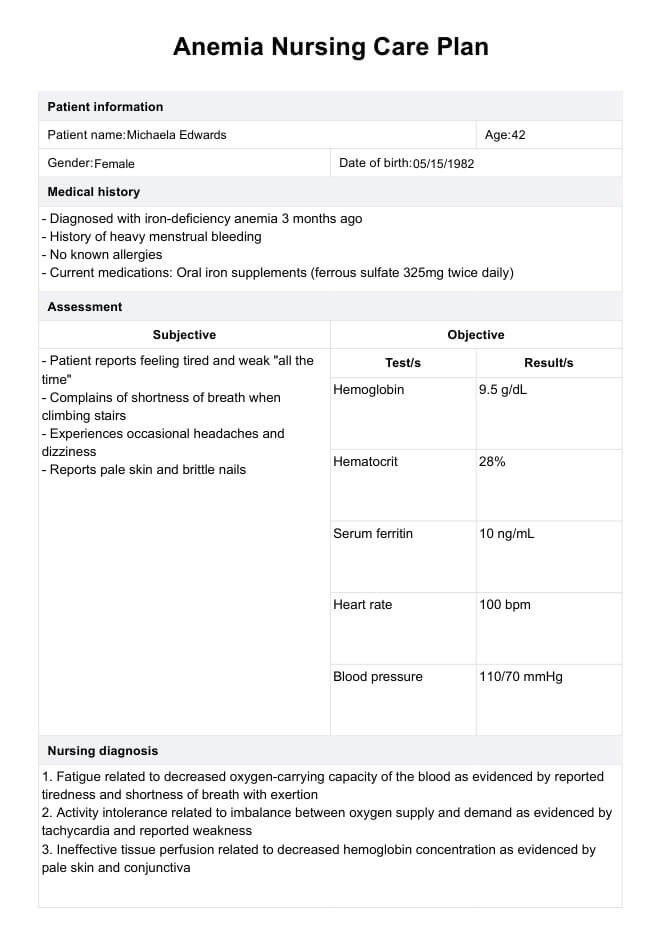
Anemia Nursing Care Plan Example
What is the Anemia Nursing Care Plan Template?
The Anemia Nursing Care Plan Template is a structured framework designed to guide healthcare providers in delivering comprehensive, patient-centered care for individuals diagnosed with anemia. This template is a valuable tool for organizing assessment data, identifying key nursing diagnoses, setting achievable goals, and implementing effective interventions tailored to each patient's needs.
Nursing assessment
A comprehensive nursing assessment is essential for effective anemia management. Key components include:
- Medical history: Evaluate risk factors such as chronic kidney disease, rheumatoid arthritis, or bleeding disorders. Assess for any recent acute blood loss events or conditions that might impair red blood cell production.
- Physical examination: Look for signs of pallor, fatigue, shortness of breath, and changes in blood flow (e.g., cold extremities). Note any indications of increased risk for complications.
- Laboratory tests: Review results of a complete blood count (CBC) to assess red blood cell count, hemoglobin, and hematocrit levels. Examine peripheral blood smear findings for abnormalities in red blood cell morphology. Check total iron binding capacity to evaluate iron status.
- Vital signs: Monitor blood pressure, heart rate, and oxygen saturation to assess the body's compensation for decreased oxygen-carrying capacity.
- Nutritional status: Evaluate dietary intake, focusing on iron-rich foods and potential deficiencies that may contribute to anemia.
- Blood transfusion history: Document any previous blood transfusions and the patient's response to them, as this information may guide future treatment decisions.
Nursing diagnoses
Common nursing diagnoses for patients with anemia may include:
- Fatigue related to decreased oxygen-carrying capacity
- Activity intolerance related to insufficient oxygen delivery to tissues
- Ineffective tissue perfusion related to decreased hemoglobin levels
- Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to inadequate intake of iron-rich foods
Nursing interventions
Effective nursing interventions for anemia management include:
- Administering prescribed medications, such as iron supplements, vitamin B12 injections, or folic acid
- Educating patients about energy conservation techniques and the importance of a balanced diet
- Monitoring for signs of complications, such as chest pain or acute chest syndrome in sickle cell anemia
- Assisting with blood transfusions when ordered for severe and symptomatic anemia
- Providing patient education on anemia management and lifestyle modifications
How does the nursing care plan for anemia work?
The Anemia Nursing Care Plan is a structured tool designed to guide healthcare practitioners in providing comprehensive care for patients with anemia. Here's a step-by-step guide on how to effectively use this tool in clinical practice:
Step 1: Patient assessment and data collection
Begin by filling in the patient's demographic information and medical history. This provides context for the care plan. Next, a thorough assessment will be conducted, documenting both subjective (patient-reported symptoms) and objective (clinical findings and test results) data. This step is crucial for identifying the type and severity of anemia and any contributing factors or complications.
Step 2: Formulate nursing diagnoses and set goals
Based on the assessment data, develop an appropriate nursing diagnosis. These should reflect the patient's current health status and potential risks related to anemia. Then, establish both short-term and long-term goals.
Step 3: Plan and implement interventions
Develop a set of nursing interventions tailored to address the identified diagnoses and achieve the set goals. These may include administering prescribed treatments, educating patients, implementing dietary changes, or monitoring for complications. Each intervention should have a clear rationale, ensuring that all actions are evidence-based and purposeful.
Step 4: Evaluate and adjust the plan
Assess the patient's progress toward the established goals regularly. In the evaluation section, document the effectiveness of interventions and the patient's response to treatment. Based on this ongoing assessment, adjust the care plan and expected outcomes as needed. This may involve modifying goals, changing interventions, or addressing new concerns that arise during treatment.
Benefits of using anemia nursing care plans
Using anemia nursing care plans offers numerous benefits for healthcare providers and patients. These structured tools enhance the quality of care and promote better outcomes in anemia management, including the following:
Standardized approach to care
Anemia nursing care plans provide a consistent framework for patient care. This standardization ensures that all essential aspects of anemia management are addressed, regardless of the individual healthcare provider. It helps reduce variations in care quality and promotes evidence-based practice.
Improved patient outcomes
Following a comprehensive care plan can help healthcare providers more effectively manage anemia and its associated symptoms. This structured approach often leads to faster improvement in hemoglobin levels, reduced fatigue, and enhanced overall patient well-being.
Enhanced communication
Care plans serve as a central communication tool among healthcare team members. They provide a concise overview of the patient's condition, treatment goals, and progress, facilitating better care coordination across different specialties and shifts.
Individualized care
While providing a standardized framework, anemia nursing care plans allow personalization. They can be tailored to each patient's specific type of anemia, symptoms, and personal goals, ensuring that care remains patient-centered.
Commonly asked questions
Caring for a patient with iron-deficiency anemia involves a comprehensive approach that includes assessing the patient's symptoms, dietary habits, and medical history. Key interventions include educating the patient about iron-rich foods, monitoring hemoglobin levels, and adherence to prescribed iron supplements. Regular follow-ups are also crucial to assess the patient's response to treatment and adjust the care plan as needed.
The standard of care for anemia includes a thorough evaluation to determine the underlying cause, which may involve blood tests, dietary assessments, and medical history reviews. Ongoing monitoring of blood counts and patient symptoms is essential to ensure effective management and resolution of the anemia.
A common nursing diagnosis of iron deficiency anemia is "fatigue related to decreased hemoglobin levels as evidenced by patient report of weakness and lethargy." This diagnosis reflects the patient's experience of fatigue due to insufficient iron, which leads to reduced hemoglobin production and, consequently, decreased oxygen delivery to tissues.