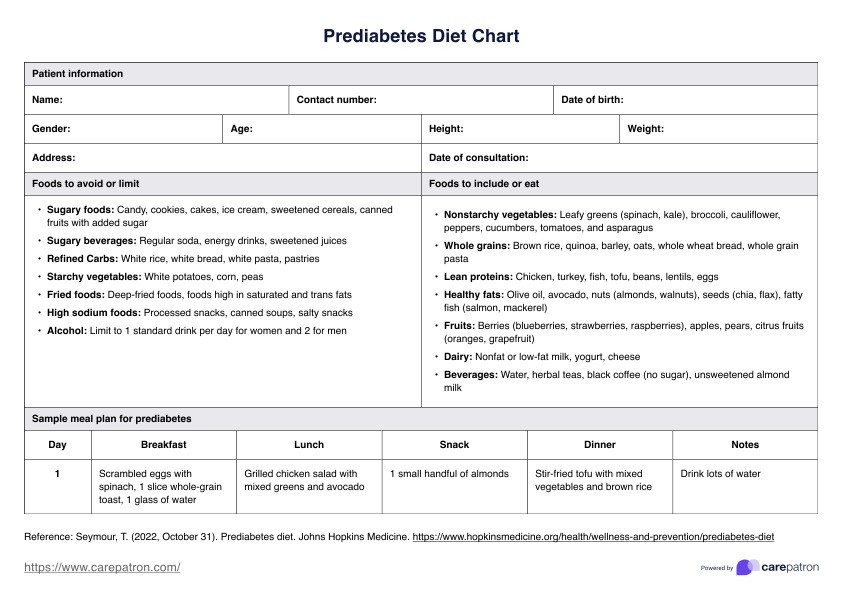
Adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes regular physical activity, a balanced diet, and weight management is the fastest way to address prediabetes. These changes help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity, reducing the risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes.
Prediabetes Diet
Discover an effective Prediabetes Diet Chart and a comprehensive example with Carepatron's free PDF download.
Use Template
Prediabetes Diet Template
Commonly asked questions
Eating meals consistently every 3-4 hours helps maintain stable blood sugar levels throughout the day. It’s best to have three balanced meals and one or two healthy snacks to prevent blood sugar spikes and dips.
Prediabetics should avoid sugary foods, refined carbohydrates, sweetened beverages, and fried or high-fat foods. Limiting processed snacks and foods with added sugars is crucial to keeping away from health complications.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











