Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart
Discover more about Oral Allergy Syndrome (OAS) with Carepatron comprehensive chart, outlining common triggers, symptoms, and management options.


What is oral allergy syndrome?
Oral allergy syndrome (OAS), also known as pollen food allergy syndrome, is an allergic condition that occurs when certain proteins in raw fruits, vegetables, or nuts cross-react with pollen allergens (American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology, 2021). It commonly affects individuals with hay fever or seasonal allergies, particularly during peak pollen season. OAS symptoms are typically mild and localized to the mouth and throat, including itching, tingling, or swelling after consuming the triggering foods.
This reaction is not a traditional food allergy but is closely linked to pollen allergies, such as birch tree, weed, or grass pollen. For example, people allergic to birch pollen may react to apples, carrots, or almonds. While symptoms are usually mild, some cases can escalate into a severe allergic reaction, though this is rare.
To diagnose oral allergy syndrome, healthcare practitioners assess the patient's history, seasonal allergy patterns, and specific food triggers. Skin tests or blood tests may confirm sensitivities to pollen or related allergens. While oral allergy syndrome is typically treated by avoiding triggering foods, cooking can neutralize the proteins and prevent reactions. Practitioners should educate patients about managing mild symptoms and recognizing signs of severe allergic reactions to ensure safety and improve quality of life.
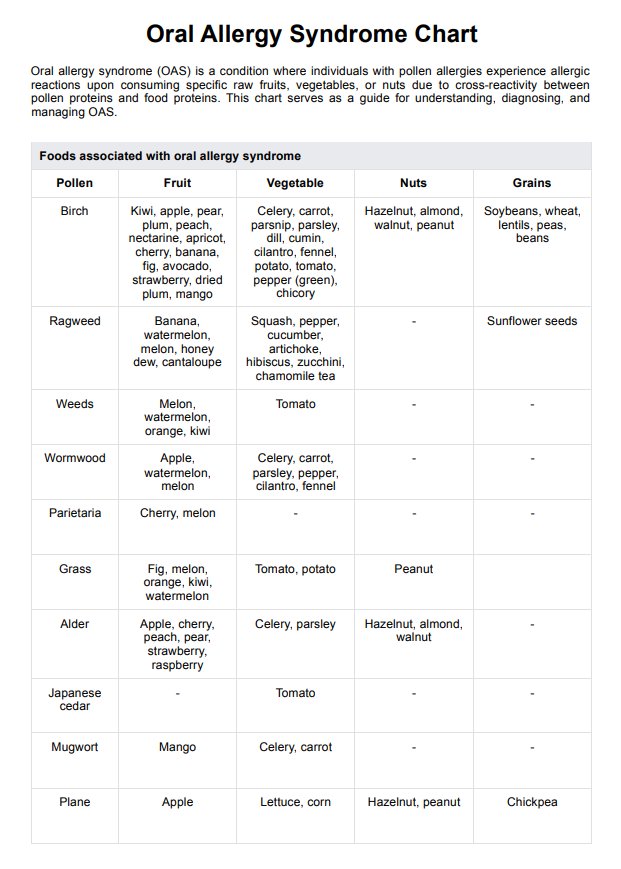
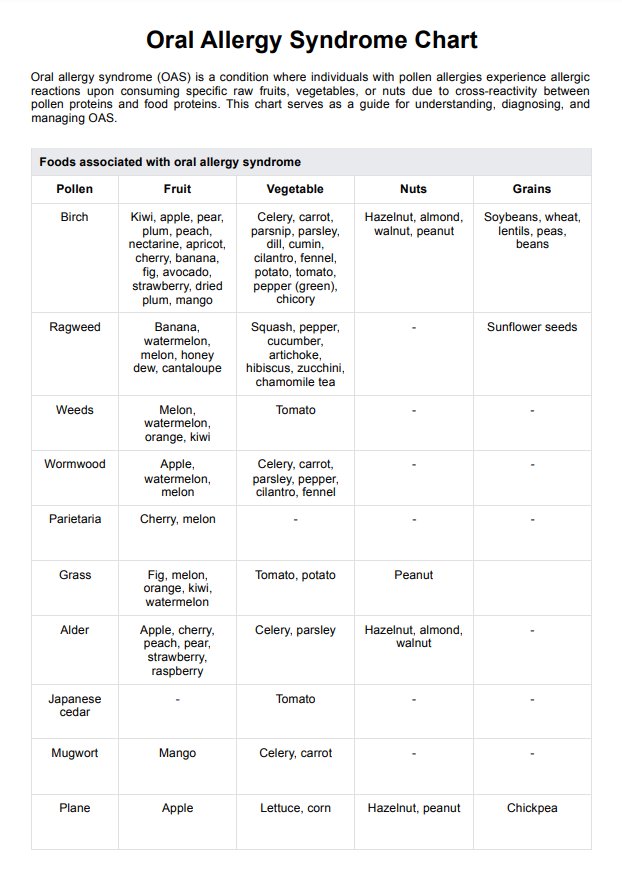
Foods associated with oral allergy syndrome
Oral allergy syndrome is triggered by proteins in various foods that cross-react with pollen allergens (Kashyap & Kashyap, 2015). Common food categories include fruits, vegetables, nuts, grains, and seeds. Specific triggers often align with the type of pollen allergy a person has.
Birch pollen is linked to reactions from apples, kiwis, pears, peaches, celery, carrots, hazelnuts, and almonds. Ragweed-related OAS symptoms may occur with bananas, melons, squashes, and zucchini (Pastorello et al., 2000). Grass pollen is associated with figs, melons, oranges, potatoes, and peanuts, while mugwort can trigger reactions from mangos, celery, and carrots. Additionally, alder pollen may cause sensitivities to cherries, peaches, and hazelnuts.
Cooking or processing these foods can often neutralize the proteins, reducing the risk of an allergic reaction. Healthcare professionals should guide patients in identifying triggers and managing their diets during pollen-heavy seasons to minimize OAS symptoms and maintain nutritional balance.
Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart Template
Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart Example
What is an Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart?
An Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart is a clinical tool designed to help healthcare professionals effectively identify and manage OAS triggers. It organizes information about cross-reactive foods and their corresponding pollen allergens, enabling practitioners to link specific foods to seasonal or environmental allergies like birch, ragweed, or grass pollen.
This chart is particularly useful in diagnosing pollen food allergy syndrome and guiding treatment plans. Detailing common triggers—such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and grains—and their associated pollens provides a quick reference to assess potential allergic reactions. It also helps track OAS symptoms and identify patterns across pollen seasons.
Healthcare providers can use this chart to educate patients on managing mild symptoms, avoiding triggers, and recognizing the risks of severe allergic reactions. Incorporating an Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart into clinical practice supports precise diagnosis and tailored dietary advice, enhancing patient care and outcomes.
How does it work?
Carepatron's Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart is a practical resource designed to streamline the identification and management of oral allergy syndrome. You can use the chart to assess patient triggers, guide dietary advice, and educate patients effectively. Follow these steps to integrate it into your practice:
Step 1: Access and use the Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart
Click "Use template" within the Carepatron app to open the chart. You can customize it to meet your needs or print it for in-person consultations. This flexibility allows for seamless integration into patient evaluations.
Step 2: Introduce the chart to the patient
Explain the chart's purpose to your patient, highlighting how it helps identify triggers and manage OAS symptoms. Discuss its role in connecting their food reactions to specific pollen allergies and how it supports personalized care.
Step 3: Discuss the components of the chart with patient
Review the chart’s sections with the patient, including associated foods, corresponding pollens, and potential OAS symptoms. Use the information to identify triggers and address specific dietary concerns or seasonal allergy patterns.
Step 4: Provide further patient education and next steps
Educate the patient about managing their symptoms, avoiding triggers, and recognizing signs of severe allergic reactions. Recommend dietary adjustments, follow-up visits, or additional allergy testing based on the findings from the chart.
Benefits of using this chart
The Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart is an essential tool for healthcare professionals managing oral allergy syndrome. The chart helps identify patterns in cross-reactive foods, ensuring oral allergy syndrome diagnosed cases are accurately managed and treated. It simplifies the process of identifying cross-reactivity between pollens and certain raw foods, such as fresh fruit and vegetable allergens, which can trigger allergic reactions in sensitive individuals.
Using the chart helps medical practitioners educate patients about how eating fresh fruit or other raw foods may cause allergic symptoms. It clarifies how food allergies tied to allergic rhinitis or pollen allergies manifest and supports dietary recommendations to minimize symptoms. Additionally, the chart highlights how stomach acid may neutralize allergens, explaining why cooked foods often do not provoke reactions.
By detailing triggers and potential risks, the chart aids in preventing mild allergic symptoms from escalating into more severe symptoms. This streamlined approach enhances care quality, reduces risks, and improves patient outcomes in managing food-related allergies.
References
American Academy of Allergy Asthma & Immunology. (2021). Oral allergy syndrome: Symptoms, diagnosis & treatment. AAAAI. https://www.aaaai.org/Tools-for-the-Public/Conditions-Library/Allergies/Oral-allergy-syndrome-(OAS)
Kashyap, R. R., & Kashyap, R. S. (2015). Oral allergy syndrome: An update for stomatologists. Journal of Allergy, 2015, Article 543928. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/543928
Pastorello, E. A., D’Ambrosio, F. P., Pravettoni, V., Farioli, L., Giuffrida, G., Monza, M., & Ortolani, C. (2000). Evidence for a lipid transfer protein as the major allergen of apricot. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 105(2), 371–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0091-6749(00)90090-3
Commonly asked questions
Oral allergy syndrome is treated by avoiding raw foods that trigger reactions and substituting them with cooked or processed alternatives. In cases of severe symptoms, antihistamines or other medications may be prescribed, and patients should be educated on recognizing and managing allergic reactions.
The Oral Allergy Syndrome Chart identifies potential food triggers linked to pollen allergies during consultations. It is particularly valuable when patients with allergies, such as a birch pollen allergy, report severe allergic reaction symptoms.
Healthcare professionals use the chart to document cross-reactive foods and symptoms linked to what is called oral allergy syndrome. It serves as a guide for diagnosing oral allergy syndrome, often triggered by allergens like birch tree pollen and helps in patient education and management.