Peroneal Tendon Tear Test
Learn about the Peroneal Tendon Tear Test and use our template to record results!


What is a peroneal tendon?
The peroneal tendon comprises two tendons: peroneus brevis tendon and peroneus longus tendon. The former is attached to the outer part of the midfoot. The latter runs under the foot.
The peroneal tendon’s function is to stabilize the foot and ankle and protect them from getting sprains as best as possible.
Peroneal Tendon Tear Test Template
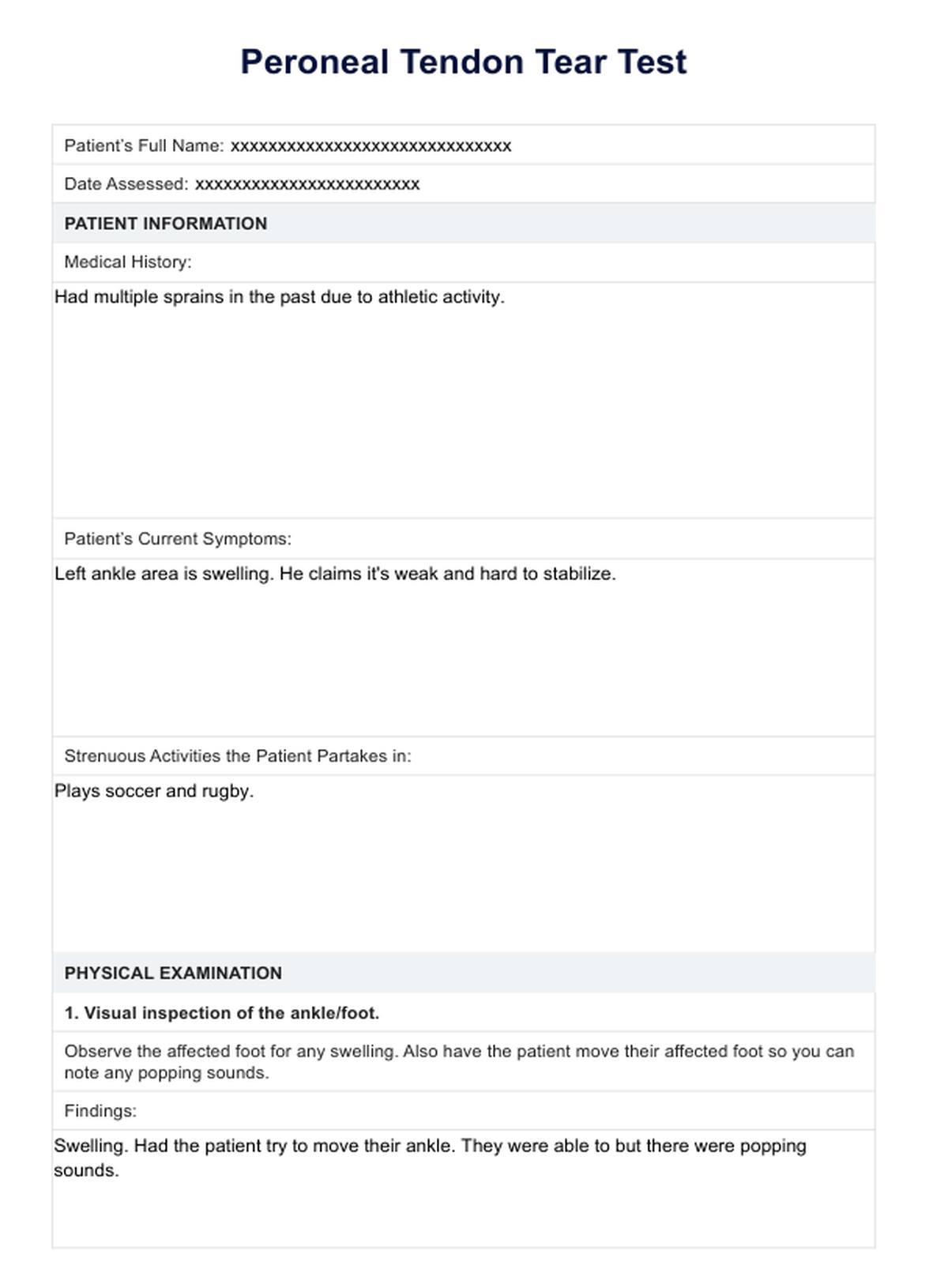
Peroneal Tendon Tear Test Example
What are peroneal tendon tears?
A torn peroneal tendon is a kind of injury that causes ankle pain. Tears can either be mild, moderate, or severe.
A mild tear isn’t anything to worry about because it can stabilize the foot and ankle. However, it’s possible for swelling to emerge. It’s not a tear and more of the tendon being overstretched.
A moderate tear is a partial tear of the tendon. There will be swelling, and the ankle and foot will suffer mild or moderate instability.
A severe tear is a complete rupture of the tendon. This will result in excruciating pain, and severe foot and ankle instability.
Symptoms of peroneal tendon tears
Whether the person has a peroneus brevis tendon tear or the other, here are the symptoms of people who have a peroneal tendon injuries:
- Swelling
- Foot and ankle instability (instability depends on the severity of the tear)
- Foot and ankle weakness
- Ankle pain
Causes of peroneal tendon tears
Peroneal tendon tears (or any other peroneal tendon pathology) are usually caused by trauma to the foot and ankle, commonly because of ankle sprain.
It can also be caused by chronic ankle and foot overuse, leading to problems like chronic lateral ankle instability.
Other factors contributing to potential peroneal tendon tears include something as simple as wearing uncomfortable shoes and playing sports that require a lot of footwork and ankle movements.
What is a Peroneal Tendon Tear Test?
A healthcare professional will perform a Peroneal Tendon Tear Test to diagnose peroneal tendon tears. This comprehensive examination involves the following:
- Interviewing patients about strenuous activities they recently did or participated in
- Visual inspection of the ankle to check for swelling
- Palpation of the ankle (especially the lateral malleolus region) to check for swelling, tenderness, pseudo-tumors, and if there is hindfoot alignment
- Observation of popping sounds by having the patient move their ankle/foot on their own
- Provocation tests to replicate symptoms (apprehension test, compression test, active circumduction, and ankle drawer testing)
- An imaging test (X-ray or MRI)
How are the results interpreted?
Suppose a patient feels pain at any point during the examination, and signs show that their feet and ankles have difficulty stabilizing themselves and that there is weakness. In that case, healthcare professionals will conduct an imaging test to confirm the specific problem and its severity. This will likely be an X-ray or MRI.
The patient’s treatment will depend on what the imaging test confirms, whether it’s a peroneal tendon rupture or something like peroneal tendonitis.
How does our Peroneal Tendon Tear Test template work?
We at Carepatron created a template for recording patient results to assess people who potentially have peroneal tendon tears.
It’s easy to use! All you need to do are the following:
- Fill out the patient’s medical history
- Note down what strenuous activities they’ve been doing
- Note down the pain they’re feeling
- Record results (foot and ankle strength, stability, warmth, and movements)
If the possibility of a peroneal tendon tear or another kind of injury seems high based on those examinations, it would be best to conduct an X-ray or MRI. A section for this on the template will have professionals indicate the imaging test they performed and what the findings are.
That’s it! If you print physical copies, you can fill out this test result recording sheet using a pen. You can totally go paperless if you wish since the PDF is interactive.
Benefits of this test
It can help determine and diagnose peroneal tendon tears
This test involves various methods of gathering information, from discussing symptoms with patients to physical examinations of the foot and ankle. Suppose there is pain during the physical examinations. In that case, healthcare professionals can narrow down the potential causes of pain and then conduct an imaging test to confirm and diagnose the actual problem.
It can be used to determine treatment
Since this test will end with an imaging test to confirm the problem, healthcare professionals can determine what to do for the patient, depending on the imaging test results. Does the patient need to simply rest? Do they need physical therapy to rehabilitate their foot and ankle? Do they require surgery? These questions will be answered once the imaging test produces results.
It can be used to monitor patients
Let’s stipulate that an official peroneal tendon tear diagnosis is made.
A professional can schedule a routine examination to check if the pain is still there and if it’s improving. If the pain is still there and still hurts to the same degree as before, perhaps making adjustments to a patient’s treatment plan would be best.
If the pain is still there but is considerably less painful, then it’s safe to assume the plan is working.
The imaging test portion can see if it’s healed or if it’s worse.
Peroneal tendon tear treatment
Treatment of peroneal tendon may include the following and will depend on the severity of the tear:
Resting and taking anti-inflammatory medicine
For mild peroneal tendon tears, conservative treatment will include taking a rest and ensuring that the affected foot is immobile. People with peroneal tendon tears can do this by decreasing their amount of daily physical activity, especially those involving their feet.
They can also wear a brace or foot and walk around with crutches to avoid exerting weight on the affected foot.
Anti-inflammatory medicine can whittle the pain until it’s gone and even reduce swelling. The dosage will depend on what’s prescribed by their healthcare provider.
Taking physical therapy
Physical therapy will likely be recommended for moderate tears and those recovering from severe ones to help rehabilitate the affected foot so it can regain its strength and ability to stabilize. This will involve several routine exercises to be done for smooth recovery.
Peroneal tendon surgery
If the tear is severe and can’t be addressed by conservative treatments, the last resort is surgery. Depending on how severe the tear is, surgeons may opt for any of the following:
- They take out the damaged part of the peroneal tendon and sew the remaining part to it
- Reconstruct it using a peroneal tendon donated to the provider
- Reconstruct it using another tendon from the foot
Commonly asked questions
It can take eight to twelve weeks. If it was repaired via surgery, it may take four months.
If a peroneal tendon tear isn’t addressed and left untreated, the affected foot might lose stability, feel chronic pain, and can make a person prone to recurring ankle sprains. These may eventually lead to disability and decreased mobility.
Yes. It’s best to take preventive measures and properly rehabilitate the affected foot to lessen the chances of it recurring.