Comprehensive Health Assessments in Nursing
Enhance patient care with Comprehensive Health Assessments in Nursing, ensuring thorough evaluations for better diagnosis, treatment, and improved health outcomes.


What is a comprehensive health assessment in Nursing?
A Comprehensive Health Assessment in Nursing systematically and thoroughly examines an individual's physical, mental, and emotional well-being. It is a foundational element in healthcare (specifically nursing practice), providing a holistic view of a patient's health status and aiding a healthcare team in forming sound clinical judgment.
This type of health assessment goes beyond the immediate health concerns and delves into various aspects of a person's life, contributing valuable information for personalized care plans.
The critical components of a comprehensive health assessment are:
- Psychosocial assessment: It is crucial to understand the patients admitted and their mental and emotional state. This focused assessment evaluates their mental health, social support systems, lifestyle factors, and any psychosocial stressors that may impact their well-being.
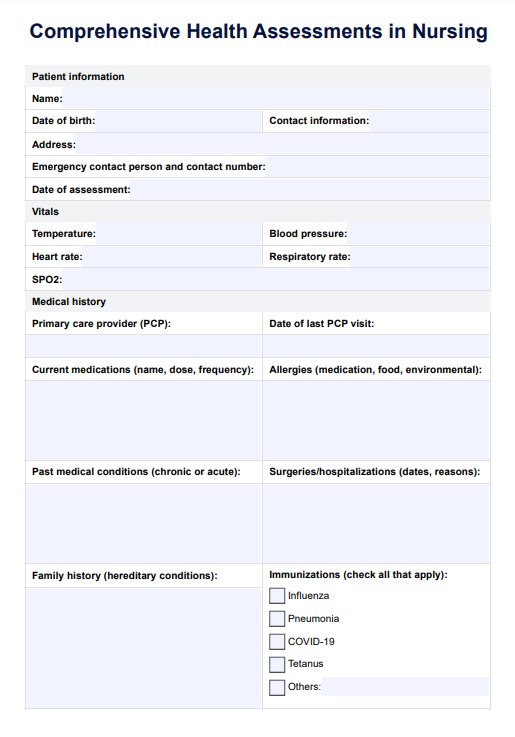
- Medical history: It is essential to gather a comprehensive medical history. This includes information about past health history, illnesses, surgeries, medication history, allergies, and family medical history.
- Cultural considerations: Recognizing the influence of cultural factors is crucial in providing patient-centered care. A comprehensive health assessment considers the patient's cultural background, beliefs, and practices.
- Head-to-toe assessment: Nurses conduct a detailed Head-to-Toe Assessment assessing vital signs, specific body systems, and overall body function. This helps identify any existing health status and potential risks. This physical examination helps in obtaining objective data.
Comprehensive Health Assessments in Nursing Template
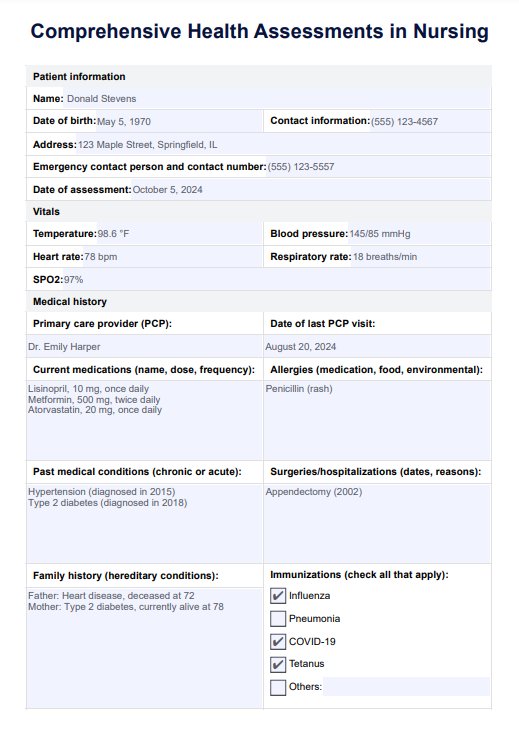
Comprehensive Health Assessments in Nursing Example
How does it work?
This comprehensive health assessment template is designed to streamline the process of evaluating your patients’ overall health. Follow these steps to effectively use our template and ensure a holistic approach to patient care:
Step 1: Access the template in Carepatron
Log into Carepatron and navigate to the templates section. Ensure the necessary patient details and tools are complete, such as a stethoscope, thermometer, and blood pressure cuff for the physical exam.
Step 2: Complete patient information and medical history
Start by filling in the patient’s name, date of birth, and contact details. Document their current medications, any known allergies, and significant family history of chronic illnesses (e.g., diabetes, heart disease). This is crucial for understanding their baseline health and planning appropriate interventions with the healthcare provider.
Step 3: Perform the psychosocial and cultural assessments
Use therapeutic communication to understand the patient’s emotional well-being, support systems, and cultural considerations. Document any mental status observations and religious or cultural preferences that may affect the care plan. This helps foster a trusting relationship and gather vital information for personalized care.
Step 4: Conduct the head-to-toe assessment
Begin the physical exam by assessing the patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and temperature. Proceed with a thorough evaluation of all body systems, from neurological to gastrointestinal. If any problem-focused assessment is necessary (e.g., due to a complaint of pain in a specific area), ensure to document it while maintaining a holistic approach.
Step 5: Add notes and sign off
Summarize the findings from the comprehensive assessment. Finally, review notes for accuracy, sign the document, and ensure the patient understands the next steps. Use the complete health assessments to form nursing diagnoses and formulate a nursing care plan for the patient.
How to conduct nursing comprehensive health assessments
A nursing comprehensive health assessment can empower healthcare professionals seeking comprehensive insights into a patient's well-being. This resource is a practical guide outlining systematic steps to conduct a thorough evaluation.
By following these steps, nurses can ensure patient-centered care and contribute to positive health outcomes:
Preparation and introduction
Begin by preparing the necessary tools and creating a conducive environment for patient medical assessment. Introduce yourself to the patient and explain the purpose and importance of this procedure. This stage is crucial to establishing rapport and obtaining the patient's consent.
Vital signs assessment
Systematically measure and record vital sign indications, including heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and body temperature. These indicators offer initial insights into the patient's physiological state and provide a baseline for further assessment.
Health history collection
Engage the patient in a detailed discussion to gather information about their past illnesses, surgeries, medications, allergies, and family medical background. This step offers a comprehensive understanding of the patient's medical background and informs the assessment process.
Psychosocial and psychological assessment
Assessing the patient's mental and emotional well-being can help explore their mental health, social support systems, lifestyle factors, and psychosocial stressors. This holistic approach provides valuable information for developing personalized care plans.
Cultural considerations
Recognize and respect the influence of cultural factors on the patient's health. Inquire about their cultural background, beliefs, and practices, ensuring that care plans are tailored to align with their cultural preferences.
Physical exam begins (head-to-toe assessment process)
Conduct a thorough physical exam, systematically assessing each organ system and overall body function. This step involves palpation, auscultation, and observation, allowing for the identification of existing health issues and potential risks.
The importance of comprehensive assessments
A comprehensive nursing assessment encompasses a holistic approach to evaluating a patient's health, going beyond the surface to uncover nuanced details essential for tailored care. Nurses conduct comprehensive health assessments to ensure patient satisfaction by critically understanding that all aspects of a patient's health are thoroughly evaluated and addressed.
The process involves meticulously examining vital signs, which serve as invaluable indicators of a patient's physiological state:
Vital signs monitoring
Tracking parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, respiratory rate, and body temperature provide critical insights into potential health issues and guide subsequent interventions.
Health history analysis
Equally pivotal is scrutinizing a patient's health history. A comprehensive health assessment involves delving into past illnesses, surgeries, medications, allergies, and familial medical backgrounds. This historical context is foundational in understanding the present health status and predicting potential risks or complications.
Expert conduct of assessments
In their role, nurses are adept at conducting comprehensive health assessments, utilizing their expertise to assimilate and interpret these multifaceted elements.
Proactive physical assessments
The art of a complete health assessment extends beyond the tangible to encompass the intangible aspects of a patient's well-being. A physical assessment, an integral component of this process, systematically examines organ systems and overall bodily function.
Commonly asked questions
A focused assessment targets a specific health issue or body system, while a CHA examines the entire patient. For example, a focused assessment might look only at cardiovascular health, while a CHA would evaluate all body systems and aspects of health.
In most healthcare settings, registered nurses (RNs) conduct health assessments. However, nurse practitioners, physicians, and other healthcare providers may also perform them.
The length of this assessment varies depending on the patient’s health status and complexity. It can take anywhere from 30 minutes to an hour or more, depending on the depth of the assessment needed.