Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior
Use this Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior to identify triggers, reduce harm, and provide structured care for safer, supportive patient interactions.


What is a Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior?
Managing aggressive behavior in nursing requires a comprehensive approach beyond merely controlling outbursts. A Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior addresses the root causes of unacceptable behavior while ensuring the safety and well-being of everyone involved. By understanding the triggers, interventions can be tailored to promote positive change and reduce the risk of harm to the patient and others.
Such a plan provides a structured approach for healthcare professionals to respond effectively, fostering a safer, more therapeutic environment that supports the patient's emotional needs. It also ensures consistency in care, builds trust, and improves the patient's overall well-being. In extreme cases, de-escalation techniques and safety measures may be necessary, but they are used alongside efforts to address underlying issues. Education plays a vital role as patients learn the impact of their actions and develop tools for managing stress. At the same time, caregivers gain the knowledge needed to create a supportive environment essential for recovery.
Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior Template
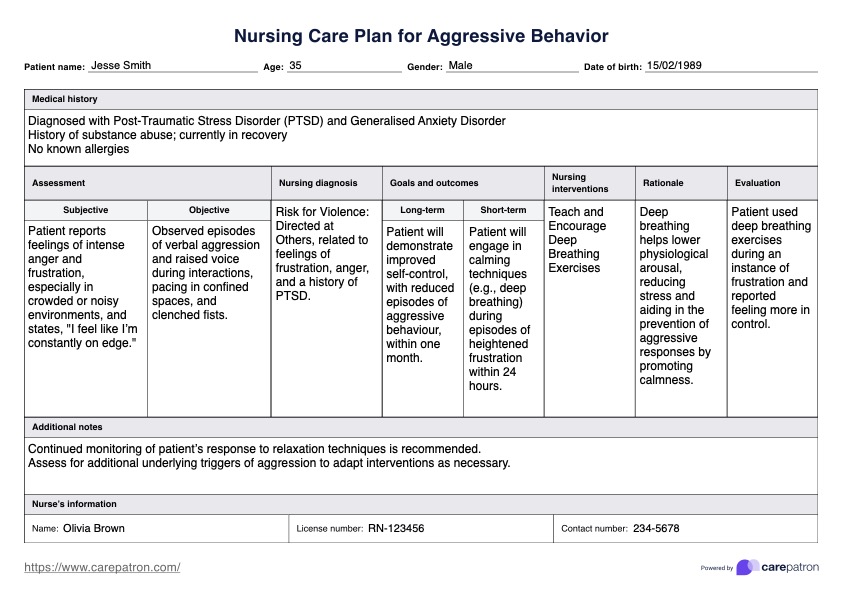
Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior Example
How do you use a Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior?
Using a nursing care plan can guide you in managing aggressive patient behavior. Here's how to incorporate this in your practice:
Step 1: Download the template
Begin by downloading the Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior template. This structured template provides a clear framework for managing aggressive behavior and supports psychiatric mental health nursing.
Step 2: Fill in patient information
Complete the patient's details, including name, age, medical history, and any mental disorders or substance abuse issues. This baseline information is essential for creating a tailored nursing care plan and identifying underlying factors contributing to behavioral problems.
Step 3: Start with the assessment
Use this section to assess aggressive behaviors, including physical aggression, verbal aggression, and impulse control issues. Documenting both subjective and objective data helps establish a safe, therapeutic environment and aids in diagnosing other potential problems, such as antisocial personality disorder or impaired social interaction.
Step 4: Formulate a nursing diagnosis
Analyze the assessment data to identify the patient's health problems and behavioral needs and formulate a clear nursing diagnosis. This diagnosis guides the care plan, effectively ensuring targeted interventions to address specific issues.
Step 5: Develop goals and nursing interventions
Create specific, achievable goals and nursing interventions based on your diagnosis and assessments. Focus on anger management techniques, coping skills, and fostering a therapeutic relationship to improve interpersonal relationships and overall mental health.
Step 6: Review and modify your nursing care plan
Monitor the patient's response to nursing interventions regularly and update the care plan as needed. Document the patient's progress and any plan changes in the template's evaluation section to track goal achievement and make necessary adjustments.
Managing aggressive behavior
In healthcare settings, aggressive behavior can be a challenging reality. But nurses aren't alone in facing it. Here are some ways to manage and handle the situation:
- De-escalation is the first line: Nurses are trained in calming the storm. Techniques like staying calm, using non-threatening language, and maintaining a safe distance help de-escalate tense situations before they escalate further.
- Safety first, always: Protecting everyone is paramount. This might involve using physical restraints (when necessary), calling for backup, or moving patients to a calmer environment.
- Teamwork makes the dream work: Nurses don't do it alone. They collaborate with doctors, social workers, psychologists, and security personnel to ensure a comprehensive and coordinated approach to managing aggression.
- Document every incident: Every incident, including triggers, interventions, and outcomes, is documented. This information is valuable for future assessments and helps refine protocols for better management.
- Continue learning: Nurses are committed to ongoing education. Training in de-escalation, crisis intervention, and cultural competence ensures they can handle diverse situations effectively.
- Adhere to ethics and legality: Adhering to legal and ethical standards is essential. Patient care, confidentiality, and informed consent are always at the forefront when managing aggressive behavior.
By following these and combining their expertise with compassion, healthcare professionals can navigate the challenges of aggressive behavior, creating a safer and more supportive environment for everyone involved.
Benefits of using a nursing care plan for behavioral problem
A pre-formatted care plan for behavioral problems can save time and make your work efficient. Other than that, here are some of the benefits it can bring you:
Ensures safety protocols for aggressive behavior
A well-structured nursing care plan for behavioral problems allows you to outline essential safety measures for managing aggressive behavior and violent behavior in healthcare settings. The plan helps reduce physical harm risks for both the patient and others by implementing de-escalation techniques and setting clear behavioral limits.
Builds a supportive therapeutic environment
This care plan creates a therapeutic environment that facilitates a trusting relationship between patients and healthcare professionals. By addressing unacceptable behaviors, guiding patients in expressing feelings, and managing aggression, the plan promotes a supportive space for interpersonal relationships and social interaction.
Targets underlying factors in aggressive behavior
The plan emphasizes thorough assessment and identifying patterns to address underlying factors like mental disorders, antisocial personality disorder, and substance dependence. Understanding risk factors helps tailor nursing interventions to manage negative behaviors and support appropriate behavior effectively.
Enhances coping skills and social skills
With a plan in hand, you can plan out and implement anger management skills and social skills training so that patients develop coping skills and impulse control. By teaching techniques to express anger appropriately and handle negative feelings, patients can work towards positive behaviors and better social interaction.
Commonly asked questions
The Nursing Care Plan for Aggressive Behavior involves a thorough assessment of triggers for criminal and violent behavior, implementing safety measures, teaching coping skills, and promoting communication to manage aggression effectively.
Nursing an aggressive patient involves establishing a therapeutic relationship, using de-escalation techniques for verbal aggression and physical harm, providing a safe environment, and implementing behavioral interventions tailored to the individual's needs.
Nursing interventions for anger patients include teaching relaxation techniques, promoting effective communication, identifying triggers, implementing environmental modifications, a treatment regimen using positive feedback, and monitoring progress.