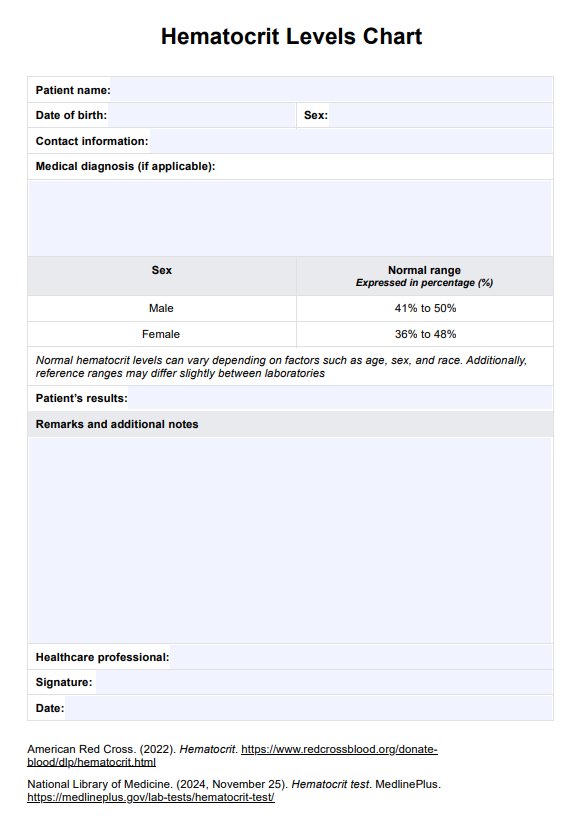
A hematocrit level is concerning when it falls below or rises above the normal range. According to the American Red Cross, in adults, normal hematocrit levels for men are typically between 41% and 50%, and for women, the normal range is 36% % to 44%. Routine blood testing can help identify if your levels are outside these ranges, which may signal issues like fewer red blood cells (anemia) or other blood cell disorders.
Hematocrit Levels
Get a Hematocrit Levels Chart PDF to track blood health effectively. Record, monitor, and personalize patient care during hematocrit blood tests.
Use Template
Hematocrit Levels Template
Commonly asked questions
If your hematocrit is low, you have fewer red blood cells than needed to carry enough oxygen throughout the body. This can cause fatigue, dizziness, shortness of breath, and other symptoms of a lack of red blood cells.
A safe hematocrit level is one that falls within the normal range for your age, sex, and race. For adult men, this range is 41%—50%, and for women, it’s 36%—48%.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











