Glaucoma Test Reports
Access a free Glaucoma Test Report template and example. Learn how to document patient results with ease.


What is a Glaucoma Test?
Glaucoma is a serious and progressive eye condition that primarily affects the optic nerve, the critical link that carries visual information from the eye to the brain. This condition is most often caused by increased intraocular pressure resulting from a buildup of fluid in the front part of the eye. Over time, high intraocular pressure can damage the optic nerve, leading to vision loss or even blindness. Glaucoma is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making regular eye examinations crucial for early detection and treatment.
In a Glaucoma Test, an ophthalmologist or optometrist will use a tonometer to measure the intraocular pressure in the patient's eye. This procedure is painless and typically takes only a few minutes to complete. The test results recorded in a Glaucoma Test Report and any other diagnostic tests will help determine if the patient has glaucoma and what treatment plan is best for them.
Regular glaucoma testing is vital for the early detection and management of this progressive eye condition. By regularly monitoring intraocular pressure and other diagnostic factors, healthcare professionals can provide timely treatment to slow the progression of glaucoma and preserve a patient's vision.
Glaucoma Test Reports Template
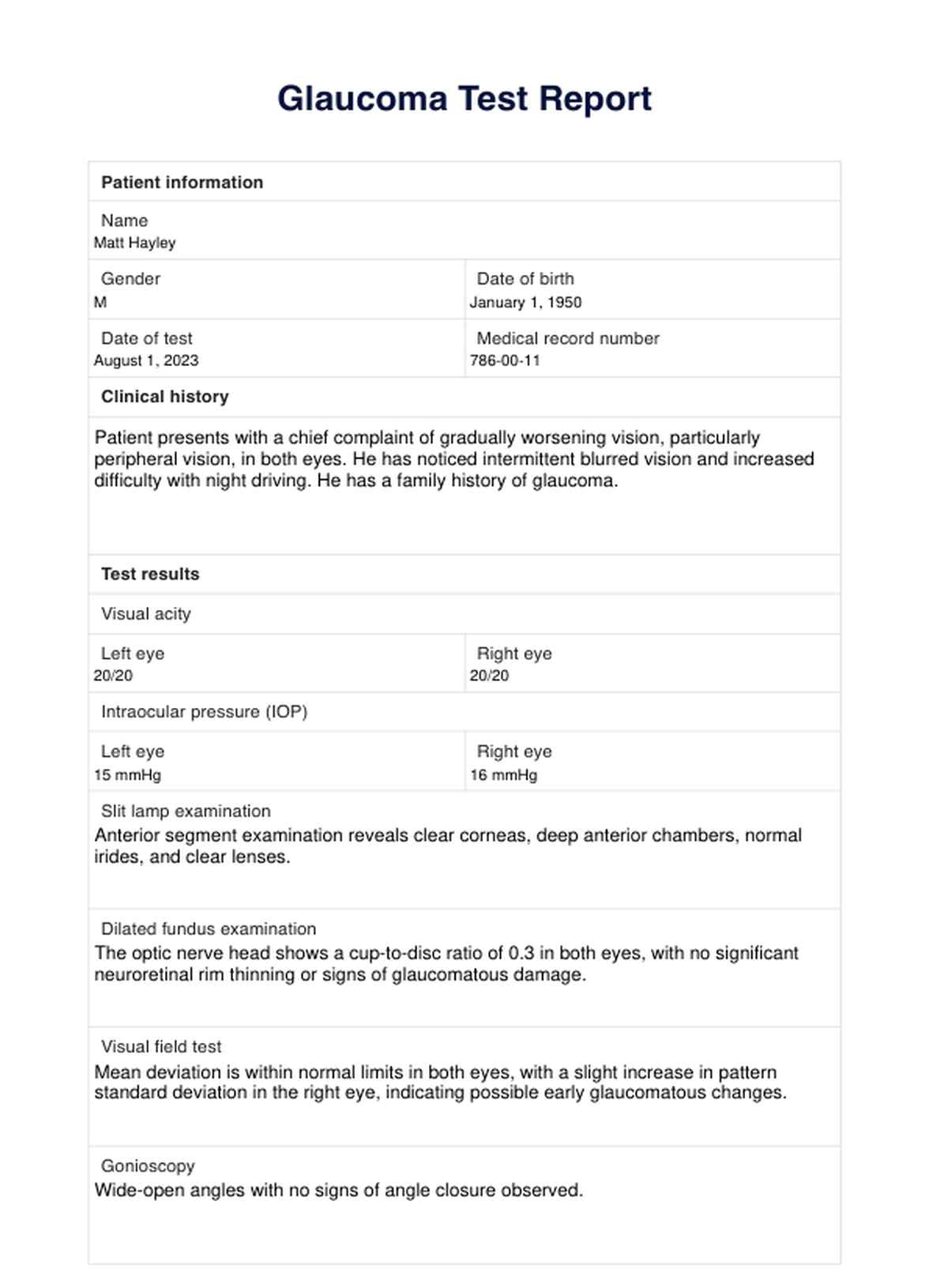
Glaucoma Test Reports Example
How does it work?
Carepatron's free Glaucoma Test Report template lets you document and track your patient's glaucoma test results quickly and efficiently. Here's how to get started:
Step One: Download the template
Get a copy of the printable Glaucoma Test Report template using the link on this page. You may also obtain it from the Carepatron app or our practice management software's resources library.
Step Two: Fill in patient information
Enter the patient's name, date of birth, and other necessary personal details in the designated fields. This information will help keep your patient's records organized and easily accessible.
Step Three: Record test results
Record the results of the glaucoma test, including intraocular pressure readings and any other relevant tests performed. You can easily add or remove sections as needed to tailor the report to your specific needs.
Step Four: Make notes and recommendations
Make any necessary notes and recommendations for the patient's treatment plan based on the test results. This can include prescribing medication, scheduling follow-up appointments, or referring to a specialist.
Step Five: Save and share
Once completed, save the Glaucoma Test Report to your patient's electronic health records using Carepatron's secure cloud storage. You can also easily share the report with other healthcare professionals involved in the patient's care.
When would you use this test report?
You can use Carepatron's Glaucoma Test Report template to document the results of any glaucoma tests performed on your patients. This report can be used for initial diagnosis, progress monitoring, and treatment effectiveness. Moreover, you can use this template to:
Share important information with your patients and their caregivers
The Glaucoma Test Report is a great tool for educating your patients and their caregivers about the disease, its progression, and the importance of regular testing and treatment. It can also help them understand their test results and any necessary lifestyle changes they may need to make.
Communicate with other healthcare professionals
As mentioned earlier, you can easily share the Glaucoma Test Report with other healthcare professionals involved in the patient's care. This can help facilitate effective communication and collaboration between different providers, leading to better overall care for the patient.
Track progress and make treatment decisions
Regularly filling out this report allows you to track changes in your patient's test results over time and use this information to make informed treatment decisions. This can be especially helpful in cases where the effectiveness of a certain treatment needs to be closely monitored.
Educate medical students and junior physicians
You can also use this template to educate medical students and junior physicians about glaucoma testing and documenting results. This can help them better understand the disease and its management, ultimately improving their ability to provide quality care to patients in the future.
What do the results mean?
The results section of the Glaucoma Test Report provides important information about the patient's test results, including visual field tests, intraocular pressure measurements, and optic nerve evaluations. This information is crucial in determining the severity of glaucoma and making treatment decisions. It is important to interpret these results accurately and communicate them effectively with the patient.
Visual acuity
Using an eye chart, the visual acuity test measures how well the patient can see at different distances. Results are typically recorded as a fraction, with 20/20 considered normal vision. A lower number indicates poorer vision, while a higher number indicates better vision.
Intraocular pressure (IOP)
The IOP test measures the pressure inside the eye, which can indicate glaucoma risk. Normal IOP ranges from 10 to 21 mmHg but can vary based on age and corneal thickness. Higher IOP may be an early sign of glaucoma but is not definitive and requires further testing.
Slit lamp examination
The slit lamp examination evaluates the anterior eye structures, including the cornea, iris, and lens. It helps detect abnormalities or signs of glaucoma. Results are recorded as normal or abnormal, with further testing if abnormalities are noted.
Dilated fundus examination
The dilated fundus examination allows viewing of the eye's interior, including the optic nerve and retina. It helps detect glaucoma-related damage, such as optic nerve thinning or changes in blood vessel appearance. Results are either normal or abnormal.
Visual field test
The visual field test assesses peripheral vision and detects abnormalities indicative of glaucoma. Results are typically plotted as a graph against normal values. Deviations from the norm may suggest potential vision loss due to glaucoma.
Gonioscopy
Gonioscopy evaluates the drainage angle of the eye where fluid flows out. It identifies blockages or abnormalities that may increase glaucoma risk. Results are recorded as open (normal), closed, or narrow-angle.
Optical coherence tomography (OCT)
OCT is a non-invasive imaging technique that produces high-resolution cross-sectional eye images using light waves. It detects changes in eye structures, such as optic nerve thinning or retinal layer changes indicative of glaucoma. Results are recorded as normal or abnormal.
Scanning laser polarimetry (SLP)
SLP measures the thickness of the retinal nerve fiber layer using light waves. It detects thinning or changes in this layer, indicating possible glaucoma. Results are recorded as within normal limits or outside normal limits.
Commonly asked questions
Glaucoma Tests are usually requested by eye doctors or ophthalmologists to assess a patient's risk for developing glaucoma or to monitor the progression of the disease. In some cases, optometrists may also request these tests if they suspect a patient may have glaucoma.
Glaucoma Tests are used to evaluate the eye's health and detect any abnormalities that may indicate a risk for developing glaucoma. They may also be used to monitor glaucoma progression in individuals already diagnosed with the disease.
The duration of a Glaucoma Test can vary depending on the specific tests being performed. Generally, it takes around 30 minutes to complete all three standard tests (nioscopy, OCT, and SLP). However, this may vary based on individual factors and the healthcare provider's equipment.