EMT Trauma Assessment
Discover the crucial benefits of mastering EMT Trauma Assessment in emergency medical care. Learn how it enhances patient outcomes, response efficiency, and overall care quality.


What is a trauma assessment?
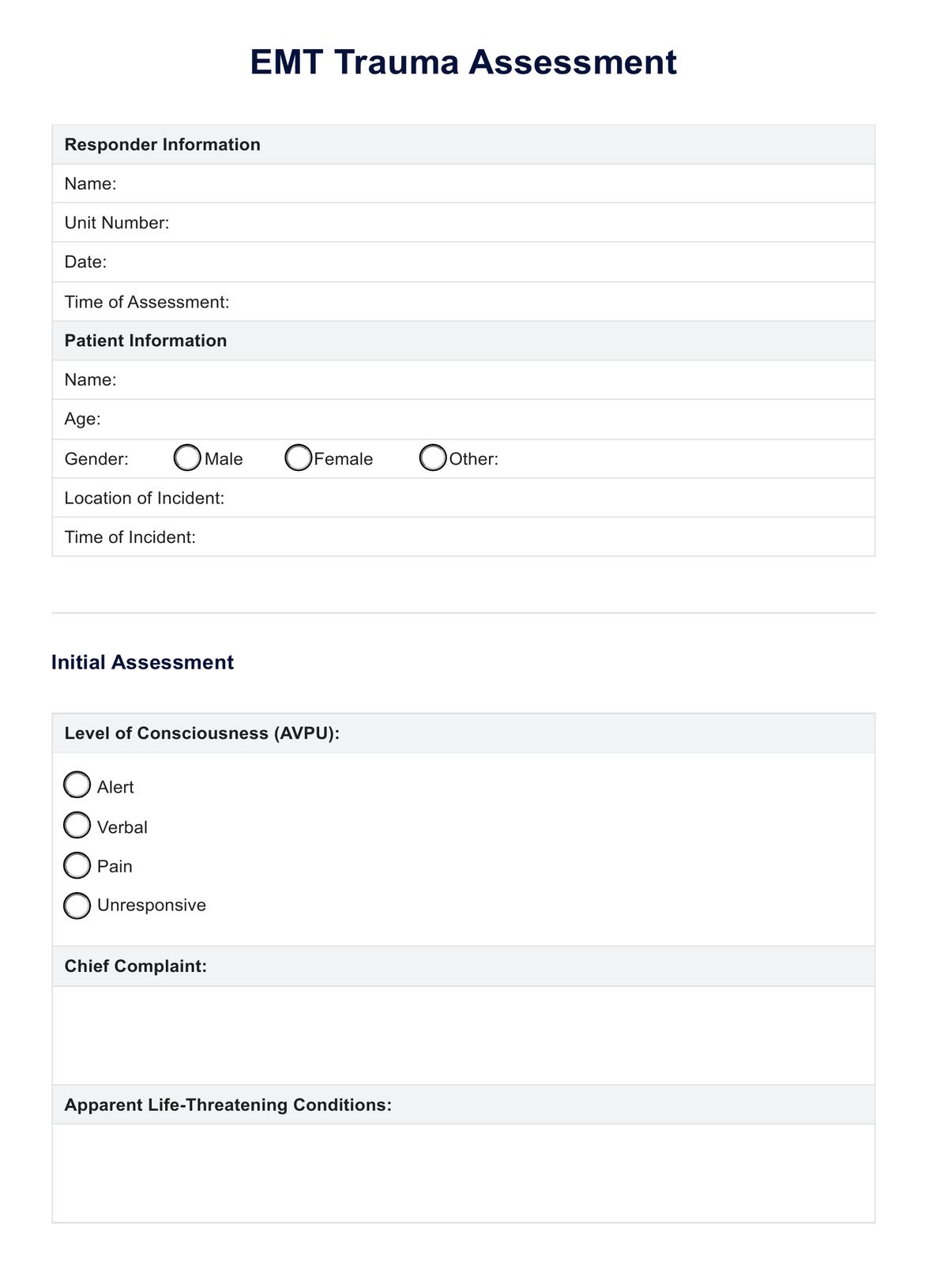
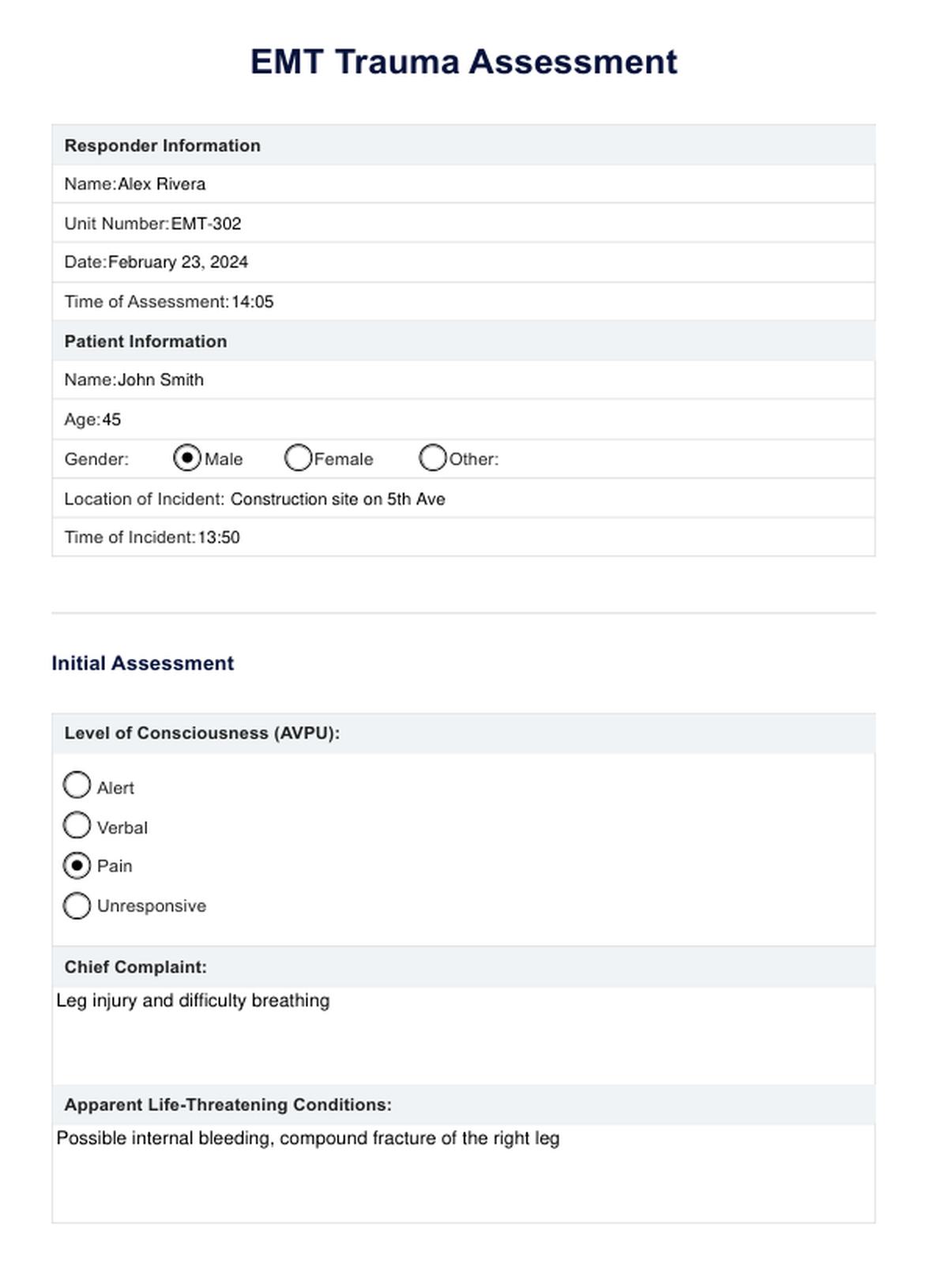
A trauma assessment is a vital procedure performed by Emergency Medical Technicians (EMTs) to evaluate and manage trauma patients swiftly. It involves a systematic approach to identify life-threatening injuries and provide immediate medical care.
Upon arrival at an emergency scene, EMTs assess the situation for safety and understand the injury mechanism, which is crucial for predicting potential internal injuries. The primary survey follows the ABCDE approach: Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, and Exposure. This includes ensuring a clear airway, assessing breathing and circulation, conducting a quick neurological evaluation using the AVPU scale, and checking for hidden injuries.
If the patient is stable, a secondary survey involves a detailed physical examination and reviewing the patient's medical history. This comprehensive patient assessment is essential for gathering information about the patient's condition.
Throughout the process, EMTs continuously monitor the patient and document findings to ensure continuity of care. This systematic trauma assessment is critical in emergency medical care, enabling EMTs to promptly identify and treat life-threatening injuries, improving patient survival and recovery.
EMT Trauma Assessment Template
EMT Trauma Assessment Example
What do EMT assessments include?
EMT assessments are comprehensive evaluations that include several critical components to ensure a thorough examination of the trauma patient. These assessments are designed to be systematic and efficient, enabling EMTs to identify all potential injuries and provide appropriate care.
Rapid trauma assessment
This is the initial evaluation conducted to identify any obvious or life-threatening injuries. It is a quick, systematic process that begins with assessing the patient's consciousness level and then scanning for major bleeding, deformities, or other signs of injury. This assessment is particularly crucial in situations with a significant mechanism of injury, such as a fall from a height or a high-speed vehicle collision, where the likelihood of multiple injuries is high.
Extremity trauma
EMTs pay special attention to extremity trauma, which includes injuries to the arms and legs. These injuries can range from fractures and dislocations to amputations and can significantly impact the patient's mobility and overall condition. Assessment involves checking upper extremities for deformities, swelling, and bruising and assessing circulation, sensation, and movement in each extremity. Proper management of extremity injuries is crucial to prevent further harm and to ensure optimal recovery.
Obvious injury
Identifying obvious injuries is a key component of the EMT assessment. This includes visible wounds such as lacerations, burns, and penetrating injuries. EMTs assess these injuries for severity, potential for blood loss, and risk of infection. Immediate management may involve controlling bleeding, protecting the wound, and preparing for rapid transport to a medical facility.
Spinal precautions
If the mechanism of injury suggests a potential spinal injury, EMTs take spinal precautions. This involves immobilizing the patient's spine to prevent further injury. Spinal injuries can be particularly dangerous and may lead to permanent paralysis or other severe complications if not properly managed.
Patient's airway
Ensuring the patient's airway is clear and protected is a top priority. This involves checking for obstructions, such as blood, vomit, or foreign bodies present, and ensuring the airway remains open. Techniques such as jaw thrust or chin lift may be used, and in more severe cases, advanced airway management techniques may be necessary.
Mechanism of injury
Understanding the mechanism of injury is crucial as it provides valuable clues about potential internal injuries. For example, a patient who has fallen from a significant height may have internal injuries even if there are no obvious external signs of trauma. EMTs use this information to guide their assessment and prioritize treatment.
EMT assessments are multifaceted and require high skill and attention to detail. They are essential in providing immediate and effective care to trauma patients, ultimately improving patient outcomes and saving lives.
Assessment outcomes
The outcomes of an EMT trauma assessment are critical in determining the patient's immediate and long-term treatment plan. These outcomes can vary widely depending on the nature and severity of the injuries but generally include:
- Identification of life-threatening injuries: The primary goal is to identify and manage any immediate threats to life. This includes securing the airway, controlling significant bleeding, and stabilizing major injuries.
- Prioritization of care: Based on the assessment, EMTs prioritize medical interventions. For instance, in multiple injuries, care is directed first to the injuries that pose the greatest threat to life.
- Transport decisions: The assessment outcomes help determine the urgency of transport and the most appropriate facility for the patient. Patients with severe or multiple injuries may need to be transported to a specialized trauma center.
- Informing hospital care: The findings from the field assessment provide valuable information to the hospital staff, allowing them to prepare for the patient's arrival and expedite necessary care.
- Documentation for continuity of care: Accurate and detailed documentation of the assessment findings is essential for ensuring continuity of care as the patient transitions from pre-hospital to hospital treatment.
Effective EMT trauma assessments are integral to patient outcomes, significantly impacting treatment and overall recovery.
Next steps
After the initial trauma assessment and stabilization, the next steps involve further medical evaluation and treatment. These typically include:
- Transport to a trauma center or emergency department: Based on the assessment, the patient may be transported to a trauma center or emergency department for advanced care. The severity of injuries influences this decision, the patient's overall condition, and the resources available at the receiving facility.
- Secondary survey in the hospital: Upon arrival at the hospital, a secondary survey, which is a comprehensive head-to-toe examination, is conducted. This survey may reveal injuries that were not apparent during the initial assessment.
- Diagnostic tests: The hospital team may perform various diagnostic tests, such as X-rays, CT scans, or blood tests, to further evaluate the patient's condition.
- Specialized treatment: Depending on the injuries, the patient may require specialized treatment, including surgery, intensive care, or specific medical interventions.
- Recovery and rehabilitation: Post-stabilization, the focus shifts to recovery and rehabilitation, which may involve physical therapy, counseling, and ongoing medical care.
Understanding these next steps is crucial for EMTs as it helps prepare the patient for the transition to hospital care and ensures a seamless continuum of treatment.
The benefits of understanding how to conduct a trauma assessment
Here are the benefits of knowing how a EMT Trauma Assessment works:
Rapid identification of life-threatening injuries
Enables EMTs to quickly recognize critical conditions, such as airway obstructions or severe bleeding, facilitating immediate and targeted treatment.
Improved patient outcomes
Accurate assessments lead to better-informed decisions about emergency care, significantly enhancing patient survival and recovery rates.
Enhanced efficiency in emergency response
Proficiency in trauma assessment allows for effective resource allocation, including backup, specialized equipment, or rapid transport, optimizing the emergency response.
Seamless continuum of care
The initial assessment and thorough documentation provide essential information for hospital staff, ensuring uninterrupted and appropriate care upon the patient's arrival.
Psychological impact management
Skilled EMTs can reduce panic and reassure patients and bystanders, establishing trust and safety in emergencies.
Foundation for effective training
Understanding trauma assessment is crucial in training new EMTs, ensuring upcoming responders are well-equipped to handle field challenges.
Overall quality enhancement in emergency medical care
Mastery of trauma assessment techniques contributes to the quality and effectiveness of emergency medical services, benefiting public health and safety.
Commonly asked questions
Understanding the mechanism of injury helps predict potential internal injuries and guides the focus of the assessment.
Spinal precautions prevent further injury to the spinal cord in cases where spinal injuries are suspected, reducing the risk of long-term disability or death.
Rapid trauma assessment focuses on identifying and managing life-threatening conditions, while the secondary survey is a detailed examination to identify all injuries.

.jpg)