D-Dimer
Be more familiar with the D-dimer test. Click here for a quick guide, a free request form, and a clinical notes template.
�?�


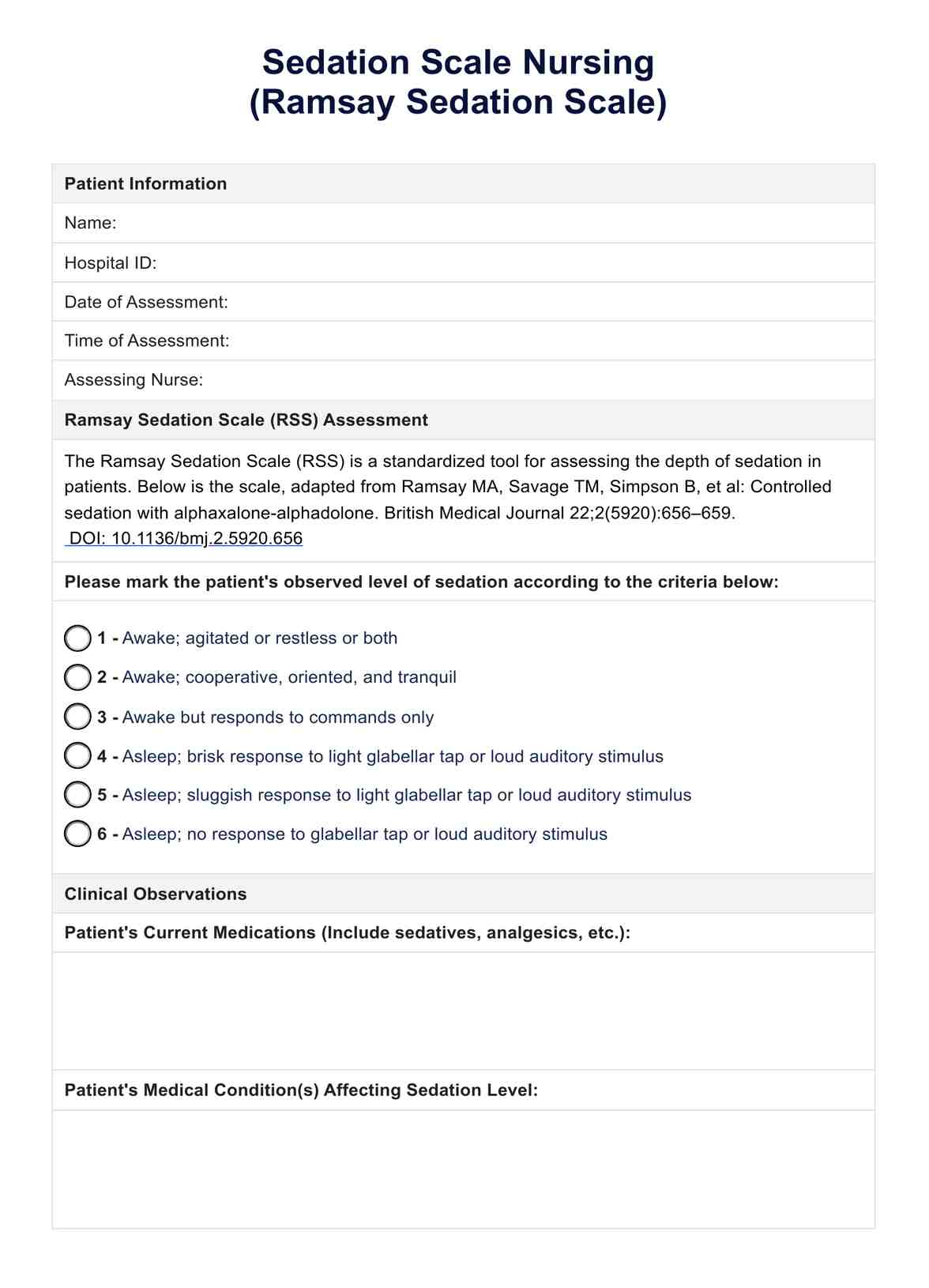
What is a D-Dimer Test?
A D-dimer test is a blood test that measures the D-dimer protein, a protein fragment that is produced when blood clots dissolve in the body. The test is typically used to determine if one has a blood clotting condition and needs additional blood tests and imaging procedures for a diagnosis. Some conditions it can help diagnose are pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, and stroke.
D-Dimer Template
D-Dimer Example
How does it work?
Step One. Access and Download the Template
Have a digital and printable copy of the D-dimer test that doubles as a request form and document for interpretation. Grab a copy by doing either of the following:
- Clicking the �??Use Template�?� or �??Download Template�?� button
- Searching �??D-dimer Test�?� on Carepatron�??s template library�??s search bar on the website or app
Step Two. Interview, Assess, or Examine the Patient
Before requesting, they must interview, assess, or physically examine the patient to determine if they need the test. If they do, use the template as a request form and fill out all the needed information.
Step Three. Perform the Test
On the test day, the patient must bring the filled-out template to the practitioner responsible for collecting the sample. The document will prove that you requested the D-dimer test.
Step Four. Analyze and Interpret the Results
Once the test results are available, you may use the template to write the analysis and interpretation based on the results. That way, should you need a document you can rely on when formulating a diagnosis or treatment plan, you have one.
Step Five. Securely Store the Template
Whether you use it as a document for notes or a request form, you must store the document at a secure physical location or on Carepatron, a HIPAA-compliant clinical documentation software, with other medical records of the patient in the patient portal.
When would you use this test?
A physician, physician�??s assistant, or nurse practitioner may use this test when they suspect that the patient has a problem with blood clotting or if they exhibit the symptoms of the following conditions:
- Deep Vein Thrombosis
- Pulmonary Embolism
- Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Aside from those, the test may be used to monitor those receiving Anticoagulant Therapy and to rule out thrombosis.
Note that even if the test can indicate the presence of a clot, it cannot be used to determine the location of the clot.
What do the results mean?
You can expect to find the exact measure of D-dimer found in the patient�??s blood and the typical range of D-dimer that must be in a person�??s blood.
The D-dimer level must typically be less than 0.50 milligrams per liter (mg/L) of fibrinogen equivalent units (FEU). Suppose the patient�??s D-dimer level is equivalent to or higher than the level mentioned, indicating a positive test. In that case, they are more likely to have a clotting disorder and must undergo further testing to diagnose.
However, it�??s also important to consider that certain situations may raise a person�??s D-dimer level, such as an autoimmune disorder, immobilization, and recent surgery.
Research & Evidence
Even if usage frequency by healthcare practitioners can be used as evidence for the D-dimer test�??s usefulness, studies still prove what it is useful for. One of them is a journal article from Clinical Chemistry that enumerates the practicality of the D-dimer test. According to the writer, the results of the D-dimer test, in combination with other medical tests, can be used to:
- Exclude Venous Thromboembolism (VTE) in symptomatic outpatients
- Assess the risk of recurrent Venous Thromboembolism
- Reveal the duration of secondary prophylaxis
- Diagnose and monitor Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Aside from that, there�??s another journal article from Clinical Advances in Hematology and Oncology that states that the D-dimer test can also be used to exclude Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT) and Pulmonary Embolism (PE) as well as monitor anticoagulation therapy.
References
- Armando Tripodi, D-Dimer Testing in Laboratory Practice, Clinical Chemistry, Volume 57, Issue 9, 1 September 2011, Pages 1256??1262, https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2011.166249
- The role of D-Dimer testing in clinical hematology and oncologHematologyOncology. (n.d.). https://www.hematologyandoncology.net/archives/august-2017/the-role-of-d-dimer-testing-in-clinical-hematology-and-oncology/
Commonly asked questions
Physicians, their assistants, and nurse practitioners are the healthcare professionals who typically request a D-dimer test.
They are used when the referring physician suspects that the patient is suspected of having a blood clotting condition because of their symptoms or when they�??re undergoing anticoagulant therapy sessions.
The sample collection can take a few minutes; however, the processing, analysis, and interpretation of results.