Sedation Scale Nursing (Ramsay Sedation Scale)
Discover key sedation scales used in nursing, including RASS and Ramsay Scale, for accurate patient sedation assessment in critical care settings.


What is patient sedation?
Patient sedation refers to administering medications or techniques to help relax, calm, or induce sleep in patients undergoing various medical procedures or treatments. The primary goal of sedation is to ensure patient comfort, minimize pain and anxiety, and help manage the patient's agitation or restlessness, especially in settings such as the Intensive Care Unit (ICU) or during surgical procedures.
Sedation levels vary from light, allowing the patient to relax while remaining awake, to deep sedation, where the patient is in a state close to unconsciousness but can be aroused with significant stimulation.
Why do nurses and doctors sedate their patients?
Nurses and doctors sedate ICU patients to facilitate medical procedures that might be uncomfortable, painful, or require the patient to remain still. Sedation is also critical in managing adult patients who are mechanically ventilated, ensuring they do not experience distress or discomfort while receiving life-saving treatment. Additionally, sedation manages critically ill patients' agitation, ensuring their safety and promoting optimal healing conditions.
How do they sedate patients?
Patients are sedated using various sedative medications administered through different routes, including oral, intravenous, or inhalational. The choice of sedation level and medication depends on the patient's health status, the procedure's nature, and the expected duration of sedation. Sedation protocols and clinical practice guidelines help ensure that sedation is administered safely and effectively, tailoring the approach to each patient's needs.
What is light sedation, moderate sedation, and deep sedation?
Sedation levels, categorized into light, moderate, and deep, describe the depth of sedation and the patient's response to stimuli. Understanding these levels helps healthcare providers choose the appropriate sedation for different medical situations, ensuring patient safety and procedure efficacy.
Light sedation
Light sedation, also known as anxiolysis, is the mildest level of sedation where patients are relaxed but fully awake and coherent. They can understand and respond to verbal commands and physical prompts without assistance. Despite the sedation, patients retain full control over their protective reflexes and can maintain unassisted airway function.
This level of sedation is typically used for minor procedures or in situations where the primary goal is to alleviate anxiety while allowing the patient to remain comfortable and communicative.
Moderate sedation
Moderate sedation, or conscious sedation, involves a deeper level of sedation than light sedation, where patients may drift in and out of a light sleep but remain responsive. They can respond purposefully to verbal commands alone or with light tactile stimulation. Although their cognitive functions and coordination may be impaired, patients under moderate sedation can maintain their airway reflexes and spontaneous ventilation without assistance.
This sedation level is commonly employed in procedures that require the patient to be more relaxed and less aware of the surroundings but not fully unconscious, such as during endoscopies or minor surgical interventions.
Deep sedation
Deep sedation places patients in a state that borders on unconsciousness, where they cannot be easily aroused but may respond to repeated or painful stimulation. Under deep sedation, patients may need assistance maintaining their airway and ensuring adequate spontaneous ventilation. Protective reflexes may also be diminished or absent. This level of sedation is often used for more invasive procedures that require patients not to have any awareness of the procedure and to minimize movement.
Due to the increased risk of respiratory and cardiovascular depression, deep sedation requires careful monitoring by trained healthcare professionals, typically in a hospital or surgical center setting.
Each sedation level serves distinct purposes within clinical practice and is chosen based on the specific needs of the patient and the nature of the medical procedure. The primary aim is to ensure the patient's comfort and safety while providing an adequate soothing effect that allows medical interventions to be carried out effectively.
Sedation Scale Nursing (Ramsay Sedation Scale) Template
Sedation Scale Nursing (Ramsay Sedation Scale) Example
What are sedation scales?
Sedation scales are tools healthcare professionals use to assess and monitor the depth of sedation in patients, ensuring that sedation levels are appropriate for the patient's condition and the medical procedure. These scales provide a systematic way to evaluate a patient's response to sedation and adjust sedative medications as needed.
Sedation scales used by nurses
Nurses and other healthcare professionals rely on several standardized scales to effectively evaluate and communicate patients' sedation levels. These tools are integral to sedation protocols and sedative medication administration, helping to prevent the complications associated with both under and over-sedation.
In the critical and often high-stakes healthcare environment, particularly within intensive care units and during various medical procedures, the accurate assessment of a patient's level of sedation is paramount. Here are some key sedation scales used widely in clinical settings:
Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS)
The Richmond Agitation Sedation Scale (RASS) is a comprehensive tool adopted by nurses and healthcare professionals, especially in intensive care units (ICUs), to assess a patient's level of sedation or agitation accurately. RASS scores range from -5 (indicating unarousable deep sedation) to +4 (severe agitation).
RASS facilitates the evaluation of patients under sedation, particularly those who are mechanically ventilated, by providing a clear, standardized method to communicate about a patient's sedation status. It ensures that sedation is maintained appropriately to ensure patient comfort and minimize the risks associated with oversedation.
Inova sedation scale
The Inova sedation scale serves as a vital tool in the nuanced monitoring of sedation levels, focusing primarily on the patient's responsiveness to verbal or physical stimulation. This scale is instrumental in guiding the administration of sedative medications, ensuring that patients receive the correct dosage to achieve the desired level of sedation without compromising their safety.
The Inova sedation scale is beneficial when maintaining a specific sedation level is crucial for patient recovery and comfort, such as in postoperative care or when managing critically ill patients.
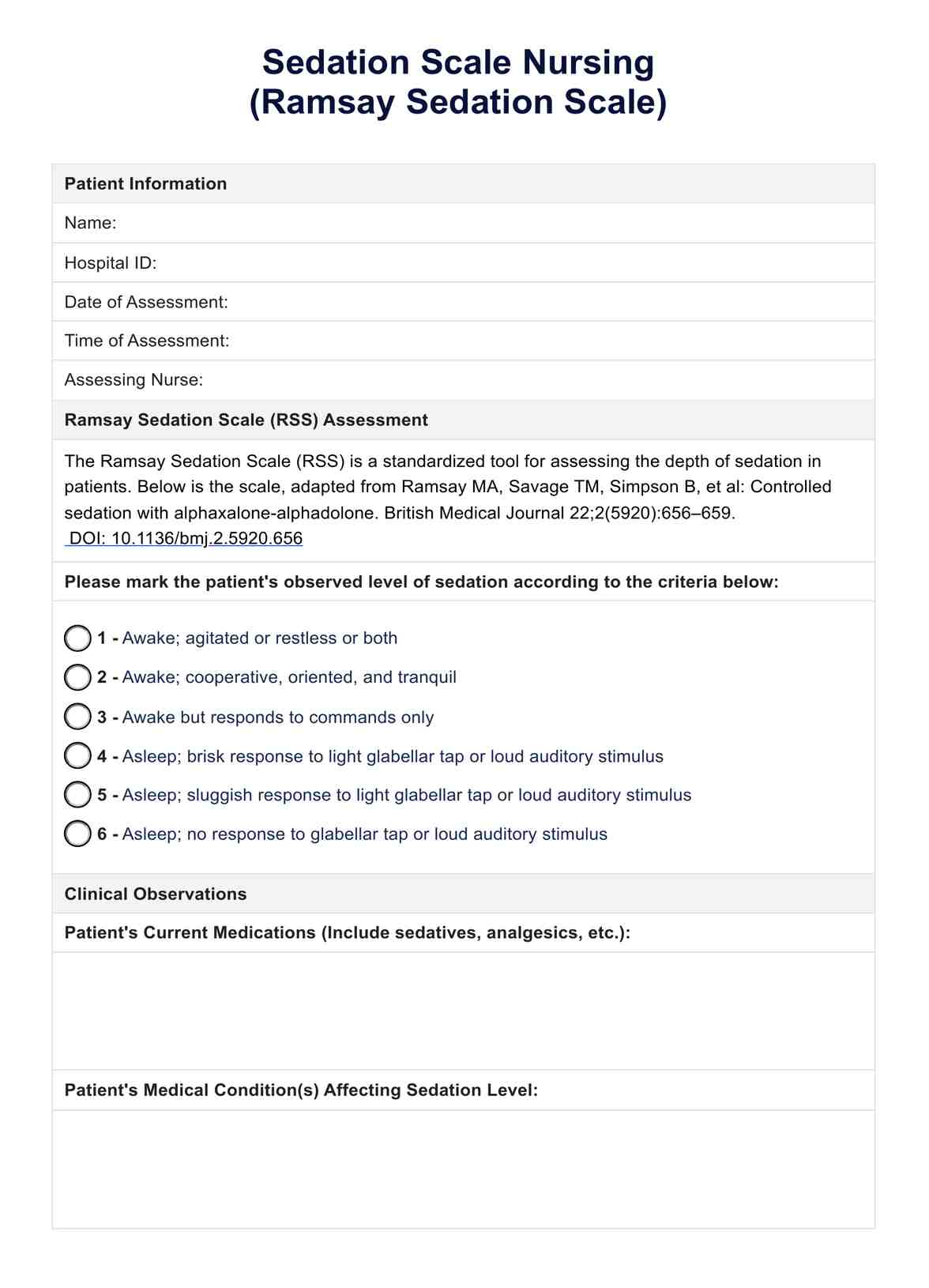
Ramsay Sedation Scale
The Ramsay Sedation Scale, one of the first assessment tools developed, remains a cornerstone in evaluating sedation depth. It provides a simple yet effective framework for categorizing patients' responses to stimuli, with scores ranging from 1 (the patient is anxious and agitated) to 6 (no response to stimulus, indicating deep sedation).
The Ramsay Sedation Scale's straightforward approach makes it a valuable resource in various clinical settings, from ICUs to surgical units, enabling consistent and accurate sedation level assessments. This scale helps tailor sedative administration to individual patient needs, promoting safety and comfort during medical procedures.
Each sedation scale plays a crucial role in clinical practice, offering a systematic approach to monitoring and managing sedation in hospitalized patients. By employing these tools, nurses and healthcare professionals can ensure optimal sedation levels, improving patient outcomes and enhancing the overall quality of care in critical care and surgical settings.
How is the Ramsay Sedation Scale scored?
The Ramsay Sedation Scale scores range from 1 (patient is anxious and agitated or restless) to 6 (patient exhibits no response to stimuli). This scale helps clinicians titrate sedative medications to achieve the desired level of sedation, ensuring patient comfort while maintaining safety.
What are the next steps after assessing a patient using the scale?
After assessing a patient with the Ramsay Sedation Scale, healthcare professionals adjust sedation medication dosages to maintain the desired sedation level. Continuous monitoring is essential to respond to changes in the patient's condition or sedation needs, especially in mechanically ventilated or critically ill patients.
Benefits of using this sedation scale
Using the Ramsay Sedation Scale offers several benefits:
Providing a standardized method for assessing sedation
The Ramsay Sedation Scale is highly beneficial for its standardized assessment of patient sedation levels. By offering a clear and consistent framework for evaluation, this scale helps accurately determine the depth of a patient's sedation. This uniformity is crucial for ensuring that all healthcare team members have a common understanding of the patient's status, which is essential for routine care and in situations where rapid decisions are necessary.
Enhancing patient safety by preventing over-sedation
One of the key advantages of employing the Ramsay Sedation Scale is its role in enhancing patient safety. By providing specific criteria for different levels of sedation, the scale aids healthcare professionals in administering the appropriate amount of sedative medication, thereby significantly reducing the risk of over-sedation. Over-sedation can lead to adverse outcomes, including respiratory depression and prolonged recovery times. Thus, the Ramsay Sedation Scale is important in safeguarding patients against these risks.
Facilitating effective communication among healthcare providers
Effective communication among healthcare providers is vital for cohesive patient care management, particularly in critical care settings. The Ramsay Sedation Scale facilitates this communication by providing a common language for describing a patient's sedation level. Whether updating a colleague during a shift change or discussing a patient's condition in a multidisciplinary team meeting, the scale ensures that all healthcare professionals are aligned in their understanding of the patient's sedation status, promoting coordinated care and optimal treatment outcomes.
Incorporating this Richmond agitation sedation scale template can strengthen your practice and client results. This resource assists clients in developing actionable improvement plans.
Commonly asked questions
Adjusting sedation levels in mechanically ventilated patients often involves using sedation protocols that include daily sedation interruption or targeted sedation levels based on sedation scales.
Sedation levels in hospitalized patients, especially those in critical care settings or undergoing specific treatments, should be assessed regularly. The frequency of assessments can vary based on the patient's condition, the type of sedation administered, and the clinical setting. Continuous monitoring is generally recommended for mechanically ventilated patients or those on continuous sedative infusions, with adjustments made to maintain optimal sedation levels.
Yes, sedation scales can be adapted for use in pediatric patients, although specific scales have been developed to cater to the unique needs and responses of children. Pediatric sedation scales consider factors such as developmental stages and non-verbal cues to assess sedation levels in younger patients accurately. Healthcare providers should select a validated scale for pediatric use to ensure the safety and efficacy of sedation in this population.

.jpg)