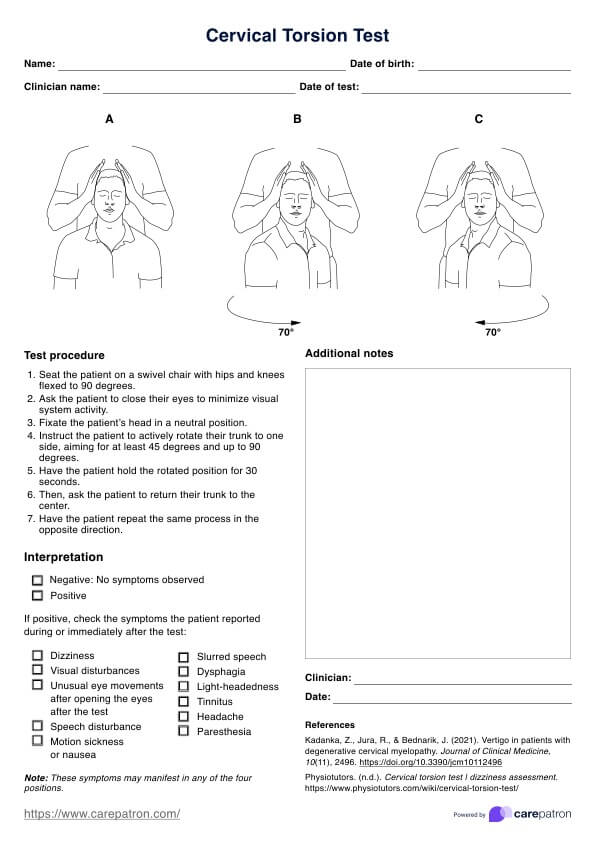
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
Understand the intricacies of Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPET), a comprehensive measure of heart and lung function during exercise.


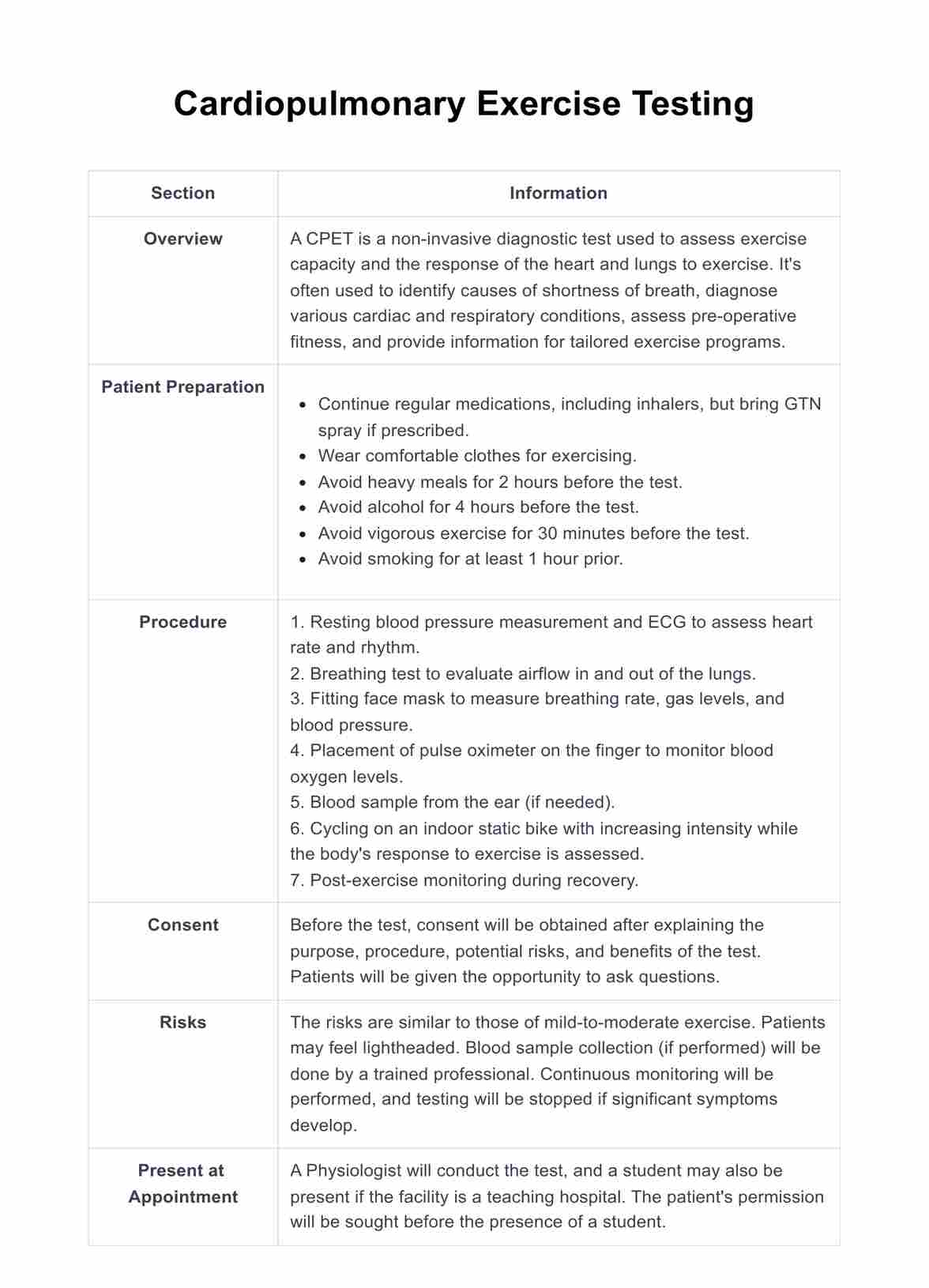
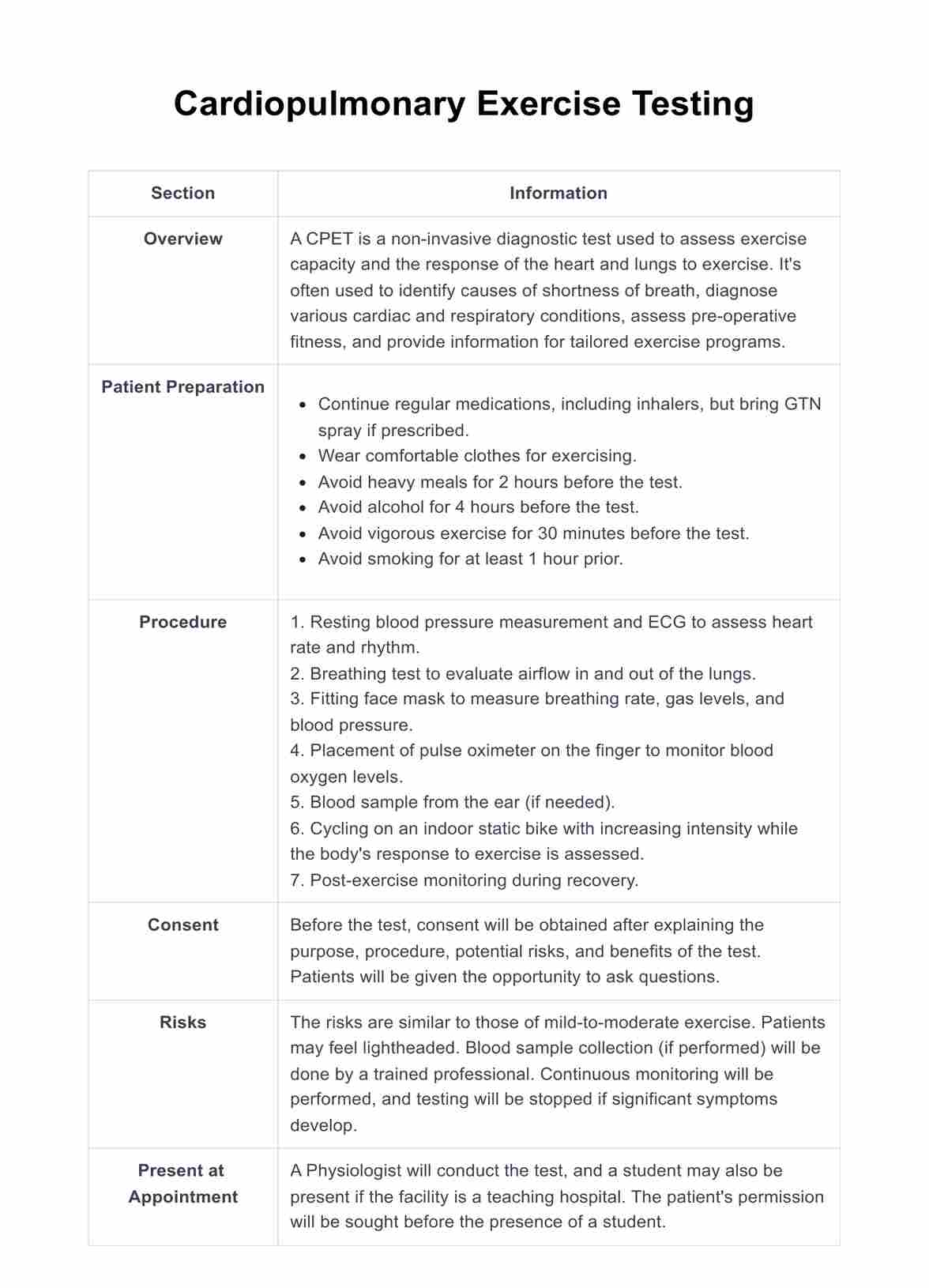
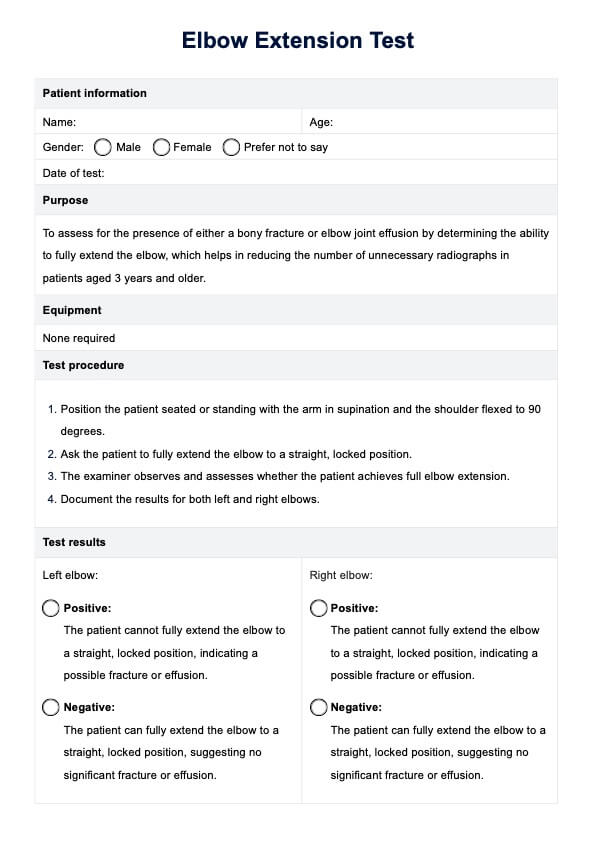
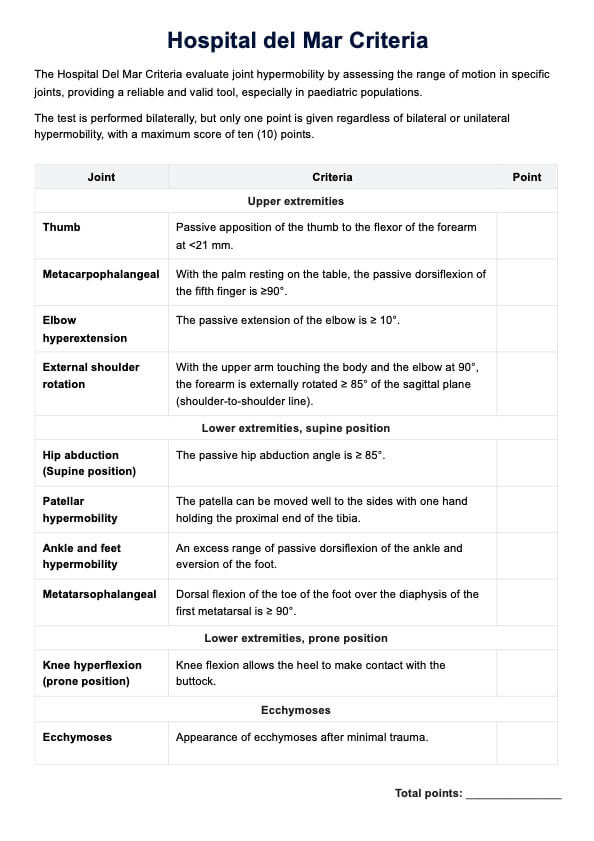
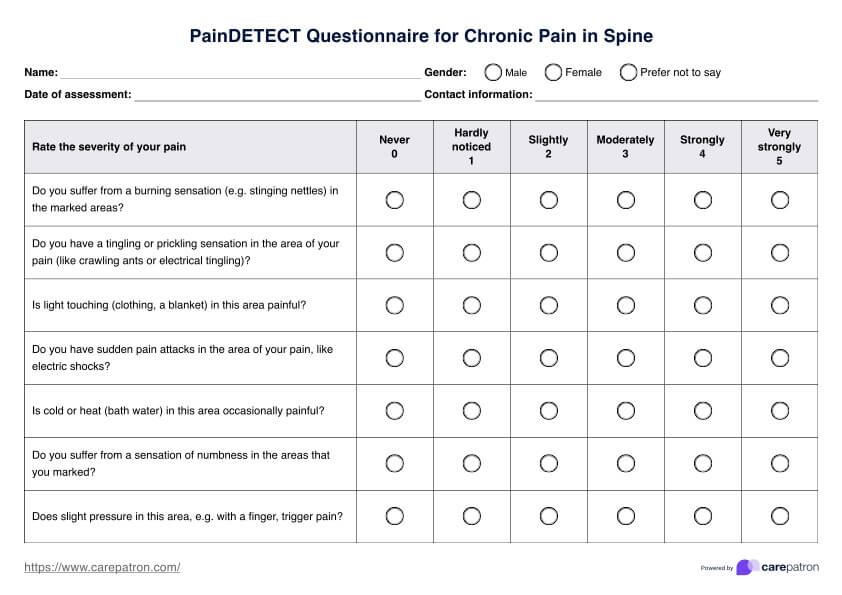
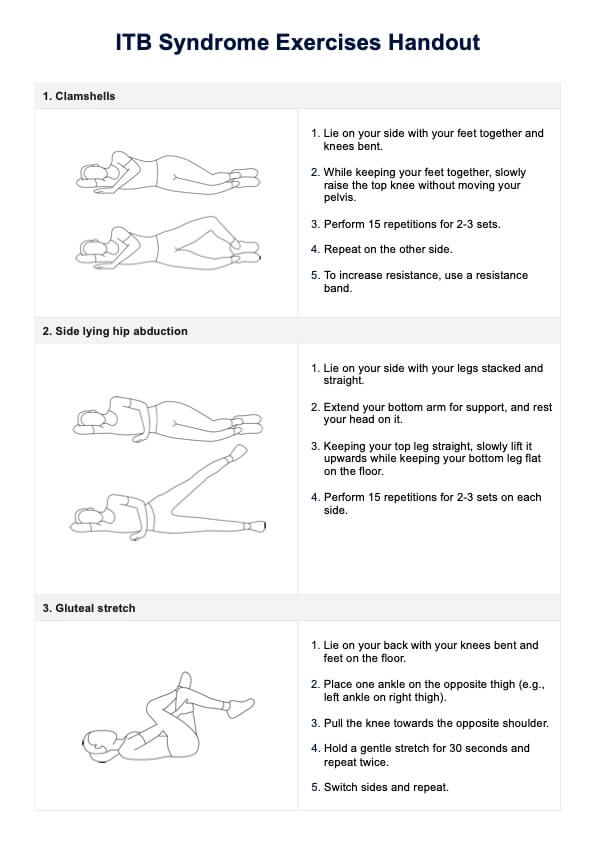
What is a Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing?
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPET) is a highly detailed and specialized form of stress testing, primarily used to assess the heart and lungs' performance during exercise. This testing method is comprehensive and integrates various physiological systems, including the cardiovascular, pulmonary, skeletal muscle, and metabolic systems.
Here's an overview of its key aspects and applications:
- Exercise testing: CPET typically involves exercises like walking or cycling on a treadmill or ergometer. The intensity of exercise is incrementally increased to assess how the body responds under stress.
- Chronic diseases sssessment: It's particularly valuable in diagnosing and managing conditions like chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), coronary artery disease, chronic heart failure, pulmonary hypertension, and interstitial lung disease.
- Measuring exercise capacity and tolerance: CPET is used to evaluate exercise intolerance, which can be a symptom of various cardiopulmonary diseases. It helps in determining the exercise capacity and exercise tolerance of an individual.
- Risk stratification: In patients with heart or lung disease, CPET can help in risk stratification, aiding in predicting outcomes and planning treatments.
- Functional and oxygen uptake assessment: The test measures peak oxygen uptake (VO2 max), which is the maximum amount of oxygen the body can utilize during intense exercise. It also assesses functional capacity and can detect impaired exercise capacity.
- Gas exchange analysis: CPET analyzes pulmonary gas exchange, focusing on oxygen uptake and carbon dioxide production. The respiratory exchange ratio (the ratio of carbon dioxide output to oxygen uptake) is a key metric.
- Clinical exercise testing: It's often used in clinical settings for diagnostic purposes, to guide therapeutic interventions, and to assess the effectiveness of exercise training programs.
- Exercise physiology insights: CPET provides insights into exercise physiology, like ventilatory threshold, ventilatory efficiency, and the anaerobic threshold, which are important for understanding an individual's exercise performance and limitations.
- Cardiac and pulmonary function tests: These tests are integral to CPET, as they provide detailed information about how the heart and lungs function during exercise.
- Applications in chronic lung diseases: CPET is particularly useful in the context of chronic lung diseases, where it helps in understanding the extent of disease impact on exercise capacity.
- Utility in clinical practice: It's a valuable tool in clinical practice for assessing patients with various cardiopulmonary conditions and tailoring exercise prescriptions.
In summary, Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing is a comprehensive tool that integrates multiple physiological parameters to assess the exercise capacity and cardiopulmonary health of individuals, particularly useful in diagnosing, managing, and treating various heart and lung diseases.
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Template
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing Example
How does this Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test (CPET) work?
The CPET process, while thorough, is well-structured and straightforward. It offers a unique lens into your body's functionality, especially focusing on your heart and lungs. The test progresses in clearly defined stages. Here's a step-by-step overview:
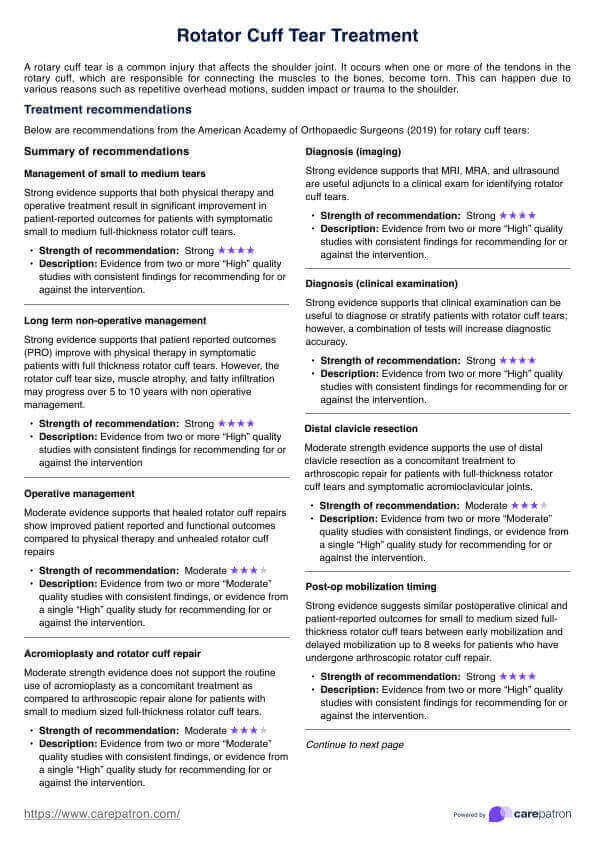
- Step 1: The first step involves preparation. Patients are asked to come wearing comfortable clothes for exercising. They should avoid heavy meals, alcohol, vigorous exercise, and smoking for certain durations before the test.
- Step 2: Resting measurements are taken. This includes a resting blood pressure measurement and an ECG to assess the heart rate and rhythm.
- Step 3: A preliminary breathing test is performed. This allows the healthcare professional to evaluate the airflow in and out of the patient's lungs.
- Step 4: Patients are fitted with a face mask. This apparatus helps in measuring breathing rates and the levels of certain gases. Blood pressure measurement is also taken during this stage.
- Step 5: Placement of a pulse oximeter on the patient's finger. This device helps monitor blood oxygen levels throughout the test.
- Step 6: A blood sample may be drawn from the patient's ear for analysis if required.
- Step 7: The actual exercise test begins. The patient is asked to start exercising on an indoor stationary bike. The intensity of the exercise is gradually increased over time.
- Step 8: Patients are encouraged to exercise as long as possible while their body's responses to the exercise are continuously monitored.
- Step 9: After the exercise is completed, there is a recovery phase. During this period, patients are monitored as their body returns to rest.
- Step 10: Once the test is completed, the results are interpreted by a healthcare professional. Based on the findings, they are then discussed with the patient to plan the best course of action.
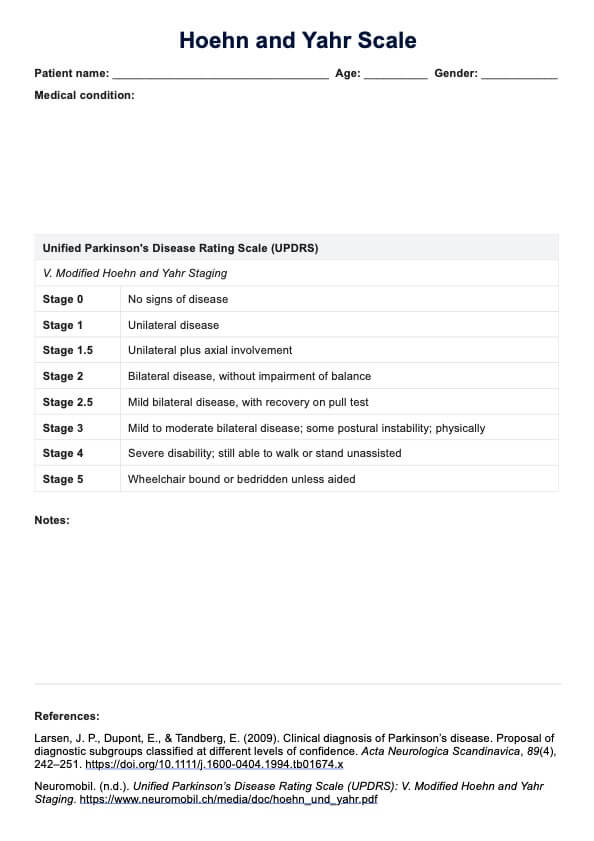
Scoring
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Test results are usually interpreted by a healthcare professional who looks at various parameters like VO2 max (the maximum amount of oxygen the body can utilize during intense exercise), breathing patterns, and heart rate responses. They will consider the peak exercise tolerance and any abnormal responses to exercise.
The "score" or interpretation helps guide diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment strategies.
When to use this Cardiopulmonary Exercise Assessment?
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPET) can be beneficial in several scenarios:
Unexplained Dyspnea
CPET can assess patients experiencing unexplained shortness of breath or dyspnea. It can help distinguish whether the root cause is cardiac, pulmonary, or due to deconditioning.
Pre-operative Assessment
For patients scheduled for high-risk surgeries, CPET can be used to evaluate their fitness levels. It helps predict post-operative risks and complications, thus aiding in surgical planning and patient counseling.
Diagnosing Cardiac and Pulmonary Conditions
CPET can be instrumental in diagnosing conditions like heart failure, ischemic heart disease, and various pulmonary disorders. The test allows for the simultaneous evaluation of both heart and lung functions during exercise, providing a more comprehensive assessment.
Exercise Prescription
For patients undergoing cardiac rehabilitation or those with chronic conditions like COPD, CPET can guide the formulation of personalized exercise programs. It helps determine the safe levels of exercise intensity and can be used to monitor progress.
Who are these Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing PDFs for?
Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing PDFs can be valuable resources for various individuals and organizations:
Healthcare Professionals
This includes physicians, physiotherapists, respiratory therapists, exercise physiologists, and nurses. They can use these resources to understand the procedure better, interpret results, and plan patient management.
Patients
For patients undergoing CPET, these resources can help them understand the procedure, what to expect during the test, and how to prepare for it. It can also aid them in understanding their results and treatment plan.
Healthcare Institutions
Hospitals, clinics, and rehabilitation centers can use these resources to train their staff or educate patients. They can also be used as references to develop institutional guidelines for CPET.
Research Institutions and Academia
These resources can provide a fundamental understanding of the test and its applications for researchers studying cardiopulmonary diseases or exercise physiology. They can also be used in academic settings for teaching students in medical and allied health courses.
Benefits of Free Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
The advent of freely accessible resources such as Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing (CPET) guidelines and examples offers several advantages. By removing the barriers to accessible information, free resources can significantly enhance patient care, improve healthcare professional skills, and foster education. Here are five key benefits:
1. Enhanced Patient Understanding
Free resources can empower patients by providing accessible information about the CPET. A better understanding of the test procedure, purpose, and interpretation of results can lead to more active patient involvement in their healthcare journey.
2. Professional Development
Healthcare professionals can use these free resources to deepen their understanding of CPET, keeping their knowledge up-to-date. This contributes to improved professional skills, leading to better patient management.
3. Patient-Professional Communication
Communication can be greatly enhanced with patients and professionals having access to the same resources. This shared understanding can lead to more meaningful discussions about test results and treatment strategies.
4. Accessible Education
Free resources democratize access to medical knowledge. They can be used for educational purposes, facilitating learning for medical students, residents, and other healthcare trainees.
5. Improved Health Outcomes
Free CPET resources can ultimately contribute to improved health outcomes by enabling better understanding, communication, and education. Well-informed patients and professionals can make better decisions, and prompt and appropriate interpretation of test results can lead to timely interventions.
Commonly asked questions
CPET is a detailed method to assess the exercise capacity and cardiopulmonary function of individuals. It's particularly valuable in diagnosing and managing chronic heart and lung conditions such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), coronary artery disease, pulmonary hypertension, chronic heart failure, and interstitial lung disease. By measuring variables like peak oxygen uptake, carbon dioxide production, and gas exchange during exercise, CPET helps in understanding the severity of these conditions and guiding therapeutic interventions.
CPET is instrumental in evaluating exercise intolerance, a common symptom in cardiopulmonary diseases. It assesses exercise capacity and tolerance by measuring peak exercise oxygen consumption, functional capacity, and the patient's ability to uptake oxygen and expel carbon dioxide. These measurements provide insights into the limitations in exercise performance and help in identifying the underlying causes, be it cardiac, pulmonary, or muscular.
Yes, CPET plays a crucial role in risk stratification for patients with heart and lung diseases. By analyzing exercise performance, oxygen uptake, and respiratory exchange ratios, CPET can predict outcomes and assist in planning appropriate treatments. It's especially useful in cases of congestive heart failure, pulmonary vascular disease, and chronic lung diseases, where exercise capacity significantly affects patient management and prognosis.
Key measurements during CPET include peak oxygen consumption, carbon dioxide output, respiratory exchange ratio, ventilatory efficiency, and anaerobic threshold. These metrics provide comprehensive information about cardiac output, pulmonary gas exchange, blood pressure responses, and muscle blood flow during exercise. Such data is invaluable in clinical assessments for diagnosing abnormal exercise responses, assessing the severity of exercise limitation, and evaluating the functional aerobic impairment in patients.
CPET is instrumental in tailoring exercise training and rehabilitation programs for cardiopulmonary patients. By establishing baseline exercise tolerance and identifying the limiting factors (like impaired muscle perfusion or ventilatory inefficiency), CPET enables chest physicians and therapists to design personalized exercise protocols. This ensures safe and effective rehabilitation, particularly for patients recovering from heart failure, undergoing lung transplant, or living with chronic pulmonary diseases. It helps in improving functional status, oxygen saturation, and overall quality of life.