Beers Criteria Template
Explore the Beers Criteria Template, guiding principles for safer medication use in older adults—essential knowledge for healthcare professionals.


What are the Beers Criteria?
The Beers Criteria, established by the American Geriatrics Society (AGS), outlines potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) for older adults. These criteria assist healthcare professionals in prescribing medications for older patients, aiming to avoid potentially harmful effects and adverse drug interactions.
The AGS Beers Criteria guides medication classes and specific drugs that may pose risks, particularly in older adults with certain diseases or health problems. It helps healthcare providers in clinical decision-making, emphasizing the importance of considering factors like renal function, reduced ejection fraction, and other relevant health issues.
The American Geriatrics Society (AGS) revises this list every three years based on new medical evidence. The most recent update is the 2023 American Geriatrics Society Updated Beers Criteria® for Potentially Inappropriate Medication Use in Older Adults. This update involved an expert panel reviewing evidence published since the last update in 2019 and modifying the criteria to enhance usability and accuracy. .
By following these criteria, healthcare professionals can optimize medication regimens, lower doses, or explore alternative treatments, especially for conditions like atrial fibrillation, heart failure, and Parkinson's disease.
Healthcare administrators and providers rely on the Beers Criteria to enhance care quality and prevent harmful side effects in older patients. These criteria are based on extensive research studies and expert panel recommendations, serving as a valuable resource for caregivers and healthcare professionals.
By adhering to the Beers Criteria, healthcare providers can mitigate risks, address substantial barriers, and promote the well-being of older adults through appropriate medication use and clinical care.
Beers Criteria Template
Beers Criteria Template Example
How are the Beers Criteria used in clinical practice?
The Beers Criteria are used in clinical practice primarily as a guideline to help healthcare professionals make informed decisions regarding medication management for older adults. Here's how they are typically utilized:
- Screening for potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs): Healthcare providers use the Beers Criteria as a screening tool to identify medications that may pose higher risks or have limited effectiveness in older adults. They review a patient's medication list against the criteria to identify potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs).
- Guiding prescribing decisions: Healthcare providers adjust medication regimens for older patients based on the Beers Criteria recommendations. They may discontinue or avoid certain medications known to be potentially inappropriate and explore alternative treatment options or adjust dosages to minimize risks.
- Educating healthcare professionals: The Beers Criteria is an educational resource that helps them stay updated on the latest evidence-based recommendations for prescribing medications in older adults. This knowledge enables them to make more informed decisions in their clinical practice.
- Facilitating interdisciplinary collaboration: The Beers Criteria promotes multidisciplinary collaboration among healthcare professionals caring for older adults. Physicians, pharmacists, nurses, and other team members work together to review medication lists, identify potential issues, and develop appropriate management strategies.
- Supporting clinical decision-making: Healthcare providers use the Beers Criteria to guide clinical decision-making regarding medication use in older adults with complex medical conditions. They consider factors such as renal function, cardiovascular status, cognitive function, and overall health when determining the appropriateness of specific medications.
- Promoting patient safety: By adhering to the Beers Criteria recommendations, healthcare professionals help promote patient safety by minimizing the risk of adverse drug events, drug interactions, and other medication-related complications in older adults.
How does our Beers Criteria Template work?
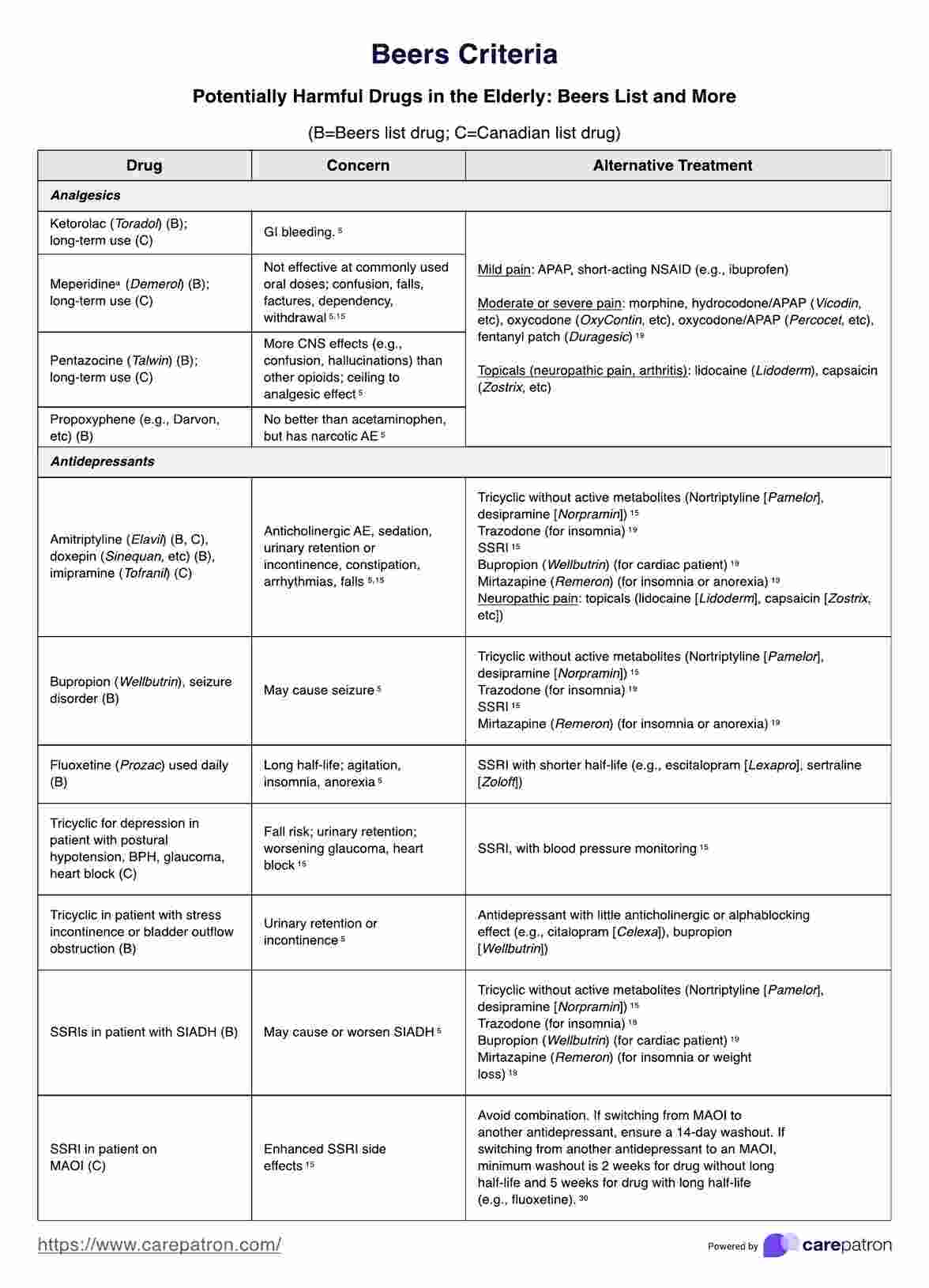
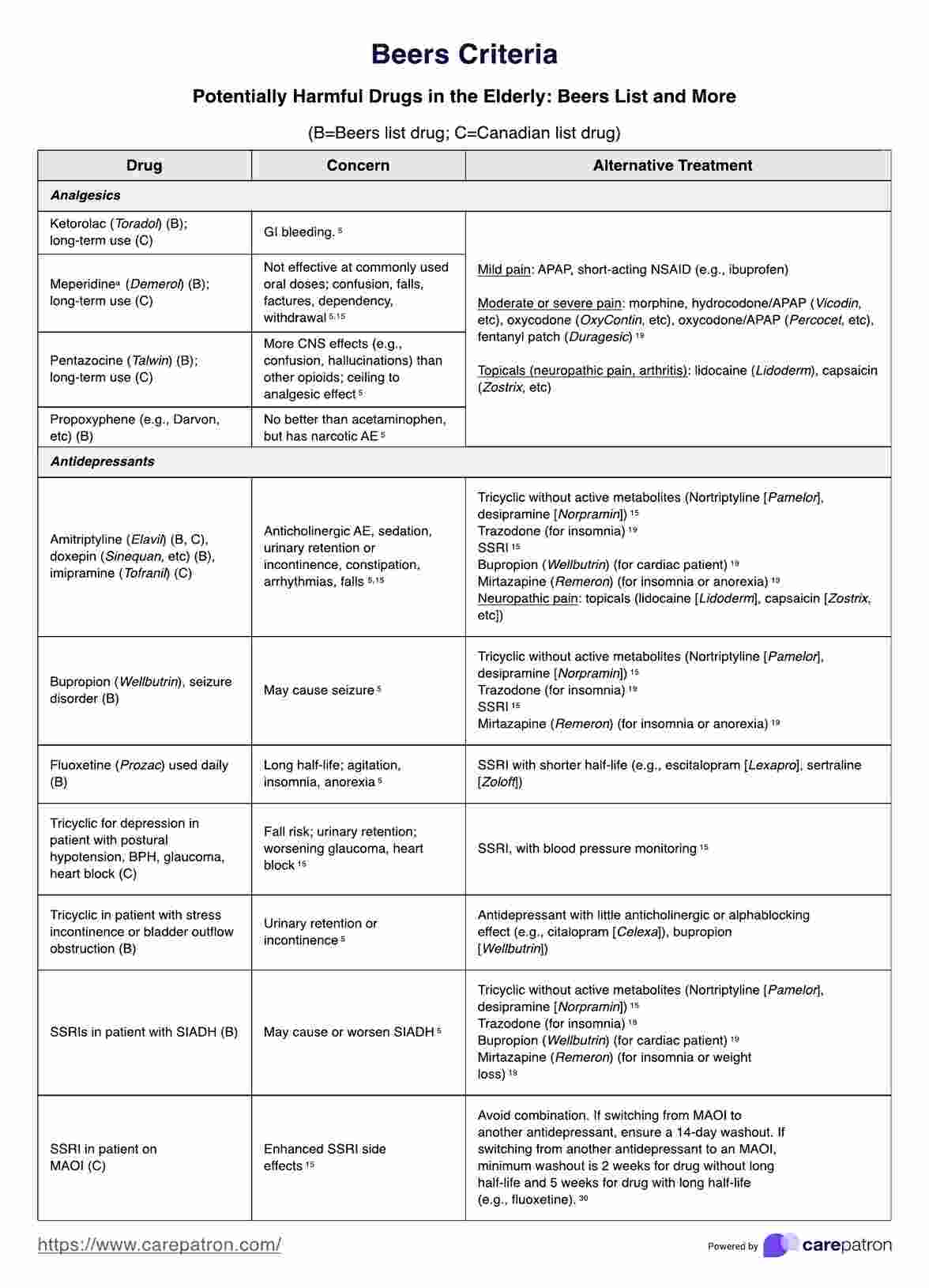
The Beers Criteria Template provides healthcare professionals with a comprehensive list of potentially harmful medications to elderly patients, the concerns associated with each medication, and suggested alternative treatments. Here's a breakdown of how it functions:
- Categorization of drugs: Medications are categorized based on their therapeutic use, such as analgesics, antidepressants, antihypertensives, etc. This categorization helps clinicians quickly find relevant information for the types of medication they're considering for their patient's treatment plans.
- Identification of risks: For each medication listed, the template outlines specific risks or concerns related to its use in the elderly. These concerns include an increased risk of gastrointestinal bleeding, confusion, dependency, renal failure, and more. Highlighting these risks helps assess the benefit-risk ratio of prescribing these medications to older adults.
- Alternative treatments: Perhaps the most actionable part of the template is its recommendations for alternative treatments. For each medication or medication class listed as potentially harmful, the template suggests safer alternatives that can be used to achieve similar therapeutic outcomes with a lower risk of adverse effects in the elderly.
- Special considerations: The template also notes special considerations, such as conditions where the risk of using a particular drug might be higher (e.g., using certain antidepressants in patients with a history of falls or seizures) or where a drug might still be used cautiously if necessary.
- Educational tool: Beyond its immediate practical use in guiding prescription choices, the template is an educational tool for healthcare providers. It raises awareness about the pharmacological vulnerabilities of the elderly and emphasizes the importance of individualized, cautious prescribing.
- Quality and safety improvement: The template aligns with efforts to improve the quality of care and safety for elderly patients. By informing providers about potentially inappropriate medications and suggesting alternatives, it contributes to reducing adverse drug events, hospitalizations, and other negative outcomes associated with improper medication use in older adults.
What are the specific criteria included in the Beers Criteria?
The Beers Criteria include specific criteria for potentially inappropriate medications (PIMs) and medication classes that may pose risks or have limited effectiveness in older adults. These criteria are regularly updated to reflect current evidence-based recommendations. Here are some of the critical criteria commonly included in the Beers Criteria:
Medication classes to avoid in older adults
- Benzodiazepines: Due to increased risk of falls, confusion, and cognitive impairment.
- Anticholinergic medications: May exacerbate cognitive decline and increase the risk of falls.
- Long-acting sulfonylureas: Higher risk of hypoglycemia in older adults.
- Nonbenzodiazepine sedative-hypnotics: Increased risk of cognitive impairment and falls.
- Tricyclic antidepressants: Higher risk of adverse effects, including orthostatic hypotension and anticholinergic effects.
Individual medications to avoid in certain situations
- Digoxin: Avoid its routine use for atrial fibrillation/flutter without heart failure.
- Aspirin or NSAIDs: Avoid primary prevention of cardiovascular disease due to increased risk of bleeding.
- Proton pump inhibitors: Limit chronic use due to increased risk of Clostridium difficile infection, fractures, and hypomagnesemia.
Medications to use with caution
- Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs): Caution is required in older adults with reduced renal function.
- Antipsychotics: Increased risk of falls, stroke, and mortality in older adults with dementia-related psychosis.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants may increase the risk of hyponatremia, falls, and bleeding in older adults.
Medications to adjust dosing or monitor closely
- Metformin: Monitor renal function closely due to the increased risk of lactic acidosis in older adults.
- Statins: Consider lower doses in older adults due to the increased risk of myopathy and potential drug interactions.
Medication use in specific disease states
Avoiding certain medications in older adults with specific diseases such as Parkinson's disease, reduced ejection fraction, and heart failure.
Who should refer to the Beers Criteria when prescribing medications?
Several healthcare professionals should refer to the Beers Criteria when prescribing medications for older adults. These include:
- Physicians and geriatricians: Primary care physicians, specialists, and geriatricians responsible for diagnosing medical conditions and managing treatment plans for older adults should consult the Beers Criteria to ensure safe and appropriate prescribing practices.
- Pharmacists: Pharmacists play a crucial role in medication management, including dispensing, conducting medication reviews, and providing medication counseling. They should refer to the Beers Criteria to identify potentially inappropriate medications and collaborate with prescribers to optimize therapy.
- Nurses and nurse practitioners: Nurses, particularly those working in senior care settings or providing direct patient care to older adults, should be aware of the Beers Criteria. They can assist in medication administration, monitoring for adverse effects, and educating patients and caregivers about medication safety.
- Other healthcare providers: Various healthcare professionals caring for older adults, such as physician assistants, nurse practitioners, and social workers, should also be familiar with the Beers Criteria. They can contribute to medication management and ensure that older patients receive safe and appropriate treatment.
- Healthcare administrators and policymakers: Healthcare administrators, policymakers, and healthcare quality improvement professionals may use the Beers Criteria to develop clinical guidelines, quality improvement initiatives, and policies to promote safe medication use in older adults across healthcare settings.
- Educators and researchers: Educators in healthcare professions and researchers in geriatric medicine may refer to the Beers Criteria for educational purposes, curriculum development, and research studies on medication safety and appropriate prescribing practices in older adults.
The primary purpose of the Beers Criteria is to improve medication safety by identifying medications that may pose risks or have limited effectiveness in older adults.
The Beers Criteria are guidelines that help healthcare professionals identify medications that may be inappropriate for older adults due to potential risks or limited effectiveness.
Yes, the Beers Criteria are evidence-based guidelines developed by the American Geriatrics Society and regularly updated to reflect current research and clinical evidence.