ABG
When assessing, diagnosing, and monitoring the progress of a patient�??s respiratory and metabolic disorders, make sure you have an ABG chart readily available.


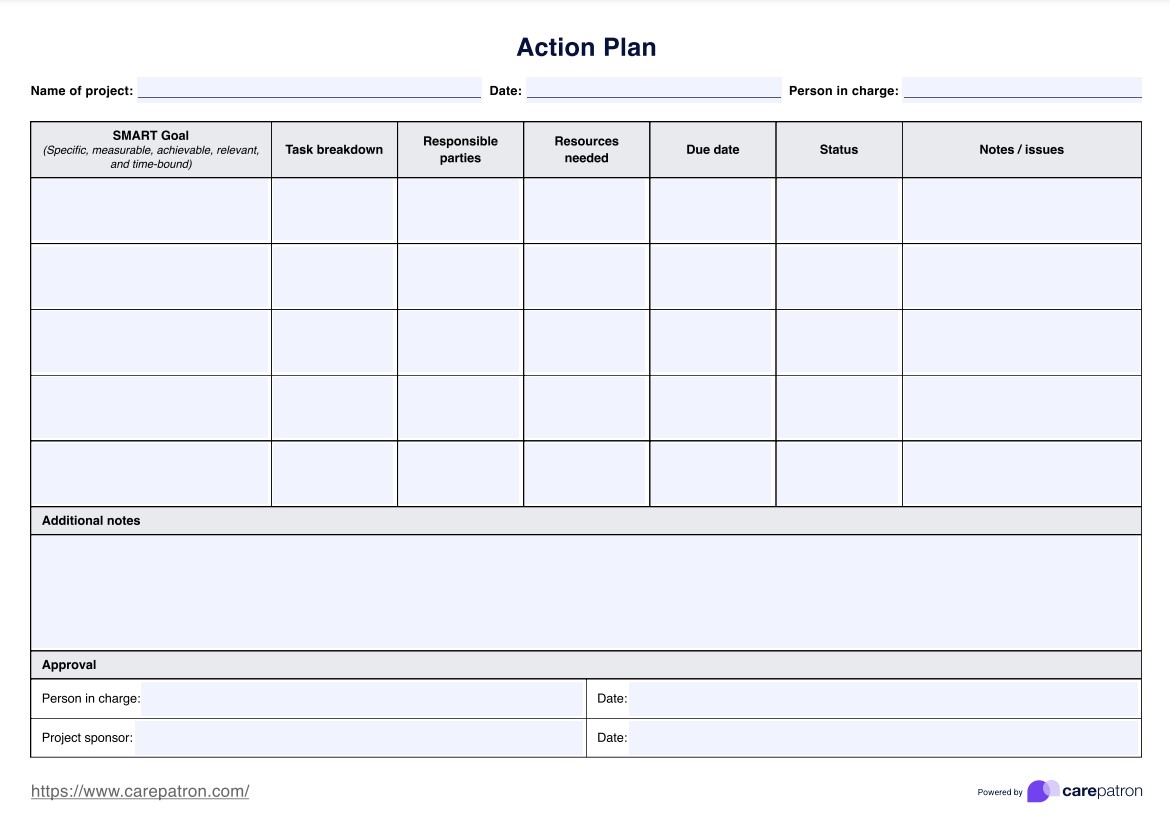
What is an ABG Chart?
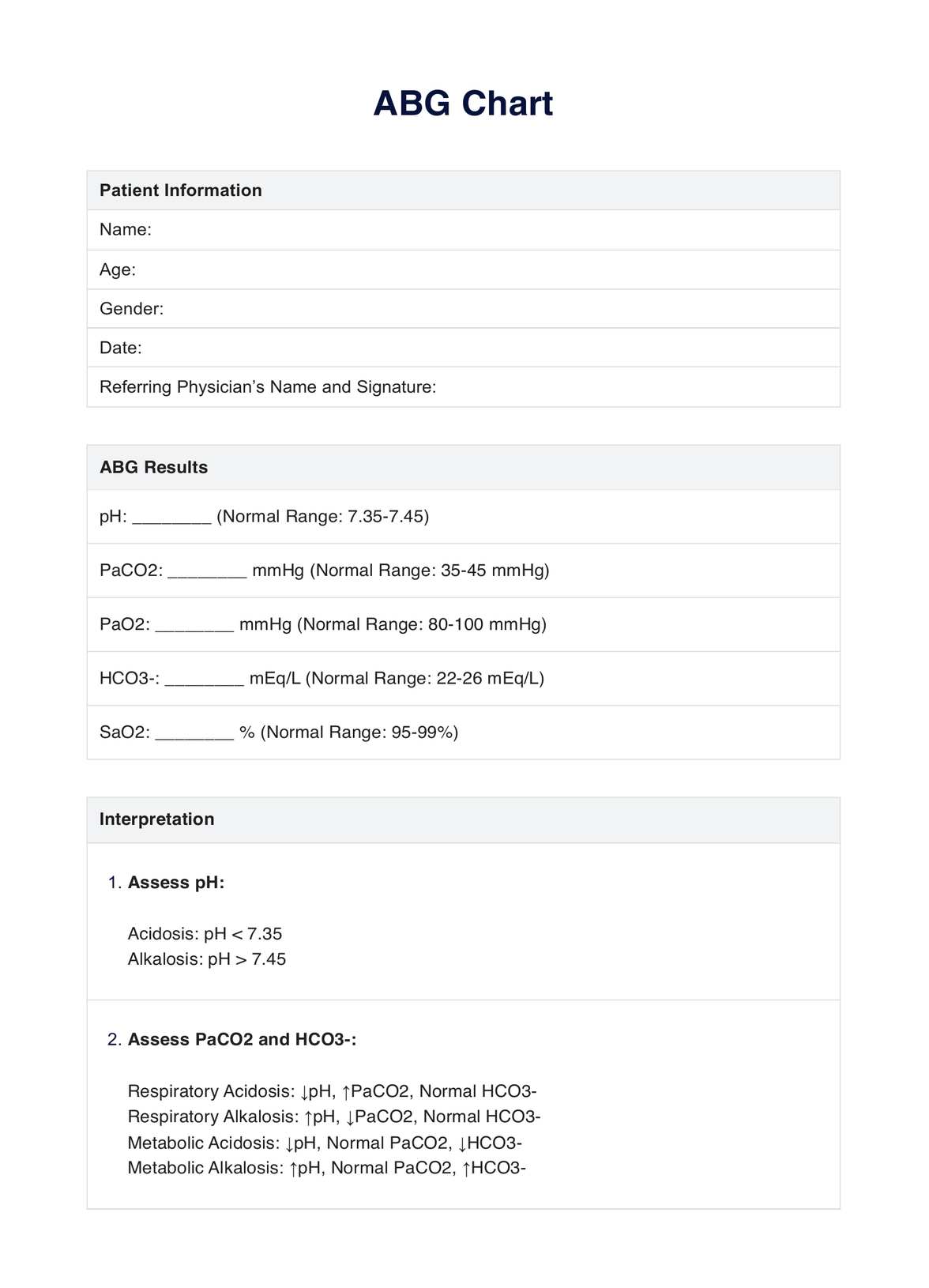
An ABG chart is a valuable tool used by healthcare professionals for assessing and deciphering arterial blood gas (ABGC) values. This comprehensive resource offers crucial insights into a patient's oxygenation levels, respiratory function, and acid-base equilibrium. These pieces of information can help one diagnose and manage diverse metabolic and respiratory disorders.
Usually, interpreting one's ABG results follows sequential steps like assessing the pH values, examining the PaCO2 and HCO3- levels, and any other compensatory mechanisms attempting to rectify the balance. The referring physician will determine if the pH, PaCO2, and HCO3 are under acidosis, alkalosis, or normal. Then, using the tic-tac-toe method, said physician can determine if the patient has acidosis or alkalosis, has metabolic or respiratory issues, or is compensating for any deficiencies in one's body.
On our ABG chart, you can expect to find established reference ranges for critical parameters like oxygen saturation (SaO2), bicarbonate (HCO3-), pH, partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2), and partial pressure of carbon dioxide (PaCO2). With these reference ranges, you can spot irregularities and pinpoint their causes. Aside from those, you can also find dedicated sections for patient information, ABG results, a summary of interpretations, and additional notes.
ABG Template
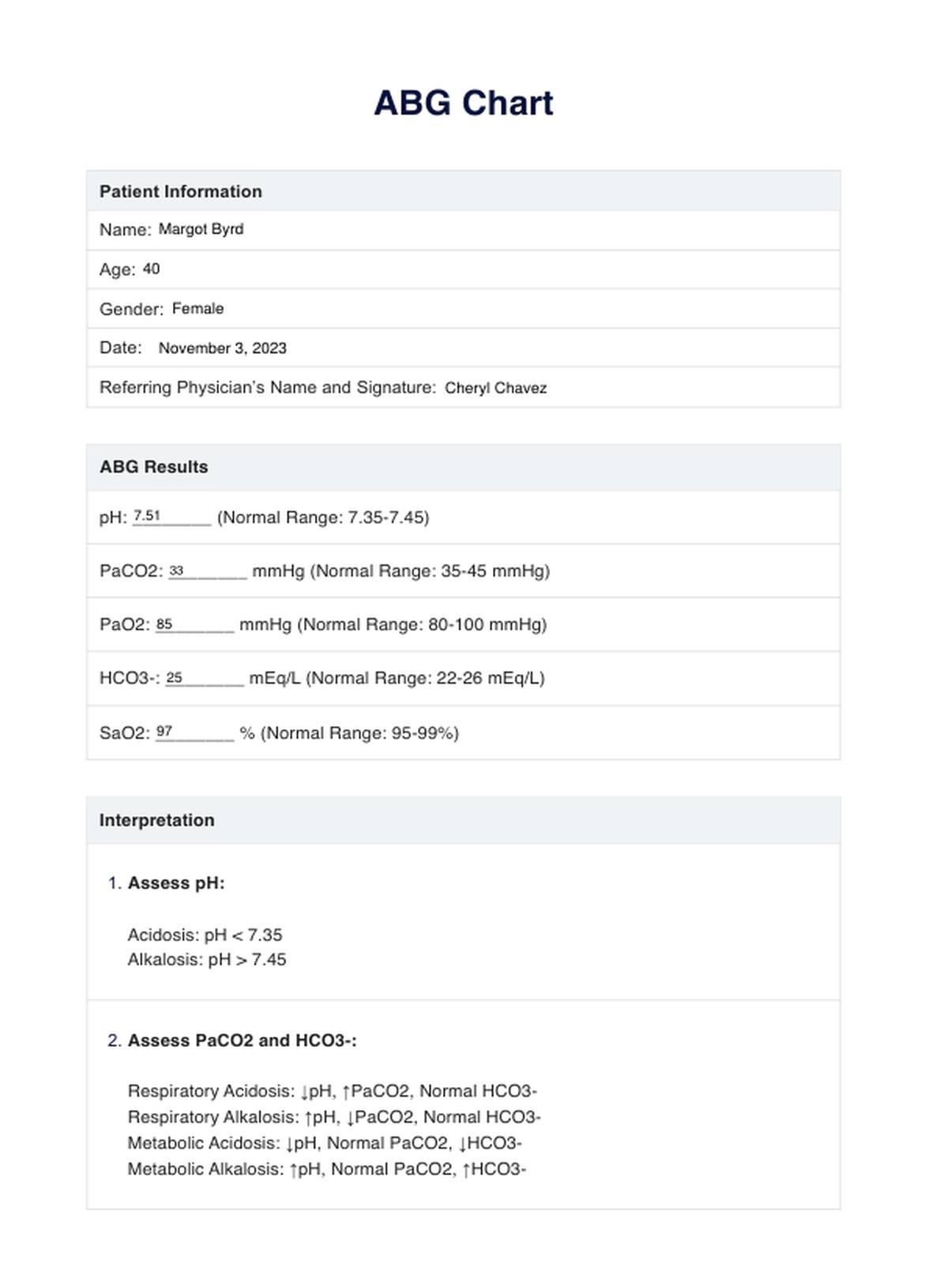
ABG Example
How does it work?
Step One. Acquire a Printable ABG Chart
To ensure quick access to the invaluable ABG chart resource, follow the following instructions:
- Click on either the Download Template or Use Template button
- Alternatively, you can find the ABG Chart within Carepatron's template library, accessible via the app or website.
Step Two. Input Vital Patient Information
Suppose your purpose is beyond merely using the chart as a visual aid for patient education on the results of the ABG chart. In that case, it is advisable to complete essential patient particulars. This includes recording the results of the arterial blood gas test.
Step Three. Compare and Analyze
Next, you can use the chart to conduct a comparative analysis between the normal, accepted arterial blood gas results and those identified in your patient's results. Consider other factors like the patient's age, gender, and current condition in your assessment.
Step Four. Record Interpretations
Within our template, you can document your observations and findings. You'll find a designated space for result interpretation. Additionally, you may utilize this space to include any supplementary notes or information regarding any necessary medical interventions or further examinations.
Step Five. Safeguard the Template
Upon concluding your consultation, it is crucial to securely store the template, restricting access solely to relevant parties. For digital copies, we recommend utilizing Carepatron, a HIPAA-compliant, free patient records software. This platform can safeguard all medical records, including completed ABG charts.
What do the results mean?
Interpreting results and comparing them with the information provided on an Arterial Blood Gas (ABG) chart is a crucial aspect of healthcare. By knowing them, they can make more accurate diagnoses and formulate treatment quicker during emergencies.
For a general understanding of what results may mean for each parameter on the chart, please refer to the information below:
- pH (Acid-Base Balance): If a patient has a pH level below 7.35, it signifies an excess of acid in the blood (acidosis), while anything above 7.45 indicates an excess of base in the blood (alkalosis). If your patient has a level that falls within the range of 7.35 and 7.45, it means that the acid and base in their blood are in equilibrium.
- PaCO2 (Partial Pressure of Carbon Dioxide): Patients whose PaCO2 levels are elevated indicate hypoventilation at the alveolar level, which may lead to respiratory acidosis. In contrast, decreased PaCO2 levels signify alveolar hyperventilation, which may then result in respiratory alkalosis.
- PaO2 (Partial Pressure of Oxygen): The only concern you may have is when the patient's PaO2 is lower than the normal range because it indicates hypoxemia or insufficient oxygen levels in the bloodstream.
- SO2 (Oxygen Saturation): Typically, the range of normal levels is between 94% and 100%. Any level below the lower limit may indicate oxygen transport issues that need further evaluation and intervention.
- HCO3 (Bicarbonate): Any deviation from the normal range provided in the chart signifies metabolic acid-base imbalances and difficulty in maintaining pH stability.
Remember that as you interpret the ABG test results, you must consider the patient's overall health, medication usage, and any other underlying chronic illnesses that may influence these values.
Commonly asked questions
Doctors who treat metabolic and respiratory disorders, specifically endocrinologists and pulmonologists, are the ones who may typically request an ABG chart.
ABG charts can be used at every point of patient care, from diagnosis to treatment evaluation.
ABG charts can be used as an educational tool, reference, and document to record the results and corresponding interpretation of the patient�??s condition.