SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template
Empower clients to take control of their diabetes with our SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template to track progress and improve their overall well-being.


What is SMART goal setting for diabetes management?
The importance of SMART goal setting in diabetes care and management cannot be overstated. It is a cornerstone for improving blood sugar control and fostering healthy lifestyle choices. Utilizing the SMART goal framework—which is widely used in project management, personal development, and organizational planning—to set clear and achievable objectives can help individuals gain greater control over their diabetes.
This approach heightens motivation and commitment toward long-term health objectives and facilitates the creation of personalized management plans that cater to individual needs and preferences. Furthermore, it significantly enhances communication between patients and healthcare providers.
This is crucial, as it ensures a more collaborative effort in tracking progress, evaluating the effectiveness of management strategies, and making timely adjustments to treatment plans as needed. This is helpful not only in diabetes management but also in managing other patient conditions. If you're a nurse, you can align your goals with improving patient outcomes, safety, and satisfaction with another resource called the SMART Goals Nursing Template.
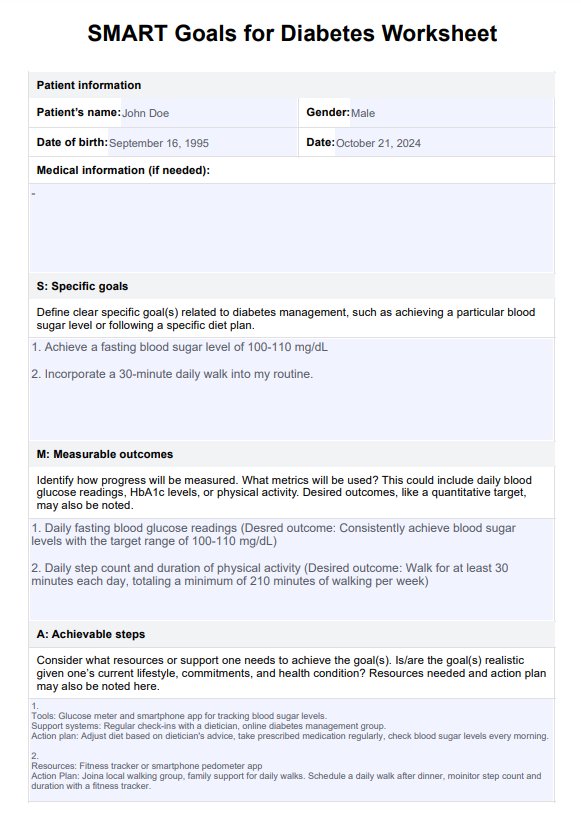
SMART Goals For Diabetes Template
SMART Goals For Diabetes Example
How to use our SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template?
Help your patient manage their diabetes more effectively by using our worksheet template. Utilize it to the maximum by following our set of instructions below:
Step 1: Download or access the worksheet
Obtain a copy of the SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template by downloading or accessing it in this guide.
Step 2: Fill out personal information and general goal
Once you have a copy in your hands, give it to the patient and ask them to fill out the fields for their personal information. Afterward, ask them the primary goal they want to achieve; this will be the goal you will flesh out further in the following sections.
Step 3: Fill out the SMART sections
Have your patient fill out each section in the worksheet. You may prompt them or help them out as they do so.
Step 4: Review and adjust
As a final step, review your patients' entries to ensure they have clear and realistic goals. Adjust any goals that need improvement as necessary.
Benefits of using a SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template
A SMART Goals for Diabetes Worksheet Template benefits the patient and healthcare provider for several reasons. Here are a few of them:
- Specificity leads to better focus: A worksheet where patients can set and write down specific goals provides clearer direction and focus, making it easier for them to know precisely what to do.
- Measurability ensures trackable progress: The worksheet allows individuals to create measurable goals that help them track their progress concretely. This can be motivating and help them make informed adjustments to their management plan.
- Achievability encourages success: This worksheet can serve as a visual guide for realistic and attainable goals that prevent frustration and burnout, boost confidence, and improve adherence to management plans.
- Relevance to personal health goals: Individuals can also use this worksheet as a reminder to create and follow only relevant information that the individual's efforts align with their health objectives, whether to lose weight or increase physical activity.
- Time-bound structure: With a worksheet, individuals and their healthcare team or provider can set a deadline or timeline for goals to create urgency and help prioritize tasks. The worksheet also provides a timeframe for evaluation, allowing individuals to track progress and make necessary changes.
Good examples of SMART goals
Should you or your patient need ideas, here are SMART goals for diabetes examples.
Check blood sugar levels
- Specific: Check blood sugar levels every morning before breakfast.
- Measurable: Record the readings in a logbook or digital app.
- Achievable: Ensure you have a reliable glucometer and necessary supplies.
- Relevant: Regular monitoring helps in managing diabetes more effectively.
- Time-bound: Do this daily for three months and then review with your doctor.
Do 30 minutes of moderate exercise every day
- Specific: Engage in activities like brisk walking or cycling.
- Measurable: Use a fitness tracker to monitor your activity.
- Achievable: Start with 15 minutes and gradually increase to 30 minutes.
- Relevant: Exercise helps control blood sugar and improve overall health.
- Time-bound: Aim to establish this routine over the next two months.
Take medication as prescribed
- Specific: Take your prescribed medications at the same time each day.
- Measurable: Use a pill organizer or reminder app to track adherence.
- Achievable: Consult your doctor for any help needed in medication management.
- Relevant: Consistent medication helps maintain stable blood sugar levels.
- Time-bound: Review medication adherence and effects in your next doctor's appointment.
Eat healthier
- Specific: Include at least two servings of vegetables daily.
- Measurable: Keep a food diary to track your vegetable intake.
- Achievable: Start with familiar vegetables and gradually try new ones.
- Relevant: A balanced diet is crucial for diabetes management.
- Time-bound: Evaluate your eating habits with a nutritionist after one month.
Schedule diabetes visits
- Specific: Schedule regular check-ups every three months.
- Measurable: Keep a calendar or set reminders for your appointments.
- Achievable: Coordinate with your healthcare provider for feasible dates.
- Relevant: Regular check-ups are essential for monitoring your diabetes.
- Time-bound: Book your next appointment at the end of each visit.
Attend education sessions
- Specific: Attend a diabetes management workshop or class.
- Measurable: Participate in one session per week or month.
- Achievable: Choose sessions that fit into your schedule.
- Relevant: Education sessions provide valuable information for managing diabetes.
- Time-bound: Complete a specific course or number of sessions in a set time frame.
Commonly asked questions
SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound objectives that help individuals with diabetes manage their condition more effectively. These well-defined goals ensure focus and clarity in managing diabetes.
Achievable goals for diabetes management might include monitoring glucose levels every morning, taking diabetes medications as prescribed, or incorporating 30 minutes of moderate exercise into your daily routine. An achievable goal should be realistic and attainable for the individual.
Setting measurable goals is crucial as it allows the healthcare team and individuals to track their progress. For instance, measuring changes in glucose levels or weight helps evaluate the management plan's effectiveness.
Time-bound goals provide a deadline for achieving objectives, which can motivate and help individuals stay on track. For example, aiming to reduce HbA1c levels within six months is a time-bound goal.
Lifestyle changes, including a healthy diet and regular exercise, are foundational in managing diabetes. These changes can significantly impact blood sugar control and overall health.
A specific goal, such as eating a balanced meal with vegetables at every dinner, provides clear direction and makes it easier to focus and achieve the desired outcome.