Patient Assessment of EMT
Learn about EMT Patient Assessment. Download our free to template and use it for your practice.


What is an EMT Patient Assessment?
Patient assessment is a fundamental process in emergency medical services (EMS) and a crucial aspect of an emergency medical technician’s (EMT) role. It involves a systematic approach to evaluating an individual’s health status, identifying potential issues, and determining the appropriate course of action for providing optimal care.
In a patient assessment, EMTs follow a structured protocol to evaluate various aspects, including the patient’s airway, breathing, circulation, and overall mental status. They also recognize various disease processes better to understand immediate life threats for a more effective assessment. This holistic approach allows for a comprehensive understanding of the patient’s immediate needs and aids in prioritizing interventions based on the severity of their condition.
A thorough patient assessment is the foundation for making informed decisions, initiating appropriate treatments, and ensuring the patient's safety and well-being. Beyond its immediate significance, a well-executed patient assessment facilitates seamless communication with other healthcare professionals, ensuring a continuum of care.
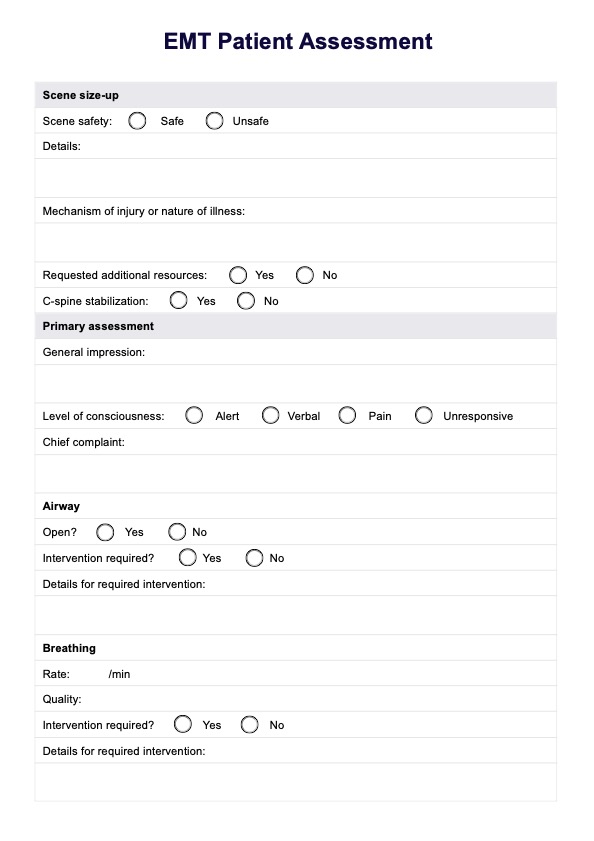
Patient Assessment of EMT Template
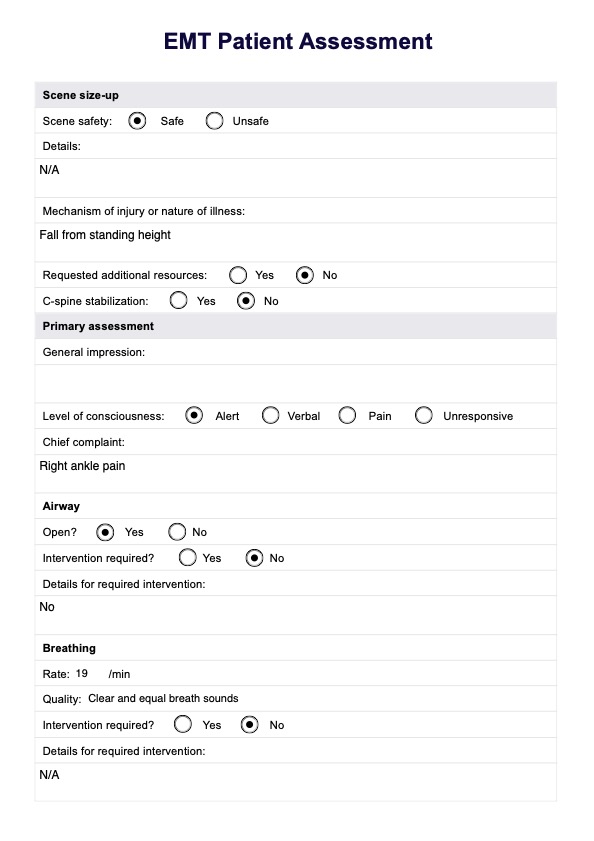
Patient Assessment of EMT Example
Purpose of the EMT assessment
The patient assessment conducted byEMTs serves a multifaceted purpose, encompassing critical aspects that collectively contribute to effective pre-hospital care. Understanding the significance of each facet—patient history, physical exam, patient care, scene safety, and general impression—is vital for EMTs to navigate emergencies competently.
Scene safety
Ensuring the safety of the scene is paramount. EMTs must assess the environment for potential hazards, such as traffic, fire, or unsafe conditions. Establishing safety protects the EMT and the patient and facilitates a more focused and efficient assessment and treatment process.
General impression
A rapid yet comprehensive general impression of the patient aids EMTs in prioritizing their interventions. This initial impression guides the immediate actions based on observations of the patient's overall appearance, behavior, and vital signs.
Patient's history
The initial step in the assessment process is a thorough exploration of the patient’s medical history that enables EMTS to tailor their approach, anticipate potential complications, and make informed treatment decisions. This comprehensive or sample history involves gathering information about existing medical conditions, medications, allergies, and any pertinent details that could influence the current health crisis.
Physical exam
Conducting a comprehensive physical assessment is a cornerstone of the patient assessment. EMTs systematically evaluate the patient’s skin color, airway, breathing, circulation, and neurological status. This hands-on examination is crucial for identifying visible injuries, abnormalities, or signs of distress.
Patient care
The ultimate goal of the assessment is to guide appropriate patient care. The information gleaned from the patient's medical history and physical examination informs the EMT's decision-making process. This may involve administering medications, providing interventions to support vital functions, or initiating measures to stabilize the patient for transport.
How to perform a patient assessment as an EMT
Conducting a patient assessment as an EMT involves a structured, systematic approach to evaluate the patient’s condition, provide timely interventions, and ensure optimal care. Here are the critical steps to follow:
Step 1: Scene size-up
Begin by ensuring the scene is safe for yourself, your team, and the patient. Assess for hazards such as traffic, fire, unstable structures, or other dangers. Determine the number of patients and identify if multiple individuals require triage. If additional resources or specialized teams are needed, request them immediately. If the mechanism of injury suggests potential spinal trauma, prepare for cervical spine immobilization.
Step 2: Primary assessment
Perform a quick evaluation to identify and address any life-threatening conditions. Start with a general impression of the patient, focusing on their overall appearance and level of distress. Assess the patient’s level of consciousness using the AVPU scale (Alert, Verbal, Pain, Unresponsive) to determine their responsiveness. Identify the chief complaint or the primary reason for seeking medical attention.
Step 3: Assess airway, breathing, and circulation (ABCs)
Ensure the patient’s airway is open and clear. If it is obstructed, use appropriate techniques such as the head-tilt/chin-lift or jaw-thrust maneuver to clear it. Evaluate the patient’s breathing rate, depth, and effort. If breathing is inadequate, provide oxygen or ventilation support, such as a bag-valve mask. Check circulation by assessing the patient's pulse for rate and quality. Look for signs of shock, such as pale, cool, or clammy skin, and control any significant bleeding using direct pressure or a tourniquet if necessary.
Step 4: Obtain patient history
Gathering the patient’s history provides critical context for your assessment. Use the SAMPLE mnemonic to guide this process. Ask about the symptoms the patient is experiencing, any known allergies, current medications, past medical history, and when the patient last ate or drank. Additionally, inquire about the events leading up to the present condition to understand what might have triggered their symptoms.
Step 5: Secondary assessment and physical exam
Conduct a thorough physical examination, focusing on the patient’s head, neck, chest, abdomen, pelvis, extremities, and back. You may perform a focused or full-body assessment depending on the patient's condition. Look for visible injuries such as deformities, bleeding, swelling, or bruising. Palpate and auscultate as necessary to identify abnormalities. Reassess the patient’s vital signs, including blood pressure, pulse, respiratory rate, oxygen saturation, temperature, and blood glucose levels.
Step 6: Provide interventions and ongoing care
Based on your findings, initiate appropriate treatments. Administer medications, manage fractures, control bleeding, or apply bandages as required. Continuously monitor the patient’s response to your interventions, ensuring that any changes in condition are addressed promptly.
Step 7: Determine transport decision
Evaluate the severity of the patient’s condition to determine the urgency and method of transportation. High-priority patients requiring immediate care should be transported as quickly as possible. Decide on the appropriate mode of transport, whether by ground ambulance, air transport, or other means. Communicate effectively with your team and the receiving facility, providing all relevant information about the patient’s condition, history, and care administered.
Tips when conducting the assessment as an EMT
When doing EMT assessments, these tips below can come in handy:
- Prioritize scene safety: Ensure the safety of both you and the patients by conducting an initial scene size-up. Identify potential hazards and establish a secure environment before proceeding with the assessment.
- Effective communication: Maintain clear and concise communication with your team members, patients, and bystanders. Transmit crucial information to facilitate coordinated patient management.
- Stay calm under pressure: Emergencies can be stressful; staying composed is essential. This allows you to think critically, make informed decisions, and provide optimal patient care.
- Continuous reassessment: Throughout the assessment process, periodically reassess the patient's condition. Conditions can change, and constant evaluation ensures timely adjustments in your approach and interventions.
- Adaptability to diverse situations: Develop the ability to adapt your assessment techniques based on the unique circumstances of each emergency. Flexibility in approach enhances your ability to address a variety of patient needs.
- Thorough patient history gathering: Invest time in collecting a comprehensive patient history. This information is invaluable for determining appropriate treatments and understanding the emergency context.
- Systematic physical examination: Follow a systematic approach to the physical examination, covering all relevant areas. This systematic process helps identify injuries, abnormalities, or signs of distress like chest pain or difficulty breathing.
Commonly asked questions
Upon arriving at the scene, the priority is to conduct a thorough safety assessment. Once the area is deemed secure, the focus shifts to evaluating the patient's level of consciousness, ensuring responsiveness. The ABCs—airway, Breathing, and Circulation—are systematically assessed and addressed to address any immediate threats to life.
Gathering patient history, including medical background, allergies, and medications, simultaneously is crucial for comprehensive care. A thorough physical examination follows to identify injuries or abnormalities.
Based on assessment findings, necessary interventions are initiated to provide ongoing patient care. Finally, a transport decision is made, selecting the most appropriate mode of transportation considering the patient's condition for further medical attention.
An EMT's assessment is typically conducted in a pre-hospital setting with limited resources and time. It focuses on immediate life-saving interventions and determining the urgency of transportation. In contrast, assessments in the emergency department are more comprehensive, incorporating advanced diagnostics and a broader range of medical interventions.
The primary assessment provides essential information to emergency responders about the patient's immediate life-threatening issues. It reveals critical details about the patient's airway, breathing, circulation, and overall mental status, guiding the initial interventions necessary for stabilizing the patient's condition in the pre-hospital setting.