Otoscope Examination
Learn how to perform an otoscope examination and see an example with our Carepatron's free PDF download.


What is an Otoscope Examination?
An Otoscope Examination, also known as otoscopy, is a medical procedure used to examine the ear, specifically the ear canal and eardrum, using a device called an otoscope. This handheld instrument has a light source and a magnifying lens, allowing healthcare professionals to visually inspect the ear's internal structures (e.g., external auditory canal, tympanic membrane, etc.). This type of ear examination provides crucial insights into the ear's health and is commonly performed by physicians, audiologists, and other healthcare practitioners.
During an otoscopic exam, the practitioner gently inserts the otoscope into the ear canal, illuminating the area and enabling a detailed examination. This procedure helps identify various ear conditions, including infections, blockages, or abnormalities in the ear canal.
The otoscope's magnification allows for a close inspection of the eardrum, which is essential for detecting issues such as perforations or signs of inflammation that might contribute to potential problems like sensorineural hearing loss or conductive hearing loss in the affected ear. It can even help determine the cause of problems like middle ear effusion, middle ear infection, etc.
Such an exam can also help in routine monitoring examinations to check if a person has a normal tympanic membrane, normal hearing, etc.
The importance of otoscopic exams extends beyond diagnosing specific ear conditions. Routine otoscopy is a vital component of general health check-ups, especially for children and individuals with a history of ear-related problems. It aids in the early detection of issues that may affect hearing and overall ear health.
Moreover, otoscopic exams are crucial in monitoring and managing chronic conditions such as otitis media, earwax impaction, or disorders affecting the middle and inner ear. Early detection through regular otoscopic examinations enables prompt intervention and appropriate treatment, contributing to better overall ear health.
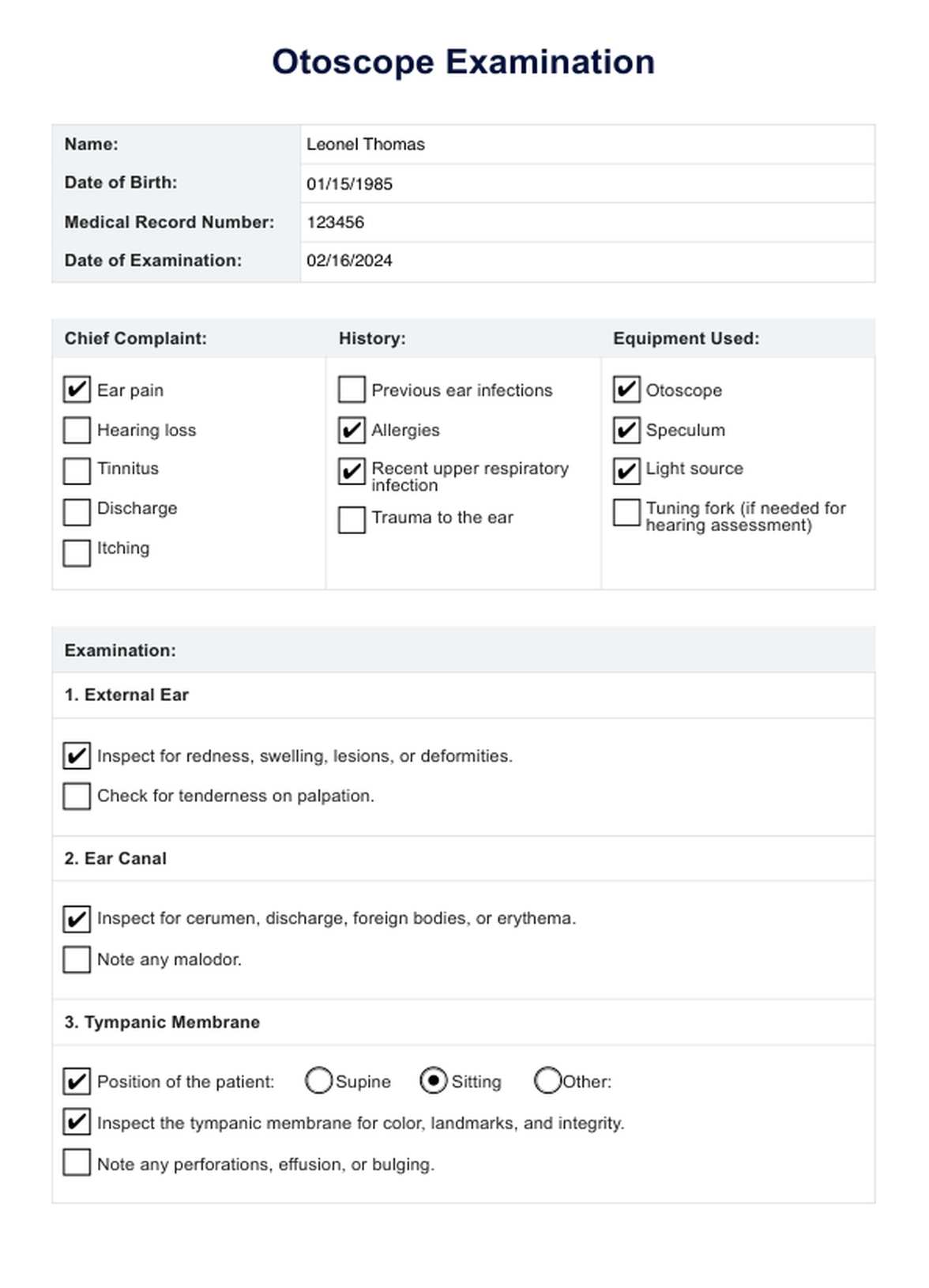
Otoscope Examination Template
Otoscope Examination Example
When to perform an otoscopic exam?
An otoscopic exam is a versatile diagnostic tool, employed in various scenarios to assess and monitor ear health. Understanding the specific instances when an otoscopic exam is necessary is crucial for ensuring timely and accurate evaluations.
Routine check-ups for children
Regular otoscopic exams are recommended for children as part of routine check-ups. Young individuals' developing ear canal and middle ear structures make them susceptible to conditions like otitis media. Early detection through regular exams aids in prompt intervention and prevents potential complications.
Ear infections and pain
When individuals, particularly children, complain of ear pain or exhibit symptoms of an ear infection, an otoscopic exam becomes essential. It helps identify inflammation, fluid accumulation, or signs of infection within the ear canal and middle ear. This prompt examination is crucial for determining the appropriate course of treatment.
Hearing concerns
In cases with concerns about hearing loss or difficulties, an otoscopic exam can reveal issues within the ear canal or middle ear that may contribute to these problems. This examination is a key step in the diagnostic process for understanding and addressing hearing-related medical conditions.
Foreign object presence
An otoscopic exam is conducted for individuals who experience discomfort or suspect the presence of a foreign object in the ear canal. The otoscope's magnification allows healthcare professionals to visualize and safely remove any lodged objects, preventing potential damage or complications.
Medical emergencies
In a certain medical emergency, such as head trauma, an otoscopic exam is performed to assess the ear canal and middle ear for signs of injury or bleeding. This rapid assessment is crucial in determining the extent of damage and guiding appropriate medical interventions.
Monitoring chronic medical conditions
Individuals with chronic medical conditions affecting the ear, like recurrent ear infections or a medical condition impacting the middle ear, require regular otoscopic exams. These routine evaluations contribute to ongoing management and help prevent complications associated with these conditions.
How is an Otoscope Examination performed?
Performing otoscopy requires precision and a gentle approach to accurately examine the ear structures. Understanding the proper technique is essential for healthcare professionals and caregivers alike.
Positioning for a person's otoscopic exam
Proper positioning is crucial when conducting an otoscopy on a patient. Ensure they are comfortable and secure, seated on a caregiver's lap or lying down. Gently stabilize the patient's head, making them feel at ease before initiating the examination.
Gently pull the ear for optimal visualization
To achieve optimal visualization of the ear canal, gently pull the outer ear upward and backward for individuals of all ages. This straightens the ear canal, providing the otoscope a clear line of sight. Careful handling is critical when examining a patient's ear to avoid discomfort.
Introduction of the otoscope
With the ear properly positioned, introduce the otoscope into the ear canal. Use a light touch and move slowly to prevent any discomfort or injury. The otoscope's light beam illuminates the ear canal, allowing the examiner to observe the ear's internal structures, including the tympanic membrane or eardrum.
Examining the tympanic membrane
The primary focus of otoscopy is the examination of the tympanic membrane. This thin barrier between the ear canal and the middle ear is crucial for hearing. Carefully inspect the membrane for abnormalities, such as signs of infection, fluid accumulation, or perforations, which can contribute to hearing loss.
Avoiding invasive measures
It's crucial to emphasize that invasive measures, such as probing the ear with sharp objects, are strictly prohibited during otoscopy. The otoscope provides a non-invasive means of examination, and any attempts at probing may result in injury or complications.
How to use the template
Utilizing an Otoscope Examination template can streamline the process, ensuring a comprehensive and organized approach to ear examinations. Follow these step-by-step instructions to make the most of the template:
Step 1: Download or create the template
Start by obtaining a copy of the Otoscope Examination template. You can download a pre-existing template or create one tailored to your needs and preferences. Ensure the template includes sections for essential information, such as patient details, examination dates, and precise observations.
Step 2: Patient information
Fill in the patient information section with accurate details, including the individual's name, age, and relevant medical history. This information is vital for tracking and referencing the patient's ear health over time.
Step 3: Examination date and time
Specify the date and time of the otoscopic examination. This timestamp is essential for tracking the progression of any ear-related conditions and can help identify patterns or recurring issues.
Step 4: Proper positioning
Incorporate a section emphasizing the importance of proper positioning during the otoscopic exam. Guide positioning of the patient's head, especially if the examination involves children. Clear instructions can contribute to a more comfortable and practical examination.
Step 5: Gentle ear maneuvers
Include a section on the proper techniques for gently pulling the ear to optimize visualization of the ear canal. Emphasize the importance of a delicate touch, particularly when examining children, to avoid discomfort or resistance.
Step 6: Detailed observations
Create spaces within the template for detailed observations during the examination. This may include descriptions of the ear canal's appearance, notes on the tympanic membrane, and any abnormalities detected. Encourage thorough and accurate documentation to support precise diagnoses.
Step 7: Interpretation and next steps
Dedicate a portion of the template to interpreting the findings and outlining potential next steps. Depending on the observations, this section may include recommendations for further testing, referrals to specialists, or specific treatment plans.
If you are a nurse, we have a guide and template for nursing ear exams. The guide you're reading now is for an Otoscope Examination. Our nursing ear exam guide is for a comprehensive examination that includes the external ear.
You can also use and ear exam template to thoroughly assess and document the condition of your clients' ears. This template ensures that all aspects of the ear examination are covered, from the outer ear to the inner structures, facilitating accurate diagnosis.
Step 8: Review and follow-up
Conclude the template with areas for review and follow-up. Note any scheduled follow-up appointments, additional tests, or interventions planned. This section ensures a systematic approach to ongoing care and monitoring.
Interpreting results
Understanding the results of an otoscopic examination is crucial for healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding patient care. The examination may yield normal or abnormal results, each providing valuable insights into the individual's ear health.
Normal results
In a normal otoscopic examination, the ear structures appear as expected, without any signs of infection, inflammation, or other abnormalities. The ear canal is clear, the tympanic membrane is intact, and there are no indications of fluid accumulation or foreign objects. Average results suggest that the individual has healthy ears without immediate concerns.
Regular otoscopic exams with average results are incredibly reassuring during routine check-ups, as they indicate that the individual's ear health is stable. This is common in cases where there are no reported symptoms of pain, hearing loss, or discomfort. Maintaining regular otoscopic examinations for individuals with average results contributes to the proactive management of ear health and early detection of potential issues.
Abnormal results
Abnormal otoscopic results may reveal various issues that require further attention. Common abnormalities include signs of infection, such as redness or swelling in the ear canal or the presence of pus. An abnormal examination may also detect a perforation in the tympanic membrane, fluid behind the eardrum (indicative of conditions like otitis media), or a foreign object.
Abnormal results highlight potential ear-related concerns requiring additional diagnostic tests, consultation with specialists, or specific treatment plans. Prompt intervention is crucial to address underlying issues and prevent complications such as hearing loss or chronic conditions.
Next steps
After conducting an otoscopic examination, certain crucial next steps should be followed to ensure a comprehensive and effective approach to ear health. These steps guide healthcare professionals and individuals in managing potential concerns identified during the examination.
Communicate with the patient
Clear communication with the patient is paramount for healthcare professionals. Share the results of the otoscopic examination, explain any abnormalities, and discuss potential causes and implications. Addressing any questions or concerns the patient may have fosters a collaborative approach to care.
Treatment planning
Healthcare providers can formulate a tailored treatment plan based on the examination results. This may involve prescribing medications for infections, recommending lifestyle changes, or scheduling follow-up appointments for further evaluation. Treatment plans aim to address identified issues and optimize ear health.
Referral to specialists
In cases where the otoscopic examination reveals complex or specialized issues, healthcare professionals may refer the patient to ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialists for further evaluation and management. Specialist input ensures a more focused and expert-driven approach to specific ear-related concerns.
Routine monitoring and follow-up exams
Routine monitoring and follow-up examinations are crucial next steps for individuals with abnormal findings. These regular check-ups allow healthcare providers to track treatment progress, assess the effectiveness of interventions, and detect any new developments in the patient's ear health.
Patient education and self-care
It is essential to empower patients with knowledge about their ear health. Healthcare providers should educate individuals on preventive measures, self-care practices, and lifestyle adjustments to maintain optimal ear health. This may include advice on ear hygiene, protection from loud noises, and strategies for preventing ear infections.
Commonly asked questions
In an otoscope, you should see a clear view of the ear canal and the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The ear canal should appear healthy without signs of redness, swelling, or blockages, and the tympanic membrane should be intact and translucent.
An ear infection through an otoscope may present redness, inflammation, and a cloudy tympanic membrane appearance. Pus or fluid accumulation behind the eardrum may also be visible, indicating an infection that requires further assessment and treatment.