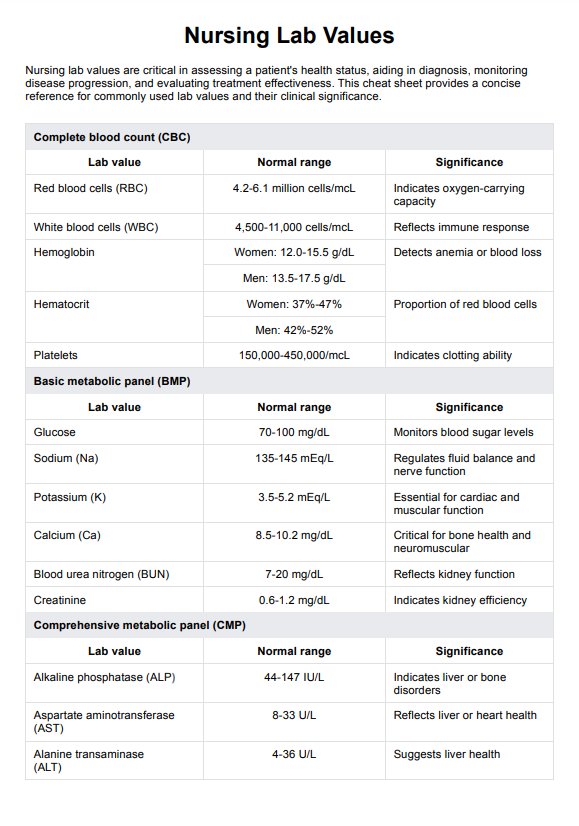
Nurses should know core values such as complete blood count (CBC), basic metabolic panel (BMP), and liver function tests (LFTs). These values aid in assessing patient health, diagnosing conditions, and monitoring treatments effectively.
Nursing Lab Values PDF
Download Carepatron's free Nursing Lab Values PDF to better understand common lab values in healthcare settings.
Use Template
Nursing Lab Values PDF Template
Commonly asked questions
For the NCLEX, nurses must focus on values like blood urea nitrogen (BUN), potassium, INR, and hemoglobin A1C. These values frequently appear in exam scenarios involving clinical decision-making and patient care.
The NCLEX does not provide normal lab values, requiring test-takers to memorize key ranges. This ensures nurses can apply their knowledge to interpret results and make appropriate clinical decisions.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











