Lean Diet Plan
Use Carepatron's free Lean Diet Plan PDF template to streamline patient nutrition management effectively.


What is a lean diet?
A lean diet is a structured diet focused on promoting weight loss and muscle building through nutrient-dense foods. It emphasizes non-restrictive high-quality proteins, fiber, healthy fats, and carbs (Zhang et al., 2018), aiming to optimize physical health and achieve the best body composition. These meal plans typically include a balanced macronutrients to support a low-calorie intake while providing enough energy for daily activities and rest days. Key components like green beans and other fibrous vegetables help fill you up without adding excess calories, making it easier to lose weight sustainably.
Furthermore, including lean proteins in every meal prioritizes skeletal muscle repair and growth (Stokes et al., 2018), essential for those looking to build muscle. The diet also highlights the importance of having a midday meal that is filling and rich in nutrition facts, aiding in steady energy levels throughout the day. This dietary approach not only supports weight loss but also enhances overall wellness by carefully selecting foods that contribute to a well-rounded and nutritious diet.
Lean Diet Plan Template
Lean Diet Plan Example
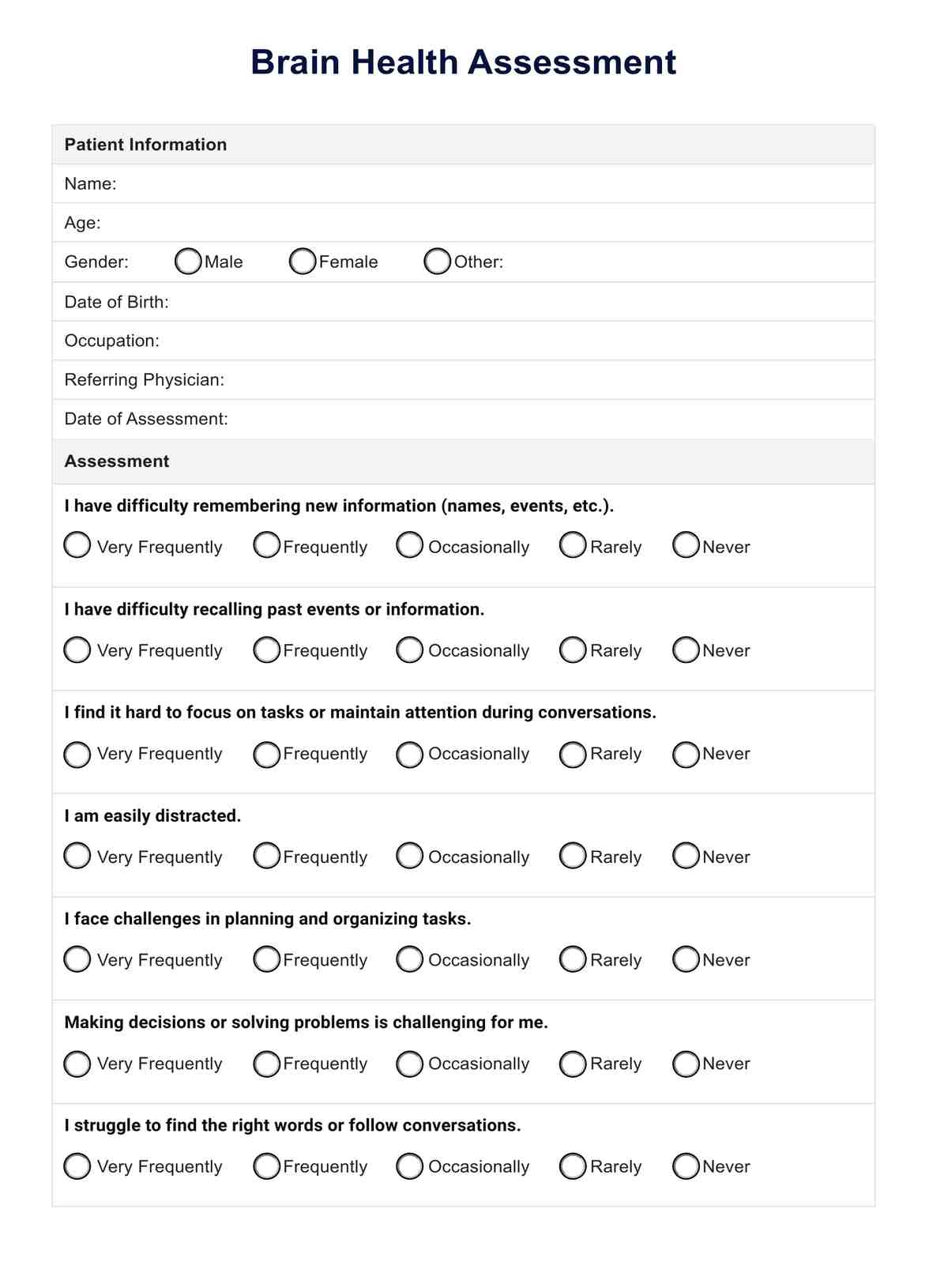
What is a Lean Diet Plan?
A Lean Diet Plan is a strategic meal plan designed to optimize protein intake and calorie management throughout the entire day, enhancing both dietary and workout success. This plan typically involves structured meals that include protein shakes, lean proteins, using cooking spray for lower calories, and carefully measured portions to control calories and cholesterol.
The plan aligns daily eating with workout schedules for best results, ensuring that every meal contributes to achieving fitness and health goals. By focusing on more protein and fewer unneeded calories, this diet plan helps individuals eat smarter and achieve their desired body composition efficiently.
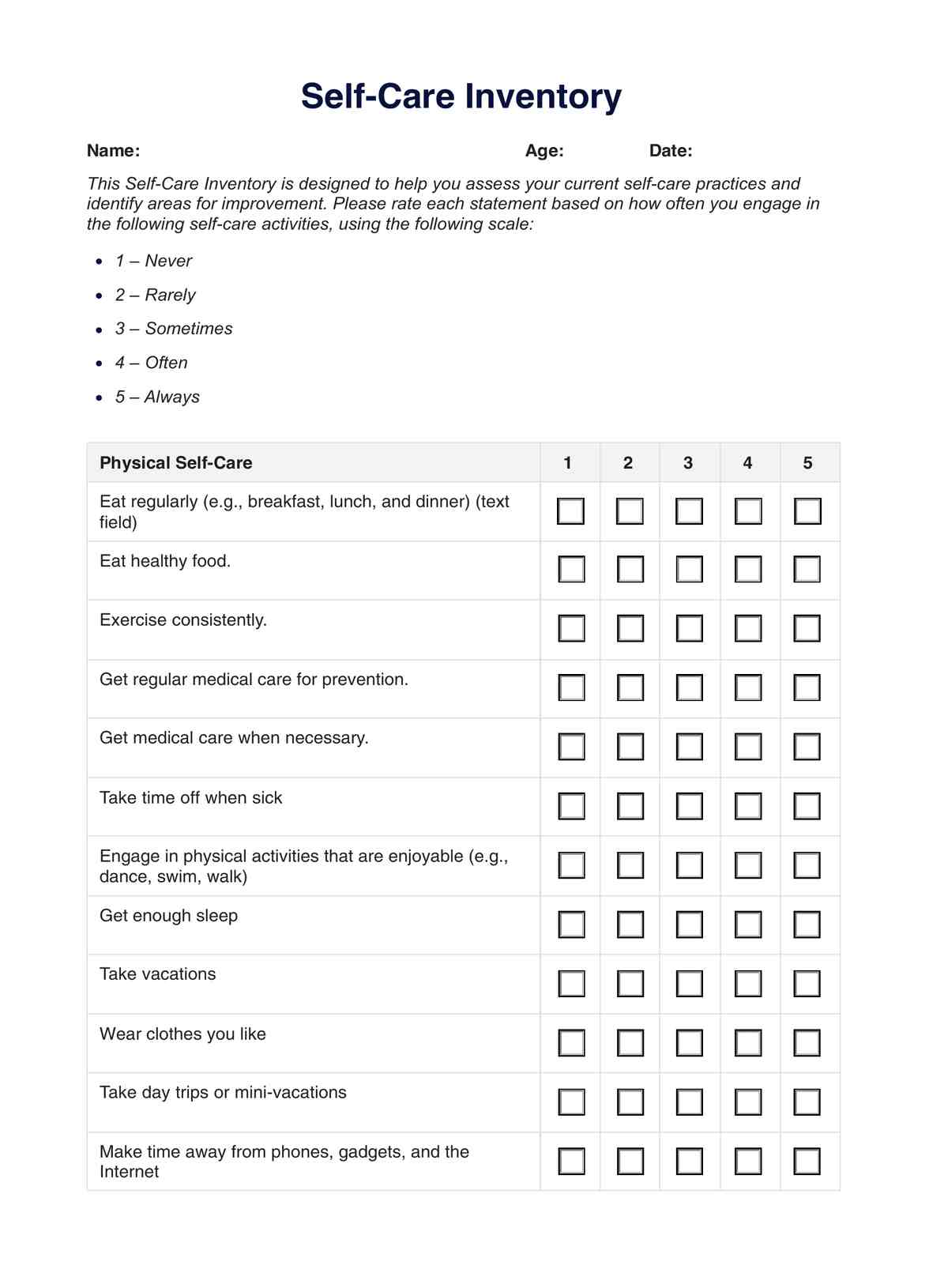
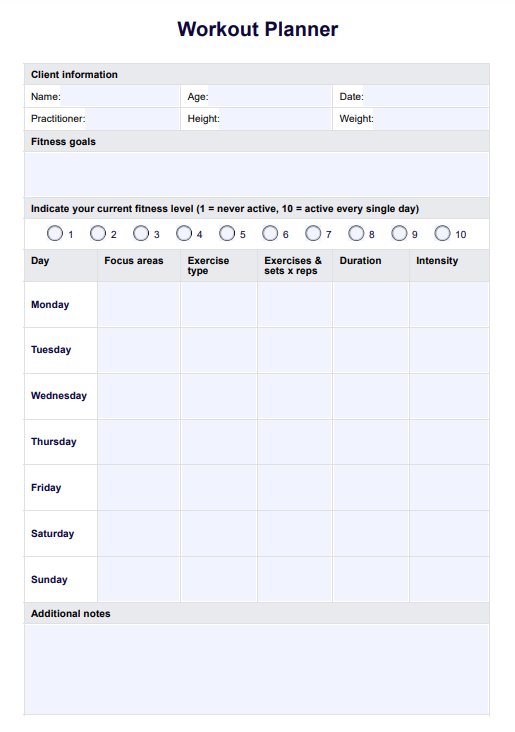
How does our Lean Diet Plan template work?
Carepatron has created a blank Lean Diet Plan to help you formulate the best diet plan for your client's needs. Follow these steps to get started:
Step 1: Access the template
Click "Use template" to open and customize the Lean Diet Plan template in the Carepatron app. The template is easy to modify, featuring fillable tables and a sample plan for everyday use, ensuring it can be tailored to each patient's specific needs.
Step 2: Input client information
Begin by filling in your client's personal details, including their name, age, weight, and height. This information will help you create a diet plan aligning with their health goals.
Step 3: Customize the meal plan
Using the fillable tables, outline a meal plan that suits your client’s preferences and nutritional needs. Include portion sizes, calorie counts, and recommended foods for each meal. Adjust the plan based on your client’s goals, such as weight loss, muscle gain, or a healthy diet.
Step 4: Add any additional notes
Include important notes, such as meal preparation tips, hydration reminders, or suggestions for physical activity to complement the diet plan.
Step 5: Share and implement
Once the plan is finalized, share it with your client. The template can be exported or shared directly through the Carepatron app, ensuring your client can easily access and follow the plan. Encourage them to provide feedback during follow-ups to refine the plan as needed.
Foods to avoid in a lean diet
When advising on a lean diet, medical professionals should recommend that patients avoid foods that hinder the goal of building lean muscle and achieving weight loss. Key items to avoid include heavily processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-fat meats, which can negate the benefits of a carefully planned meal.
For instance, instead of eating regular ground beef or processed meats high in unhealthy fats, choose lean proteins like chicken breast or egg whites that support muscle maintenance and growth without excess calories.
Other foods to limit are refined carbohydrates such as white bread and pasta, which lack the nutrition facts and benefits of their whole-grain counterparts, like whole wheat bread or brown rice. Additionally, sugary drinks and high-calorie snacks should be replaced with nutrient-rich alternatives like protein shakes or Greek yogurt, which can provide essential nutrients for a midday meal or as part of a recovery snack post-exercise.
Foods to include in a lean diet
For optimal health and effective weight management, a lean diet should include a variety of nutrient-dense foods that support the building of lean muscle and promote overall wellness. Dietitians and nutritionists should encourage clients to include lean proteins such as chicken breast, turkey, fish, cottage cheese, and egg whites, essential for muscle repair and growth.
Carbohydrates should come from whole grains like brown rice and wheat bread, providing energy and fiber. Healthy fats from sources such as avocados, nuts, and seeds are crucial for heart health and satiety between meals.
Additionally, incorporating a wide array of vegetables like green beans, leafy greens, and fruits high in antioxidants ensures a low-calorie intake while maximizing nutritional benefits. Greek yogurt mixed in a protein shake and cottage cheese are excellent choices for a protein-rich snack or as part of one meal, aiding in weight loss and muscle-building efforts.
References
Stokes, T., Hector, A., Morton, R., McGlory, C., & Phillips, S. (2018). Recent perspectives regarding dietary protein's role in promoting muscle hypertrophy with resistance exercise training. Nutrients, 10(2), Article 180. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu10020180
Zhang, L., Pagoto, S., Olendzki, B., Persuitte, G., Churchill, L., Oleski, J., & Ma, Y. (2018). A nonrestrictive, weight loss diet focused on fiber and lean protein increase. Nutrition, 54, 12–18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2018.02.006
Commonly asked questions
A lean diet focuses on maximizing nutrient intake while minimizing excess fats and sugars, emphasizing foods like lean proteins, whole grains, and fresh produce. This diet is designed to enhance overall health, facilitate weight loss, and support muscle growth by carefully balancing calorie intake.
Lean foods include skinless poultry, fish, legumes like lentils and chickpeas, low-fat dairy products, and plenty of fruits and vegetables. These foods are high in essential nutrients and protein but low in unhealthy fats, making them ideal for maintaining a lean body.
To achieve a lean physique, avoid processed foods, sugary snacks, fried items, and high-fat dairy products. These foods are high in calories and low in nutritional value, which can counteract efforts to lose weight and build lean muscle.
The best foods for maintaining a lean body include chicken breast, turkey, tofu, and other high-protein, low-fat options that support muscle repair and growth. Additionally, integrating complex carbohydrates like quinoa and vegetables that are high in fiber can aid digestion and prolong satiety.