Hearing Aid Evaluation
Learn how to conduct a thorough hearing aid evaluation with our free PDF download. This comprehensive guide includes examples and tips for success.


How do hearing aids work?
Hearing aids are sophisticated devices designed to improve hearing for individuals experiencing hearing loss. Understanding how they work is crucial for anyone undergoing a hearing evaluation and considering using them to address hearing difficulties.
Hearing aids consist of three main parts: a microphone, an amplifier, and a speaker (or receiver). When someone with hearing loss wears an aid, the microphone picks up sounds from the environment. These sounds are then converted into electrical signals and sent to the amplifier.
The amplifier increases the power of these signals, making them stronger. This is particularly important for individuals with varying hearing loss, as it ensures that even faint sounds become audible. Once amplified, the signals are transmitted to the speaker, which converts them back into sound waves and delivers them into the ear canal.
During a successful hearing aid evaluation, a hearing specialist will consider various factors, including the individual's medical history, hearing loss type and severity, and lifestyle preferences. This comprehensive assessment helps determine the most suitable hearing aid styles and settings to meet the individual's needs.
Hearing Aid Evaluation Template
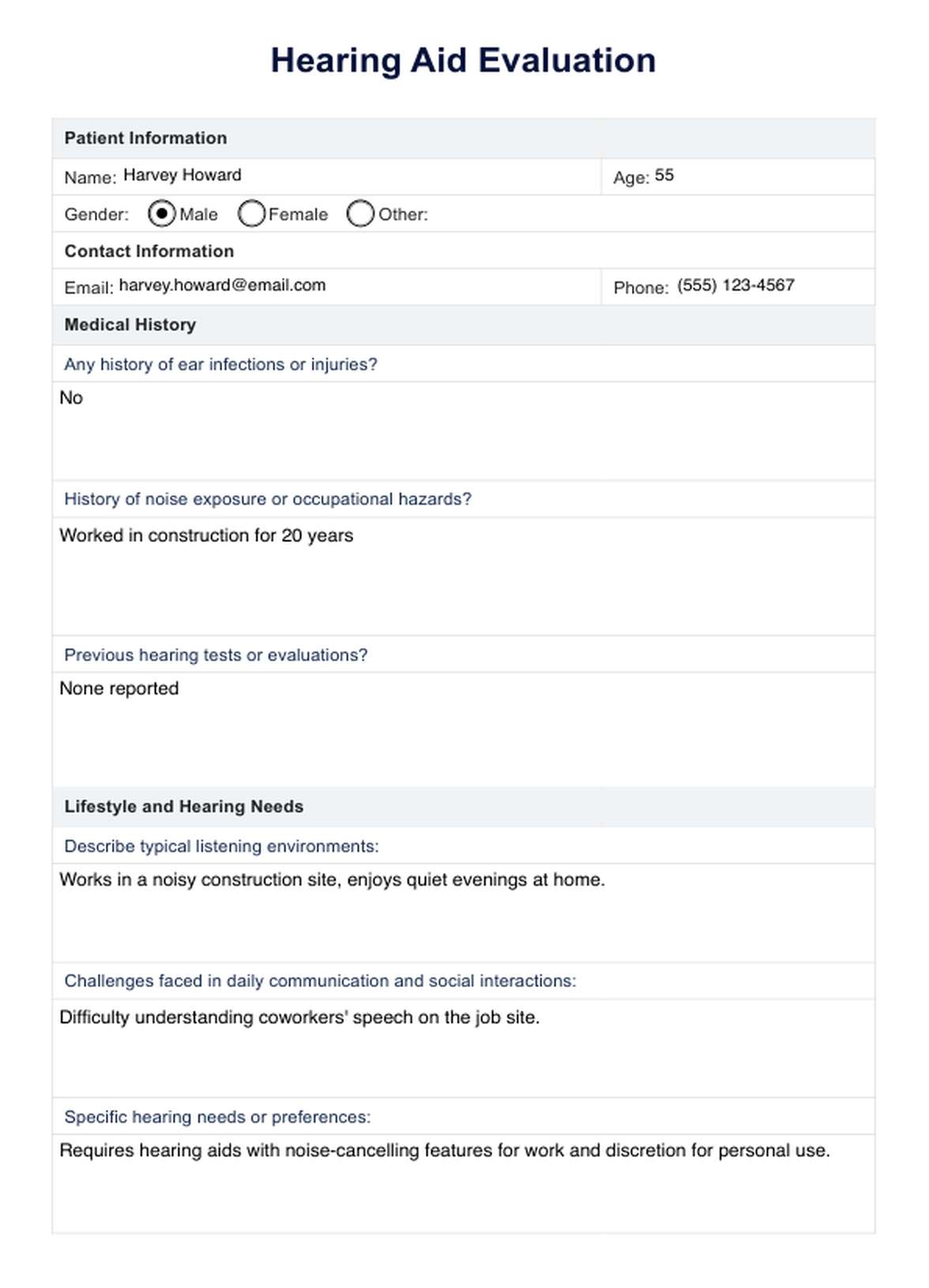
Hearing Aid Evaluation Example
Hearing aid evaluations
A thorough hearing aid evaluation is a crucial step toward finding the most suitable solution when addressing hearing loss. Here's a breakdown of how hearing aid evaluations work:
1. Initial consultation
The process begins with an initial consultation with an audiologist or hearing instrument specialist. During this consultation, the specialist will discuss the individual's medical history, lifestyle, and any concerns related to hearing loss.
2. Hearing test
The next step involves a comprehensive hearing test, also called an audiogram. This test assesses the individual's hearing ability by measuring their response to various sounds at different frequencies. The results help determine the type and severity of hearing loss.
3. Discussion of hearing aid options
Based on the hearing test results and the individual's preferences, the hearing professional will discuss suitable hearing aid options. There are various hearing aid styles available, including behind-the-ear (BTE), in-the-ear (ITE), and completely-in-the-canal (CIC), each with its own advantages and considerations.
4. Hearing aid fitting
Once a decision is made, the hearing professional will proceed with the fitting of a hearing aid. During this process, the selected hearing aids are adjusted to ensure optimal comfort and performance.
5. Trial period
After the BTE hearing aids are fitted, individuals typically undergo a trial period to assess their effectiveness in various listening environments. This allows for any necessary adjustments to be made to ensure satisfaction with the new hearing aids.
6. Follow-up care
Regular follow-up appointments are essential to monitor progress and address any concerns or adjustments needed. This ongoing support ensures that individuals benefit from their new hearing aids and helps maintain their hearing health.
How are the results interpreted?
Understanding the results of a hearing aid evaluation involves interpreting various notations on the audiogram and deciphering what they mean for your patient's hearing health. Here's a breakdown of key points to consider:
Understanding audiogram notations
Before delving into the specifics of the audiogram results, it's essential to grasp the meaning behind the various symbols and notations used. These notations provide valuable information about how hearing was tested and the specific results for each ear.
- O or Triangle (possibly in red) and X or Square (possibly in blue): These symbols represent the results from the right and left ears, respectively, measured with headphones (air conduction).
- S: Denotes information that is not specific to either ear.
- < or [: Indicates the result from your right ear measured with bone conduction.
- > or ]: Indicates the result from your left ear measured with bone conduction.
Interpreting threshold levels
The audiogram plots your threshold levels, indicating the lowest intensity level at which the individual can hear a frequency. Understanding these threshold levels is crucial for determining the extent of hearing loss and appropriate interventions.
- A steady line connecting threshold levels at the top of the chart suggests normal hearing, while rises and drops along the chart indicate hearing loss for specific frequencies.
- A downward slope for higher frequencies is often seen in age-related hearing loss, and a line lower on the chart indicates more severe hearing loss.
Deciphering hearing loss levels
Deciphering your hearing loss levels is essential for understanding how your hearing abilities may be affected in various situations. Here's a breakdown of the different levels of hearing loss and their implications:
- Mild hearing loss (26–40 decibels): You may experience difficulty hearing in noisy environments or understanding quiet speech.
- Moderate hearing loss (45–65 decibels): Conversations become challenging to hear, especially in noisy settings.
- Severe hearing loss (66–85 decibels): You may struggle to hear speech even in quiet environments and rely heavily on visual cues.
- Profound hearing loss (greater than 85 decibels): Understanding speech without amplification becomes extremely difficult, and you may rely on lip-reading or sign language for communication.
How does our Hearing Aid Evaluation template work?
Carepatron's hearing aid assessment simplifies the process of assessing hearing needs and selecting the most suitable hearing aid solution. Here's how it works:
Comprehensive assessment
The template begins with a comprehensive assessment of the individual's hearing needs and lifestyle preferences. This includes considerations such as the severity of hearing loss, preferred hearing aid styles (e.g., in-the-ear, receiver-in-the-canal, behind-the-ear), and specific challenges faced in day-to-day life, such as hearing in noisy situations.
Audiological assessment
The template includes a section for the results of an audiological assessment to be included. Conducting a thorough hearing evaluation ensures informed decisions are made, and the patient receives hearing aids that are most suited to their care needs.
Customized recommendations
Based on the information gathered, the practitioner should make an informed decision about the most suitable hearing aid for their patient. The template encourages practitioners to inform their patients about benefits, features, and how this hearing aid will impact the patient's lifestyle.
Hearing aid fitting
The template includes a section for practitioners to include fitting details, including when the hearing aid fitting appointment is to occur and information regarding specific adjustments and customization.
Follow-up
Finally, the template concludes with space for the practitioner to record any important follow-up information, ensuring the patient's needs are consistently prioritized, and their hearing aids suit their needs.
Benefits of hearing aids
Hearing aids offer numerous benefits to individuals experiencing hearing loss, enhancing their quality of life and improving their ability to engage in various environments. Here are some of the key advantages:
Improved hearing ability
Hearing aids effectively amplify sounds, making it easier for individuals to hear and communicate in different environments. Whether it's engaging in conversations at home, enjoying social gatherings, or participating in work meetings, hearing aids enable individuals to hear more clearly and confidently.
Enhanced quality of life
By addressing hearing loss, hearing aids contribute to a better quality of life for individuals and their loved ones. Improved communication and social interaction foster stronger relationships and greater participation in activities, leading to increased happiness and satisfaction.
Customized solutions
Modern hearing aids have advanced features and customization options tailored to individual needs. From custom-molded in-the-ear devices to discreet invisible-in-canal aids, individuals can choose the best hearing aid style and features that suit their preferences and lifestyles.
Commonly asked questions
A hearing aid assessment is a thorough evaluation conducted by a hearing doctor to determine the individual's hearing needs, preferences, and suitability for hearing aids.
A hearing evaluation typically includes tests to assess hearing sensitivity, speech understanding, and other aspects of auditory function, such as middle ear function and inner ear health.
A hearing aid fitting evaluation involves selecting and adjusting hearing aids to ensure optimal comfort, performance, and sound quality for the individual.