Cincinnati Stroke Scales
Download Carepatron's free Cincinnati Stroke Scale PDF template and aid rapid stroke assessment with detailed guidelines.


What is a Cincinnati Stroke Scale?
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale, also known as the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS), is a rapid neurological assessment tool used to identify stroke symptoms in suspected stroke patients (Maddali et al., 2018). It is widely utilized by emergency medical services (EMS) and healthcare providers to detect acute ischemic stroke and facilitate timely intervention.
The scale evaluates three key functions: facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities. If any of these signs are present, the patient is considered at high risk for ischemic strokes and requires immediate transport to a stroke center.
The prehospital stroke scale reproducibility of the CPSS has been validated across multiple studies (Zohrevandi et al., 2015), reinforcing its reliability in recognizing large vessel occlusion stroke. While it does not replace the NIH Stroke Scale, it is a practical prehospital stroke scale (CPSS) for rapid triage. Early detection using this stroke scale improves patient outcomes by expediting critical care for suspected stroke cases.
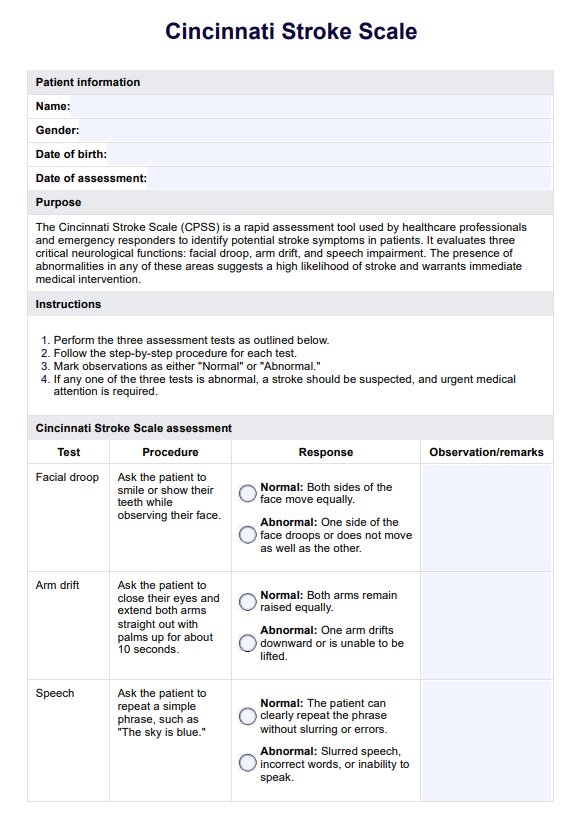
Cincinnati Stroke Scales Template
Cincinnati Stroke Scales Example
Components of the Cincinnati Stroke Scale
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale is a widely used health stroke scale designed to assess key neurological functions in suspected acute stroke patients. It has three main components: facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities.
Facial droop
Patients are asked to smile or show their teeth to assess facial muscle symmetry. A stroke patient exhibiting facial droop will have one side of the face that does not move as well as the other or appears to sag. This asymmetry results from potential damage to motor pathways controlling facial muscles. Facial droop is a critical indicator in prehospital stroke scales (Musuka et al., 2015) and is particularly relevant in identifying anterior circulation stroke. Detecting this symptom early in the prehospital setting improves the chances of rapid intervention at a stroke center.
Arm drift
The patient is instructed to close their eyes and extend both arms straight out with palms up for about 10 seconds. Arm drift is observed if one arm involuntarily moves downward or the patient cannot lift one arm. This test evaluates motor strength and coordination, with abnormalities indicating potential hemiparesis—a hallmark of ischemic stroke.
Speech abnormalities
The patient is asked to repeat a simple phrase like "The sky is blue." A positive stroke sign includes slurred speech, incorrect word usage, or an inability to articulate words. These symptoms suggest damage to the brain’s language centers, often associated with anterior circulation stroke. Speech impairment is a key diagnostic indicator in stroke patients, with a notable negative predictive value when absent, meaning a regular speech test lowers the likelihood of stroke. Recognizing these speech deficits early ensures the patient receives urgent care at a comprehensive stroke center to confirm the final diagnosis.
How does our Cincinnati Stroke Scale template work
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale is a simple yet effective tool that helps healthcare professionals quickly identify suspected stroke patients and determine the need for urgent intervention. Carepatron’s template streamlines this process, ensuring accurate documentation and decision-making. Follow these steps to integrate the assessment into your clinical workflow seamlessly.
Step 1: Access the template
Click "Use template" to instantly access the Cincinnati Stroke Scale within Carepatron’s platform. This action directs you to the Carepatron app download, where you can efficiently store, edit, and manage patient assessments. The template is designed to provide structured, real-time documentation, making stroke evaluations quicker and more organized.
Step 2: Use the template in patient assessment
Once the template is open, enter the patient's details, including name, date of birth, and symptom onset time. Accurate documentation ensures a clear timeline for stroke diagnosis and enhances communication with emergency medical services (EMS) and hospital teams, particularly if stroke center intervention is required.
Step 3: Conduct the assessment
Perform the three key neurological tests: facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities. Follow the template’s step-by-step guidance to assess each function systematically. Since time-sensitive conditions like ischemic stroke require swift evaluation, having a structured template ensures no critical signs are overlooked during the assessment process.
Step 4: Gather and interpret results
Record observations under each category and determine if the patient exhibits stroke symptoms. The prehospital stroke scale identifies acute stroke likelihood based on these findings. If any test is abnormal, immediate intervention is needed. The template’s structured format improves data consistency, supporting faster decision-making in prehospital settings and comprehensive stroke centers.
Step 5: Provide patient support and next steps
If the results suggest a suspected stroke, activate emergency medical services immediately. Use the template to document when symptoms started and communicate findings to hospital teams. This documentation aids the final diagnosis at the receiving stroke center, ensuring the patient receives appropriate care, including eligibility for thrombolytic therapy or specialized intervention.
Results and interpretation
A single abnormal finding in any of the three categories in the Cincinnati Stroke Scale suggests a high probability of stroke, necessitating immediate transport to a stroke center for further evaluation. Unlike numerical scoring systems, this prehospital stroke scale focuses on clinical signs, enabling emergency physicians and first responders to make quick, decisive interventions in the emergency department.
Early recognition and rapid response are critical in stroke management, as timely intervention can significantly improve patient outcomes. The Cincinnati Stroke Scale’s simplicity allows for quick assessments in prehospital and emergency settings, ensuring that patients with suspected stroke receive prompt neuroimaging and specialized care. This rapid triage tool supports the goal of reducing door-to-needle time for thrombolysis or other stroke treatments, ultimately improving survival rates and minimizing long-term neurological deficits.
Benefits of using this scale
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale is a critical tool for field assessment of stroke triage, allowing healthcare professionals to identify patients with potential stroke symptoms quickly. Its structured approach streamlines the initial assessment, ensuring rapid recognition of patients with acute ischemic stroke and other cerebrovascular diseases. Focusing on facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities provides a standardized method for early stroke detection.
This scale is handy in prehospital settings, where immediate evaluation is crucial. When any of the tests show abnormal findings, it prompts urgent intervention, reducing delays in stroke management. The simplicity of the assessment improves efficiency in emergency workflows, aiding paramedics and hospital staff in prioritizing stroke cases. Additionally, its use in individual patient data collection helps refine stroke protocols and enhance outcome predictions. By incorporating the CPSS into routine assessments, medical professionals improve stroke response times and optimize patient care.
References
Maddali, A., Razack, F. A., & Trichur, R. (2018). Validation of the Cincinnati prehospital stroke scale. Journal of Emergencies Trauma and Shock. https://doi.org/10.4103/JETS.JETS-8-17
Musuka, T. D., Wilton, S. B., Traboulsi, M., & Hill, M. D. (2015). Diagnosis and management of acute ischemic stroke: speed is critical. Canadian Medical Association Journal, 187(12), 887–893. https://doi.org/10.1503/cmaj.140355
Zohrevandi, B., Kasmaie, V. M., Asadi, P., Tajik, H., & Roodpishi, N. A. (2015). Diagnostic accuracy of Cincinnati Pre-Hospital Stroke Scale. Emergency, 3(3), 95. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4608338/
Commonly asked questions
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale, also known as the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale (CPSS), is a rapid assessment tool medical professionals use to identify patients with suspected stroke. It evaluates facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities to determine the likelihood of acute ischemic stroke or other cerebrovascular diseases.
The Cincinnati Stroke Scale's three components are facial droop, arm drift, and speech abnormalities. These neurological tests assess motor function and speech deficits, which are key indicators of stroke and support field assessment stroke triage.
The FAST stroke test is a simplified version of the Cincinnati Stroke Scale, emphasizing Face, Arm, Speech, and Time (FAST) to recognize stroke symptoms quickly. It reinforces the urgency of seeking medical attention when abnormalities are detected, improving early intervention and patient outcomes.
If a single abnormal finding is present on the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale, the estimated probability of stroke is approximately 72%. The likelihood increases significantly when multiple abnormalities are observed, warranting immediate emergency care and further evaluation at a stroke center.