Coping Wheel
Download a free Coping Wheel Template to help clients manage stress effectively.


What is a Coping Wheel Template?
A coping wheel is a visual tool designed to help individuals manage stress and emotional challenges by offering a range of coping strategies. The wheel is typically divided into sections, each representing various coping techniques, such as relaxation, physical activity, social support, and creative expression.
The purpose of coping strategy wheels is to provide a quick and accessible way for individuals to identify strategies that might work for them in stressful situations. By offering various options, the wheel encourages people to try different approaches and find what best suits their needs and circumstances.
Coping wheels can be customized to reflect individual preferences and can be used by anyone seeking to improve their emotional well-being. They are often used in therapeutic settings to support individuals in building resilience and developing effective stress management skills. This can also be used alongside other resources such as the feelings wheel or emotions wheel to help teach clients holistic emotion regulation. The visual and organized format of the coping strategies wheels makes it an effective tool for both immediate and long-term emotional regulation.
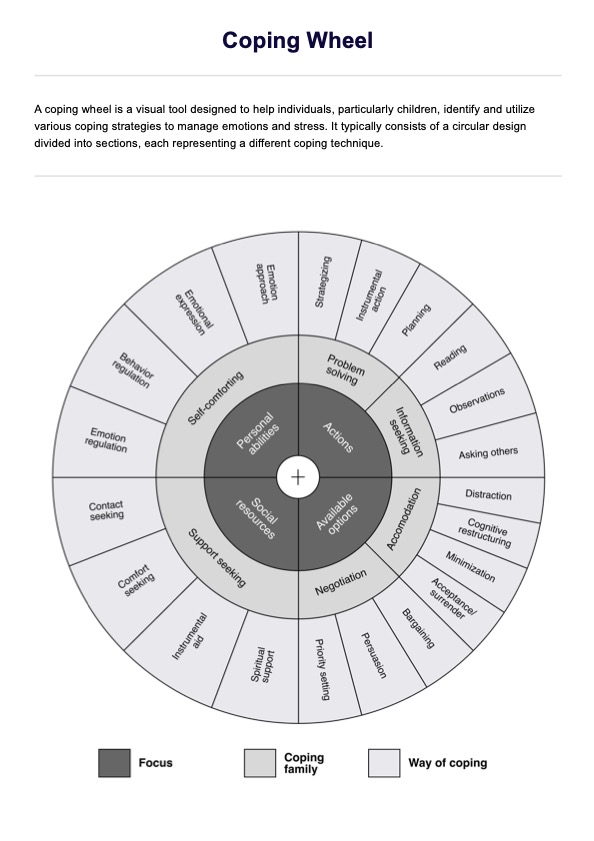
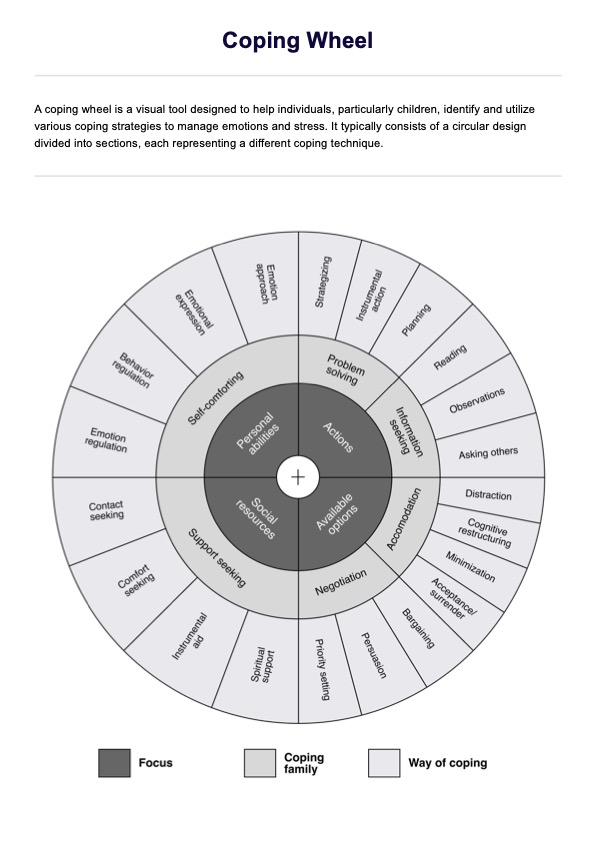
Coping Wheel Template
Coping Wheel Example
How to use our coping wheel PDF?
Our coping skills wheel is an invaluable tool for healthcare professionals to guide patients, especially children and young adults, in practicing coping strategies according to their needs. Here's a structured approach to how to implement the coping wheel in clinical or therapeutic settings:
Step 1: Access the handout
Within this guide, click "Use template" to access and edit the template within the Carepatron platform, or click "Download" to get a PDF copy of the handout.
Step 2: Familiarize yourself with the sections
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the different sections of the coping wheel. Each section represents a specific focus and contains related coping strategies.
Step 3: Assess the patient's situation
Assess the situation or challenge your patient is facing. Understanding the context in which they must cope will help you guide them towards the most appropriate section of the wheel.
Step 4: Select a coping family and a specific coping strategy
Choose a coping family from the wheel that best matches the patient's current needs. For example, if the patient is dealing with anxiety, you might select 'self-comforting' under the focus on 'personal abilities.'
Then, help the patient select a specific coping strategy from the selected coping family. For instance, if you have chosen 'self-comforting,' strategies like 'emotion regulation or 'behavioral regulation' could be appropriate.
Step 5: Implement the strategy
Guide your patient in applying the chosen coping strategy to their situation. Assist them in implementing the actions or thoughts associated with that strategy, such as engaging in mindfulness exercises or reaching out to supportive friends or family.
5 types of coping strategies
Coping strategies are essential techniques for managing stress and emotional challenges. They can be categorized into various types, each with a unique focus and approach, allowing individuals to tailor their responses to different situations. This includes the following:
Emotion-focused strategies
These strategies aim to manage the emotional response to a stressful situation, such as feeling overwhelmed, rather than the problem itself. Breathing techniques are a core element of relaxation exercises, helping individuals regulate their responses to stress.
Problem-focused strategies
These involve directly addressing the source of stress by identifying the problem, generating solutions, and taking action to resolve or mitigate the issue. Examples include time management, seeking information, and setting goals.
Meaning-focused strategies
This involves finding purpose or significance in a stressful or challenging experience, which can help individuals gain perspective and build resilience. Practices like journaling, reflecting on personal values, and exploring how adversity can lead to adopting a growth mindset are examples.
Social support
Relying on relationships with friends, family, or support groups to provide emotional, informational, or practical assistance during difficult times. Social skills are also crucial as they enable effective communication and help build support networks necessary for emotional health.
Avoidance-focused coping strategies
These strategies involve avoiding or distancing oneself from the stressor or the associated emotions. Techniques include distraction, denial, or engaging in activities that take one's mind off the stressor. For those struggling with anger, avoidance-focused strategies can initially help manage reactions before engaging in more direct anger management techniques.
Benefits of using a coping strategies wheel
Our coping wheel printable template is a practical tool designed to help individuals identify and utilize effective coping mechanisms to manage stress, anxiety, and emotional challenges. This tool offers several benefits:
- Variety of options: The wheel provides diverse coping strategies catering to different preferences and needs. It encourages users to explore both traditional and creative approaches, such as mindfulness, physical activity, social connection, and creative expression.
- Personalization: Users can customize the wheel to fit their unique situations and emotional responses. Individuals can develop a more personalized and effective approach to managing stress and emotions by selecting strategies that resonate with them.
- Easy accessibility: The visual layout of the wheel makes it easy to access and understand, allowing users to quickly identify potential strategies during moments of distress. This accessibility fosters self-reliance and empowers individuals to take charge of their emotional well-being.
- Encourages proactive coping: By regularly referring to the wheel, individuals can build a habit of proactive coping. This preparation enhances resilience, enabling them to handle future challenges with greater ease and confidence.
How to help clients master coping skills
Healthcare professionals play a vital role in helping patients master coping skills to manage stress and emotional challenges. Begin by helping patients identify their triggers—specific situations or emotions that cause stress—so they can anticipate and prepare for them. Understanding these triggers enables you to guide patients in selecting appropriate coping techniques.
Encourage patients to experiment with various strategies to discover what works best. Techniques such as deep breathing, physical exercise, journaling, or talking to a trusted friend can be recommended. Emphasize the importance of exploring different options, as each patient may respond differently to experiences and situations.
Assist patients in integrating coping strategies into their daily routines to build resilience. Encourage regular practice of these techniques. Finally, support can be provided by fostering a therapeutic relationship and encouraging patients to seek additional resources or professional help if necessary. Your guidance and encouragement can be instrumental in helping patients navigate their stress and improve their overall well-being.
Commonly asked questions
Identifying healthy coping strategies is crucial because it equips individuals with tools to effectively manage stress and emotions, improving their ability to handle life's challenges and maintain mental well-being.
Coping mechanisms can be highly effective when they are well-suited to an individual's specific needs and circumstances. They can promote resilience and reduce the impact of stress on mental and physical health.
Coping strategies may not always be helpful. Their effectiveness depends on the appropriateness of the coping strategy used for the situation and individual, as some may provide temporary relief but not address the underlying issue.



















-template.jpg)


















































































