ENT Exam
Discover the key aspects of an ENT Exam with our comprehensive template, designed for health professionals to assess ear, nose, and throat health effectively.


What happens during an ENT Exam?
An ENT examination, conducted by an otolaryngologist, is a thorough examination of the ear, nose, and throat—three interconnected systems crucial for hearing, breathing, and swallowing. These specialists focus on these areas due to their anatomical proximity and interrelated functions, often resulting in overlapping symptoms and conditions. A complete ENT examination typically involves:
Ear examination
An ENT would do the following things when examining the ear:
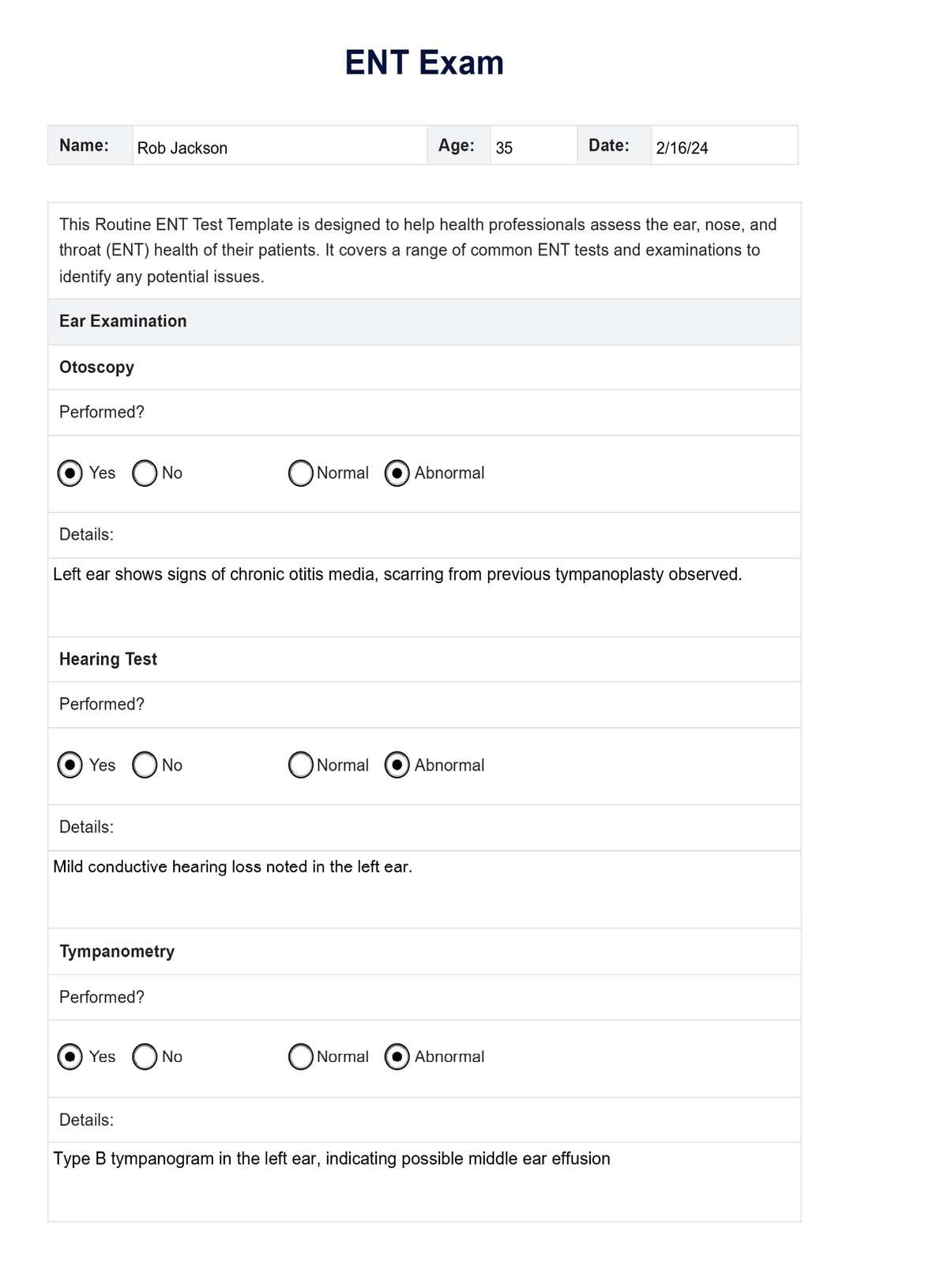
- Otoscopy: Inspection of the outer ear, ear canal, and eardrum using an otoscope to detect issues like ear infections, wax buildup, or eardrum perforations.
- Hearing test (Audiometry): Assessment of hearing function to identify any hearing loss or impairment and confirm normal hearing.
- Tympanometry: Evaluation of middle ear function to detect problems like fluid buildup or eardrum perforation.
Nose examination
The nasal examination includes:
- Anterior rhinoscopy: Assessment of the nasal passages and nasal septum for signs of congestion, polyps, or structural abnormalities.
- Nasal endoscopy: A more detailed endoscopic examination. It involves using an endoscope to view deeper nasal cavity structures and sinuses. This may also be done as part of a trans-nasal endoscopy.
- Allergy testing: If indicated, tests to identify specific allergens causing nasal symptoms.
Throat examination
The throat exam primarily includes the following:
- Oral cavity inspection: Examination of the mouth and throat for signs of infection, inflammation, or abnormalities.
- Pharyngeal examination: Assessment of the pharynx for issues like pharyngitis or tonsillitis.
- Laryngoscopy: Inspection of the larynx (voice box) to evaluate the vocal cords and diagnose voice disorders.
The ENT exam is vital for diagnosing and managing conditions affecting these areas, ensuring proper function and overall health.
ENT Exam Template
ENT Exam Example
When to conduct an ENT Exam?
An ENT exam is essential for diagnosing and managing conditions affecting the ear, nose, and throat. Sure, you can have it done whenever you get a routine examination. But if you encounter any of the following issues, you should schedule an appointment immediately:
Ear pain or discharge
Persistent or severe ear pain, often described as a sharp, throbbing, or burning sensation, may indicate an infection or other ear condition. Discharge from the ear, especially if it's milky white, yellow-colored, or foul-smelling, can indicate an ear infection or a perforated eardrum.
Hearing loss
A gradual or sudden decrease in hearing ability, difficulty understanding speech, or the need to increase the volume on devices can be symptoms of hearing loss, which may result from various causes, including age, noise exposure, or ear infections.
Nasal congestion or obstruction
Chronic nasal congestion, difficulty breathing through the nose, or a sensation of blockage can indicate issues like sinusitis, allergies, or nasal polyps. Treatment may include the use of a decongestant nose spray.
Frequent nosebleeds
Recurring nosebleeds, especially if they are heavy or difficult to control, can be a sign of underlying conditions such as nasal dryness, injury, or abnormal blood vessels.
Sore throat or hoarseness
Persistent sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or a hoarse voice lasting more than two weeks can be symptoms of throat infections, acid reflux, or vocal cord issues.
Snoring or sleep apnea
Loud snoring or episodes of breathing cessation during sleep may indicate sleep apnea, a condition that requires medical attention to prevent complications.
Dizziness or balance problems
Feelings of unsteadiness, dizziness, or vertigo can be related to inner ear disorders, which play a crucial role in maintaining balance.
Sinus pressure or headaches
Chronic sinus pressure, facial pain, or headaches, especially if they worsen with bending forward or are accompanied by nasal congestion, may suggest sinusitis or other sinus problems.
Scheduling an ENT exam when experiencing these symptoms can lead to early diagnosis and effective treatment, improving overall health and quality of life.
How to use this template?
The Routine ENT Test Template is a valuable tool for health professionals conducting ear, nose, and throat examinations. Here's how to use it effectively:
Step 1: Access the template
First, access the Routine ENT Test Template through the Carepatron app. This ensures you have a standardized and comprehensive tool for documenting ENT examinations.
Step 2: Explain the template
Introduce the template to your patients and explain its purpose. It will guide the ENT examination process and help document their ear, nose, and throat health.
Step 3: Conduct the examination
Use the template as a checklist during the ENT examination. Perform each test listed, such as otoscopy, audiometry, and nasal endoscopy, and record the findings in the corresponding fields.
Step 4: Interpret the results
After completing the examination, review the findings with the patient. Explain any abnormalities or concerns and discuss the next steps, whether it be further testing, treatment, or referral to a specialist.
Step 5: Provide recommendations
Based on the examination results, offer recommendations for the patient's ENT health. This may include medication, lifestyle changes, or follow-up appointments.
Step 6: Document and share
Ensure all findings and recommendations are documented in the template. Share this information with the patient and other healthcare providers as needed for comprehensive care.
By following these steps, health professionals can effectively use the Routine ENT Test Template to assess and manage their patients' ear, nose, and throat health, ensuring a thorough and organized examination process.
Common ENT problems
Ear, nose, and throat (ENT) issues are prevalent across all age groups, impacting daily life and overall well-being. Here are some of the most frequent issues encountered in ENT practice:
- Ear infections (Otitis media): Characterized by the inflammation of the middle ear, often accompanied by fluid buildup. Symptoms include ear pain, fever, and hearing difficulties. Ear infections are particularly common in children and can result from bacterial or viral infections. Treatment may involve antibiotics or pain relievers, and in chronic cases, surgical insertion of ear tubes for drainage.
- Sinusitis: Involves the inflammation of the sinuses, leading to symptoms like nasal congestion, facial pain, and pressure headaches. Sinusitis can be acute or chronic, persisting for 12 weeks or longer. Management includes nasal decongestants, saline rinses, and antibiotics or sinus surgery to improve drainage in severe cases.
- Tonsillitis: Refers to the inflammation of the tonsils, typically caused by viral or bacterial infections. Patients may experience sore throat, difficulty swallowing, and swollen lymph nodes. Treatment options vary from home remedies and antibiotics to tonsillectomy (surgically removing the tonsils) in recurrent cases.
- Salivary gland disorders: Problems with the salivary glands can lead to dry mouth, infections, or swelling, impacting oral health and comfort.
- Thyroid disorders: Issues with the thyroid gland, located in the neck, can also fall within the realm of ENT problems, affecting metabolism and overall health.
- Allergic rhinitis (Hay fever): An allergic reaction affecting the nasal passages, triggered by allergens like pollen, dust, or pet dander. Symptoms include sneezing, nasal congestion, and itchy eyes. Management involves avoiding triggers, using antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and, in some cases, allergy shots (immunotherapy).
- Sleep apnea: As mentioned previously, sleep apnea is a good reason to get checked. Sleep apnea is a potentially serious sleep disorder characterized by repeated pauses in breathing during sleep. Common signs include loud snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning headaches. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy, and surgical procedures to open the airway.
- Hearing loss: This can be caused by factors such as aging, noise exposure, infections, or genetics. Symptoms range from difficulty understanding speech to complete hearing loss. Management includes hearing aids, cochlear implants, and preventive measures like protecting ears from loud noises.
- Voice disorders: Conditions like vocal cord nodules, polyps, or laryngitis can lead to hoarseness, voice changes, and discomfort when speaking. Treatment depends on the underlying cause and may involve voice therapy, medication, or surgery to remove lesions.
Early detection and appropriate management of these common ENT problems are crucial for maintaining optimal ear, nose, and throat health and preventing long-term complications.
Commonly asked questions
ENT stands for Ear, Nose, and Throat, and it refers to a medical specialty that deals with conditions and disorders affecting these areas of the body. ENT may also be used to refer to the specialists themselves.
An ENT exam typically includes an examination of the ear (otoscopy and hearing tests), the nose (rhinoscopy and nasal endoscopy), and the throat (oral cavity inspection, pharyngeal examination, and laryngoscopy).
An ENT specialist diagnoses conditions through physical examinations, reviewing medical history, and conducting specific tests like audiometry, endoscopy, or imaging studies.
ENT specialists treat ear infections, sinusitis, tonsillitis, allergic rhinitis, sleep apnea, hearing loss, and voice disorders.
There is no difference; an ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat) specialist is also known as an otolaryngologist. Both terms refer to the same medical specialty.