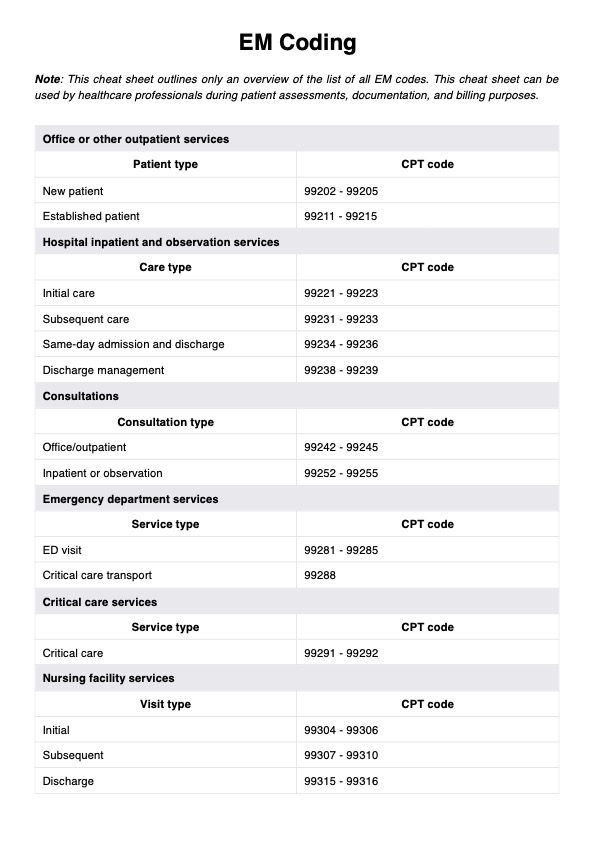
The EM code, the evaluation and management code, is used to classify patient encounters based on the complexity of healthcare professionals' evaluation and management services.
EM Coding
Learn how EM Coding supports accurate billing and documentation for evaluation and management services across outpatient, inpatient, and emergency settings.
EM Coding Template
Commonly asked questions
ED stands for Emergency Department, and refers to emergency department services in a hospital facility. EM refers to Evaluation and Management, the process of assessing and managing patient health during clinical encounters.
CPT codes identify specific medical procedures and services. EM codes, a subset of CPT, specifically classify evaluation and management encounters involving cognitive services delivered by medical service providers.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











