A specialized eating plan for dialysis helps manage potassium levels, ensures enough protein intake, and avoids certain foods that may worsen their condition. It also provides more calories or extra calories when needed to maintain energy.
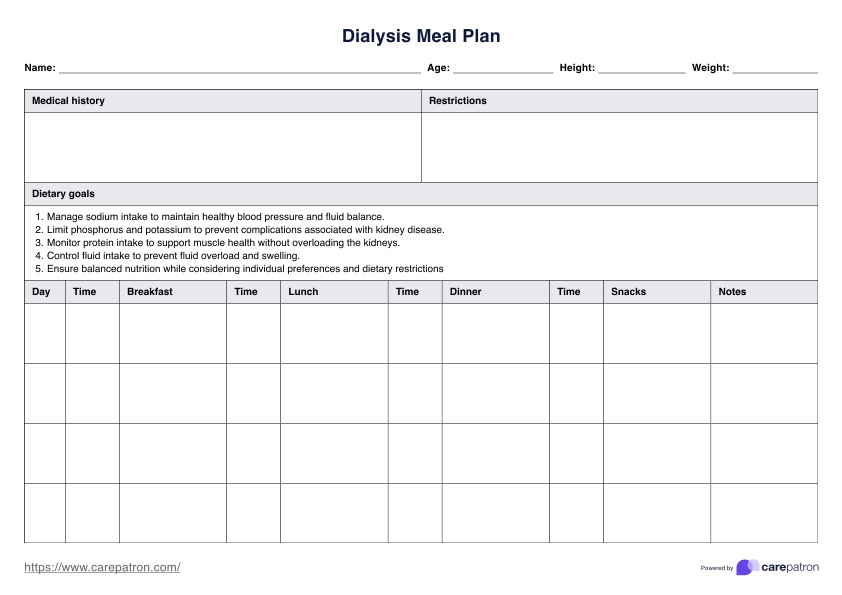
Dialysis Meal Plan
Discover a customizable Dialysis Meal Plan designed to balance potassium levels, limit sodium, and provide guidance on foods for optimal kidney health.
Dialysis Meal Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
The plan identifies foods to limit, like those high in potassium, phosphate, or extra salt, and includes alternatives such as vegetables and other foods low in these elements. It helps patients maintain potassium levels while balancing fluid intake to prevent extra fluid retention.
The flexible plan can accommodate low vision or mobility issues by incorporating simple, easy-to-prepare foods. For patients on a special diet, it can also include specific guidelines provided by their dialysis center.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











