The primary types of diabetes are type 1, type 2, and gestational diabetes. Type 1 occurs when the body produces little to no insulin, and type 2 is due to insulin resistance. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth, but it can increase the risk of developing type 2 diabetes in the future.
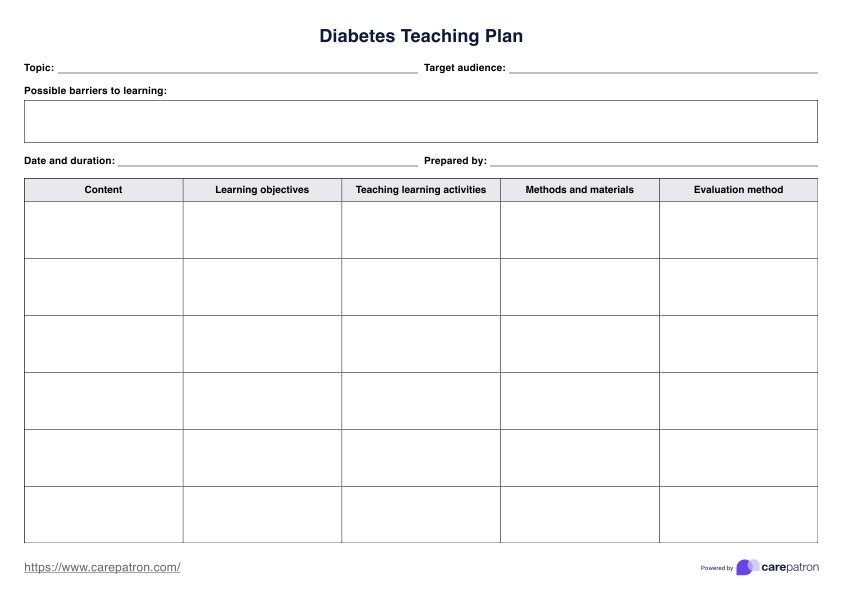
Diabetes Teaching Plan
Teach patients the essentials of diabetes with our Diabetes Teaching Plan and improve the management of this condition. Get this teaching plan template for free.
Diabetes Teaching Plan Template
Commonly asked questions
Important teaching points for diabetic patients include understanding the cause and type of diabetes, adopting healthy eating habits, monitoring blood sugar levels, managing medications, establishing exercise routines, healthy weight, and recognizing and handling complications.
Patients can effectively manage diabetes by integrating healthy lifestyle choices, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, adhering to prescribed medications, and regularly monitoring blood glucose levels.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











