Depth Perception Test
Explore our comprehensive guide to understanding depth perception and the benefits of depth perception testing in diagnostics and improving our quality of life.


What is depth perception?
Depth perception is our ability to see the world in three dimensions. It allows us to see and understand how far away objects are and accurately perceive the relative distance between objects. It works through various visual cues such as binocular vision (using both eyes), monocular vision (using one eye), motion parallax, and perspective. This ability helps us navigate our environment, judge distances, and interact with objects in everyday life.
Having accurate depth perception is important because it helps with activities of daily living, allows people to gauge their surroundings and avoid accidents, and helps people perform specific tasks required by specific professions (e.g., surgeons and their procedures, pilots and their navigation, etc.).
Understanding how a patient perceives depth and distance can help diagnose vision or brain conditions like lazy eye or injuries that could affect how well someone can judge space and distance. This understanding can also help monitor treatment. Performing assessments to test depth perception can provide insight into how to improve a patient's overall quality of life.
Depth Perception Test Template
Depth Perception Test Example
What is a Depth Perception Test?
A Depth Perception Test measures an individual's ability to perceive spatial relationships, specifically the ability to judge the distances of objects. This skill is essential for tasks requiring hand-eye coordination, precise movement, and environmental interaction. For practitioners in optometry and ophthalmology, mastering the ability to conduct and understand depth perception tests is critical.
Depth perception testing evaluates visual functioning and helps identify issues affecting normal visual function. Additionally, it can help track the progression and treatment response of such conditions.
How to use our Depth Perception Test template
The Depth Perception Test template assists healthcare providers in identifying depth perception problems. It further documents a patient's performance in standardized depth perception tests, such as stereopsis. Precisely, the healthcare provider can follow these steps:
Step 1: Gather patient information
Collect basic demographic details (age, gender, occupation). Obtain ocular and medical history. Also, note any symptoms or concerns raised by the patient.
Step 2: Perform initial depth perception testing
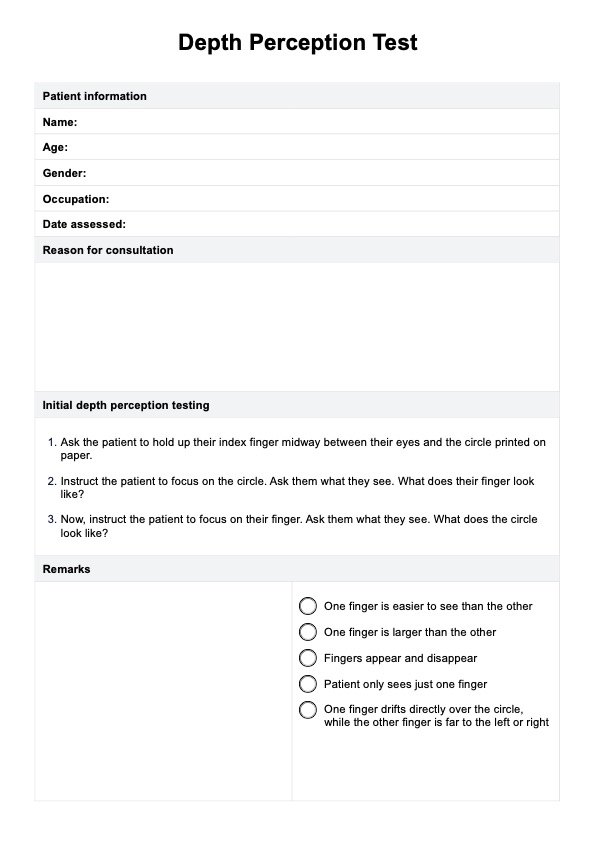
The patient should sit comfortably and hold up their index finger midway between their eyes and a circle on a test paper.
Step 3: Instruct and document observation
Instruct the patient to focus on the circle and their finger alternately. Test each eye independently by having them close one eye at a time. Observe discrepancies in the patient's perception when focusing on different points. Document if the patient reports blurry vision, double images, vision loss, or difficulty in in-depth judgment.
Step 4: Use standardized tests for in-depth analysis
There are multiple ways to test depth perception. Based on preliminary findings, select suitable and available standardized tests, such as stereopsis tests (which sometimes use special glasses called a stereoscope), Titmus fly, or Frisby test. Administer these tests following their specific guidelines. Ensure the patient is comfortable and understands each test process, especially if they have to look at a specific picture and then a different picture to discern differences in perception.
Evaluating the results of Depth Perception Tests
Interpreting the results of Depth Perception Tests is a structured, attentive process that requires understanding the patient's context, carefully evaluating each testing stage, and informed decision-making for further steps. Here's a step-by-step guide to interpreting test results:
Step 1: Review patient information
Start by reviewing the demographic details and medical history collected. Aside from aiding in understanding the patient's profile, these details provide essential context for interpreting the test results. For instance, aging might affect depth perception, as can certain medical conditions and medications.
Step 2: Analyze the initial depth perception test
Examine the observations made during the initial depth perception test. Successful depth perception should allow the patient to accurately judge the distance between their finger and the circle on the test paper. Difficulty in performing this task, especially when one eye is closed, may indicate a problem with depth perception.
Step 3: Evaluate standardized test results
Each standardized test has its scoring methodology. For instance, Stereopsis Tests usually measure the smallest disparity the patient can see, recorded in seconds of arc. Lower values typically denote good depth perception. Therefore, it is essential to understand the specific evaluation matrix for every test conducted.
Step 4: Review all findings and determine the next steps
Finally, all test results and documented observations will be examined together. Take note of any unusual or inconsistent results and identify if there is a potential trend indicating poor depth perception.
Benefits of Depth Perception Tests
As healthcare practitioners, it is crucial to understand the far-reaching implications of depth perception and how assessing it accurately can significantly enhance the overall well-being and quality of life of our patients.
Accurate diagnosis
Possibly the most valuable benefit is the test's ability to detect potential underlying vision disorders. Depth perception complications may be an early sign of strabismus (crossed eyes), amblyopia (lazy eye), or ocular nerve palsy. The test aids in detecting these issues early, allowing earlier interventions to improve depth perception.
Improving quality of life
Testing depth perception can help improve a patient's daily life. Depth perception is essential to everyday tasks like reading, operating home appliances, working, and driving safely. This has implications for a patient's independence and safety.
Better eye care
Regular Depth Perception Tests reinforce comprehensive eye care. They supplement routine eye examinations, promoting early detection and treatment of visual concerns and complications.
A clearer understanding of ocular health
The benefits extend to patients, who can more profoundly and clearly understand their ocular health. Based on test findings and follow-ups, they can make well-informed lifestyle choices, supporting their efforts to preserve eye health.
Commonly asked questions
Yes, it is possible to lose depth perception. This may be due to amblyopia, strabismus, or vision loss in one eye. Head trauma, neurological disorders, and certain eye surgeries can also affect depth perception. However, treating and restoring depth perception through various methods is possible. These may include the use of glasses, surgery, and vision therapy.
Testing for depth perception should be a component of a standard comprehensive eye exam, mainly if there are signs of potential depth perception issues. Individuals should undergo depth perception tests during regular eye exams if they are experiencing symptoms such as difficulty with hand-eye coordination and misjudging distances, if they are experiencing an eye condition or injury, and for developmental checks in children.
Eye care professionals, including optometrists, ophthalmologists, and orthoptists, primarily administer depth perception tests. Patients should seek professional help and not rely on online tests for depth perception.