COPD System Disorder
Utilize this in-depth guide to create an effective COPD system disorder template to elevate care and education around this prevalent respiratory disorder.


What is chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)?
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is a chronic lung disease marked by persistent airflow obstruction that impairs normal breathing (World Health Organization, 2024). It primarily results from prolonged exposure to lung irritants such as cigarette smoke, air pollution, and occupational hazards.
COPD encompasses two main conditions: chronic bronchitis, which involves long-term inflammation of the airways and mucus overproduction, and emphysema, where the tiny air sacs in the lungs (alveoli) are damaged, reducing oxygen exchange (Kim & Griner, 2013). Chronic obstructive lung disease develops gradually, with structural changes to lung tissue and airway narrowing over time. Key risk factors include smoking, repeated respiratory infections, and exposure to harmful substances. COPD is progressive and irreversible but manageable with appropriate interventions.
Symptoms
COPD symptoms develop slowly and often begin with mild symptoms mistaken for a cold. Early signs include a chronic cough, occasional shortness of breath after exercise, and frequent throat clearing (American Lung Association, 2023). Patients may experience breathlessness, a persistent cough with phlegm, recurrent respiratory infections, and wheezing as chronic obstructive lung disease progresses.
Severe COPD presents with significant shortness of breath even at rest, fatigue, weight loss, and swollen ankles (NHS, 2023). Exacerbations triggered by air pollution, cold air, or infections can lead to sudden symptom worsening, requiring prompt medical attention from healthcare providers.
Treatment
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease treatment aims to relieve symptoms, improve quality of life, and slow disease progression (NHS, 2013). Smoking cessation and avoiding lung irritants are essential steps. Medications such as bronchodilators, corticosteroids, and antibiotics manage exacerbations and chronic symptoms.
Oxygen therapy is prescribed for advanced cases with low blood oxygen levels (Ernstmeyer & Christman, 2021). Pulmonary rehabilitation programs provide exercise training, nutrition advice, and disease management education. For severe COPD, surgical options like lung volume reduction or transplantation may be considered (Patel et al., 2008). Vaccinations help prevent respiratory infections, reducing flare-ups during the cold and flu season.
Diagnosis
Healthcare providers comprehensively diagnose chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, 2022). Evaluation begins with a physical examination and review of the patient’s health history, focusing on chronic cough, breathlessness, and exposure to risk factors like smoking and air pollution. Spirometry is the primary diagnostic test (Johns et al., 2014), measuring airflow obstruction and determining COPD severity.
Additional tests, including chest X-rays and CT scans, assess lung tissue damage, while blood tests and arterial blood gases evaluate oxygen levels. Early detection and accurate diagnosis are crucial for effective disease management and timely treatment.
COPD System Disorder Template
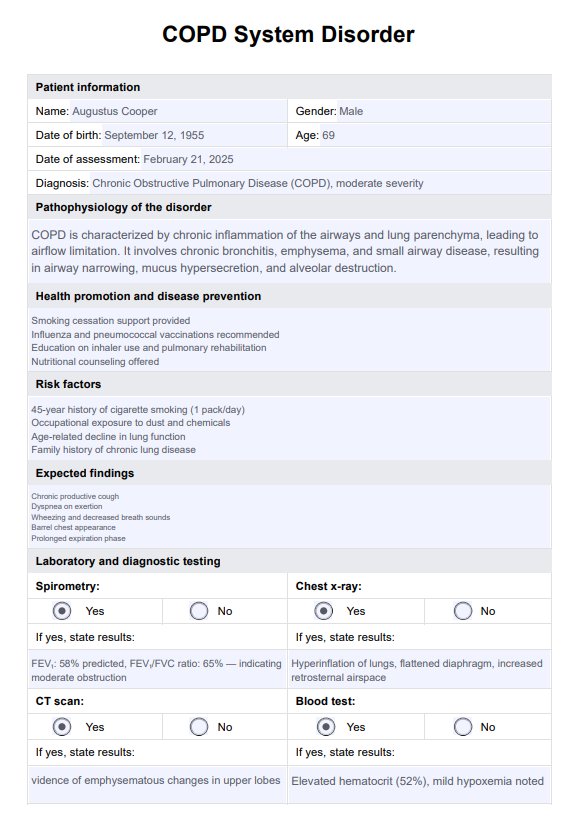
COPD System Disorder Example
How does our COPD System Disorder Template work
Carepatron’s COPD System Disorder Template streamlines patient assessments, making it easier for healthcare providers to document clinical findings and manage care efficiently. By following the steps below, medical professionals can quickly access and utilize the template within Carepatron’s platform, enhancing workflow while ensuring comprehensive patient evaluations.
Step 1: Access the template
Click the "Use template" button to get started. You’ll be directed to Carepatron’s app download to immediately access the COPD System Disorder Template. This saves time, allowing you to seamlessly integrate patient assessments into your existing workflow without additional setup.
Step 2: Introduce the template to the patient
During consultations, explain how the COPD System Disorder Template helps document essential clinical information while guiding accurate diagnosis and treatment planning. While patient education is secondary, transparency builds trust, allowing patients to understand the structured approach used to manage their chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Step 3: Use the template in patient assessment
Utilize the template to record vital information such as patient history, risk factors, and examination findings. Sections for spirometry results, diagnostic tests, and medication plans ensure nothing is overlooked. This structured format enables thorough assessments, promotes consistency, and facilitates better clinical decisions for managing COPD.
Step 4: Provide additional patient education and next steps
After completing the assessment, use the template to guide patient discussions on disease management, lifestyle modifications, and follow-up care. Clear documentation of the next steps, including referrals to pulmonary rehabilitation or adjustments to treatment plans, helps ensure comprehensive and coordinated care for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Benefits of using this template
The COPD System Disorder Template streamlines clinical workflows by providing a structured format for documenting patient assessments, enabling healthcare professionals to treat COPD more efficiently. It ensures that critical information, such as typical symptoms like trouble breathing, difficulty breathing, and lung function decline, is consistently recorded. By covering essential details—patient history, exposure to environmental factors, genetic factors, and spirometry results—the template helps identify patients at risk of developing COPD or those with mild COPD who require early intervention.
Including sections for medication schedules reduces prescribing errors and improves treatment adherence. Documenting test results, such as arterial blood gases, enables monitoring of carbon dioxide levels and guides oxygen therapy decisions. The template’s comprehensive nature aids in recognizing disease progression and potential complications, including lung cancer and lung damage from chronic inflammation.
Addressing the destruction of small air sacs and airflow obstruction early supports better long-term outcomes. It ensures that healthcare professionals provide consistent, effective care while saving time during patient evaluations.
References
American Lung Association. (2023, April 28). COPD symptoms. https://www.lung.org/lung-health-diseases/lung-disease-lookup/copd/symptoms-diagnosis/symptoms
Ernstmeyer, K., & Christman, E. (2021). Oxygen therapy. National Library of Medicine; Chippewa Valley Technical College. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK593208/
Johns, D. P., Walters, J. A. E., & Walters, E. H. (2014). Diagnosis and early detection of COPD using spirometry. Journal of Thoracic Disease, 6(11), 1557–1569. https://doi.org/10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.08.18
Kim, V., & Criner, G. J. (2013). Chronic bronchitis and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine, 187(3), 228–237. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201210-1843ci
National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. (2022). COPD - diagnosis. https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health/copd/diagnosis
NHS. (2023, April 11). Symptoms - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-copd/symptoms/
NHS. (2023, April 11). Treatment - chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-copd/treatment/
Patel, N., DeCamp, M., & Criner, G. J. (2008). Lung transplantation and lung volume reduction surgery versus transplantation in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Proceedings of the American Thoracic Society, 5(4), 447–453. https://doi.org/10.1513/pats.200707-107ET
World Health Organization. (2024, November 6). Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd)
Commonly asked questions
While chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) is irreversible and lung tissue cannot regenerate, treatments can improve lung function, relieve symptoms, and slow disease progression. Lifestyle changes, medications, and pulmonary rehabilitation help patients manage the condition effectively.
Individuals with severe or very severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) (Stages 3 and 4) that significantly impair daily activities may qualify for disability benefits. Eligibility depends on documented breathing tests, frequent exacerbations, and limitations in work capacity.
With proper disease management, including medications, lifestyle adjustments, and pulmonary rehabilitation, individuals with mild to moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) can maintain an active, fulfilling life. Early intervention and adherence to treatment plans are crucial for preserving quality of life.
A person with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) often experiences trouble breathing, persistent coughing, fatigue, and chest tightness. Symptoms can worsen during physical activity or flare-ups, causing increased discomfort and breathlessness.