Antipsychotic Sedation Chart
Discover the essential functions of modern antipsychotic drugs, sedation charts, the benefits of medications, and how Carepatron enhances mental health treatment.


What are antipsychotics?
Antipsychotics, also known as neuroleptics, are a class of medication primarily used to manage psychosis in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and other settings such as acute agitation. These drugs can be classified into two main categories: typical (first-generation) and atypical (second-generation) antipsychotics.
Antipsychotic Sedation Chart Template
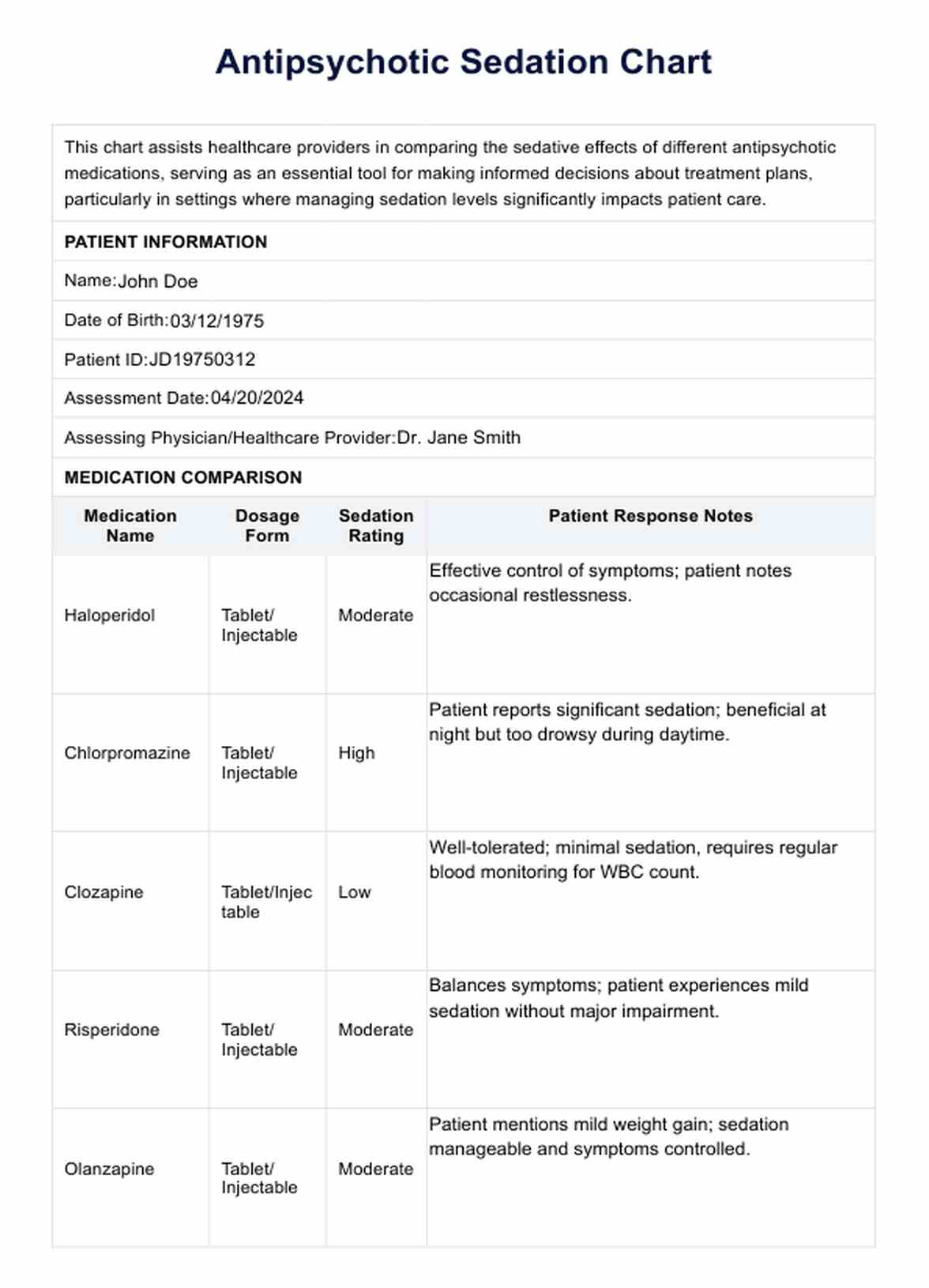
Antipsychotic Sedation Chart Example
Examples of antipsychotic drugs
Antipsychotic medications are divided into two main categories: typical or first-generation antipsychotics and atypical or second-generation antipsychotics. Each category has distinct characteristics and drug examples.
Typical antipsychotics
- Haloperidol: Haloperidol is widely used for its effectiveness in reducing acute psychotic symptoms and for its use in long-term treatment to prevent relapse. However, it carries a higher risk of causing extrapyramidal side effects, such as tardive dyskinesia and parkinsonism.
- Chlorpromazine: Known for its pioneering role in the treatment of psychosis, chlorpromazine is effective in managing symptoms like hallucinations and delusions but has notable sedative effects and a high risk of extrapyramidal symptoms.
Atypical antipsychotics
- Clozapine: Clozapine is considered one of the most effective antipsychotics, especially for treatment-resistant schizophrenia. It has a lower risk of extrapyramidal side effects but requires regular monitoring due to a potential risk of agranulocytosis, which is a serious decrease in white blood cell count.
- Risperidone: Risperidone is commonly used due to its balanced efficacy in treating both positive and negative symptoms of schizophrenia. It has a lower tendency than typical antipsychotics to cause motor side effects but can lead to metabolic issues like weight gain.
- Olanzapine: Similar to risperidone, olanzapine is effective against a wide range of psychotic symptoms and is associated with weight gain and metabolic changes, which need to be managed through lifestyle interventions and medical monitoring.
Atypical antipsychotic drugs are generally preferred over typical antipsychotics because of their lower risk of extrapyramidal side effects, making them more suitable for long-term treatment. They are also more likely to improve cognitive impairments associated with psychotic disorders, a key advantage given the cognitive challenges often faced by patients with schizophrenia and similar conditions. However, they do require careful metabolic monitoring to manage side effects like weight gain, diabetes, and cholesterol changes.
What is an Antipsychotic Sedation Chart?
An Antipsychotic Sedation Chart is a tool used by healthcare providers to track and compare the sedative effects of various antipsychotic medications. It helps in choosing the appropriate antipsychotic based on the patient's needs and the sedative profile of the medication.
What information does it convey, and how?
The chart typically lists antipsychotic medications alongside a scale or rating system that indicates their potential to cause sedation. It may include details such as dose-dependent sedation levels, time to onset of sedation, and duration of effect.
When is this chart used?
This chart is particularly useful in settings where managing a patient’s arousal level is crucial. This includes treating acute psychosis or agitation in elderly patients or avoiding excessive sedation in young patients who require less impairment, such as those in rehabilitation settings.
How does our Antipsychotic Sedation Chart template work?
Our printable Antipsychotic Sedation Chart template provides a structured format to document and visualize the sedative effects of different antipsychotics. Here's how you can make the most of it:
Step 1: Download the template
Start with our Antipsychotic Sedation Chart template. This template is specifically designed to assist healthcare professionals in monitoring and comparing the sedative effects of various antipsychotic medications effectively.
Step 2: Input medication details
The template includes designated fields for entering the names of the antipsychotic medications you are evaluating. You can also input different available dosage forms for each medication, which helps tailor treatment plans to patient-specific needs.
Step 3: Record sedation ratings
The template provides a scale or section for recording each antipsychotic drug's sedation rating. These ratings help clinicians understand each medication's potential sedative impact, which is crucial for managing patients with significant sedation levels.
Step 4: Note patient responses
There is a section to jot down notes on how each patient responds to different antipsychotic medications. Observing and recording patient responses can guide therapy adjustments to achieve optimal outcomes with minimal side effects.
Step 5: Simplify decision-making
By organizing and visualizing data on antipsychotic medications' sedative effects, the template simplifies the decision-making process for healthcare providers. This structured approach ensures that choices are based on comprehensive data, enhancing the precision of treatment plans.
Step 6: Review and adjust
The final step involves reviewing the collected information periodically and making necessary adjustments to the treatment plans based on ongoing patient responses and emerging clinical evidence. This dynamic approach helps maintain the treatment's effectiveness while minimizing adverse effects.
By using our Antipsychotic Sedation Chart template, healthcare providers can ensure a more informed, systematic, and responsive approach to antipsychotic medication management, ultimately improving patient care in clinical settings.
Benefits of using antipsychotic medications
Antipsychotic medications are crucial for managing various psychiatric disorders by reducing or eliminating psychotic symptoms, such as delusions, hallucinations, and disorganized thinking. These benefits can dramatically improve the quality of life for individuals suffering from conditions like schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
Reduction of symptoms
Antipsychotics work by altering the balance of neurotransmitters in the brain, which helps to decrease the intensity and frequency of psychotic episodes. This reduction in symptoms allows patients to function more effectively in their daily lives and engage more fully with their communities.
Prevention of relapses
Regular use of antipsychotic medications can help prevent relapses, reducing the need for hospitalization. Stabilizing the patient's condition in the long term through continuous medication adherence is key to maintaining their health and reducing the overall costs associated with acute psychiatric care.
Support in psychiatric rehabilitation
Antipsychotic medications are often a foundational part of psychiatric rehabilitation programs. They enable patients to participate more actively in various therapeutic activities and support services, including psychotherapy, community engagement, and skills training to improve their independence and social functioning.
Improvement in additional areas
Beyond the primary symptoms of psychosis, antipsychotics can also help alleviate secondary symptoms such as anxiety, depression, and severe agitation, which are often associated with psychotic disorders. By addressing these symptoms, antipsychotics contribute to a more comprehensive treatment approach, enhancing overall mental health stability.
Enabling a structured life
By mitigating the symptoms of severe psychiatric conditions, antipsychotic medications help younger patients establish a more structured routine, attend school or work, and maintain personal relationships, all of which are vital for social integration and personal fulfillment.
Overall, the therapeutic use of antipsychotic medications is a key component in the management of severe mental health disorders, contributing significantly to patient stability, societal participation, and overall well-being.
Other examples of antipsychotic treatment
Antipsychotic medications are versatile in their application, extending far beyond the treatment of classic psychotic disorders such as schizophrenia. These drugs play a critical role in several other mental health conditions, demonstrating their broad therapeutic potential.
- Bipolar disorder: In the management of bipolar disorder, antipsychotics are particularly useful during manic phases, where they help to stabilize mood and reduce symptoms such as hyperactivity, elevated mood, and impaired judgment. They may also be used during depressive episodes in combination with mood stabilizers to enhance the overall treatment effect.
- Major depressive disorder: For individuals suffering from major depressive disorder, especially those who do not fully respond to traditional antidepressants, antipsychotics can be added as an adjunct therapy. This combination is often more effective in alleviating depressive symptoms, particularly in cases of treatment-resistant depression.
- Severe anxiety and agitation: Antipsychotics are sometimes prescribed for severe cases of anxiety and agitation, where other medications might not be effective. They help reduce the intensity of anxiety symptoms and manage agitation, providing relief in acute situations.
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD): In cases where OCD symptoms are particularly severe or resistant to first-line treatments such as SSRIs, antipsychotics may be used as an adjunctive treatment to enhance the efficacy of other medications.
- Tourette syndrome and severe tics: Antipsychotics can be effective in reducing the frequency and severity of tics associated with Tourette Syndrome and other tic disorders. Their use is often considered when tics significantly interfere with daily functioning or cause social distress.
- Behavioral disorders in children and adolescents: While cautiously prescribed, antipsychotics may be used to manage severe behavioral issues and mood dysregulation in younger populations, particularly when other interventions have failed to yield sufficient improvement.
These applications highlight the adaptability of antipsychotics in the field of psychiatry, where they offer significant benefits across a spectrum of conditions, enhancing the quality of life for many patients. As with any medication, the use of antipsychotics must be closely monitored by healthcare professionals to optimize outcomes and minimize potential side effects.
Commonly asked questions
Considerations include the patient’s age, overall health, treatment setting, potential for cognitive impairment, and the need for a sedative to manage their symptoms.
Sedation must be considered because it can significantly affect a patient's quality of life and daily functioning. Managing sedation is especially important in patients who need to maintain alertness for daily activities or those who may be at risk of falls or other injuries due to excessive sedation.
While the sedation chart is a valuable tool, it must be adapted or interpreted cautiously across different patient demographics, such as the elderly, children, or those with co-existing medical conditions, due to varying sensitivities and metabolic capacities.
For patients who are particularly sensitive to sedation, it's important to choose antipsychotics with lower sedative ratings and to start with lower doses, gradually adjusting as needed based on the patient's response and tolerance.
Healthcare providers assess the accuracy by comparing the chart’s ratings with observed patient responses and side effects during treatment. Patients' sedation level feedback also plays a crucial role in validating and adjusting the ratings.

.jpg)