Thoracic back pain is less joint than lower back pain due to the stability provided by the rib cage and reduced mobility of the thoracic spine. However, it still affects many people, particularly those in sedentary occupations or with poor postural habits.
Thoracic Back Pain Red Flags Checklist
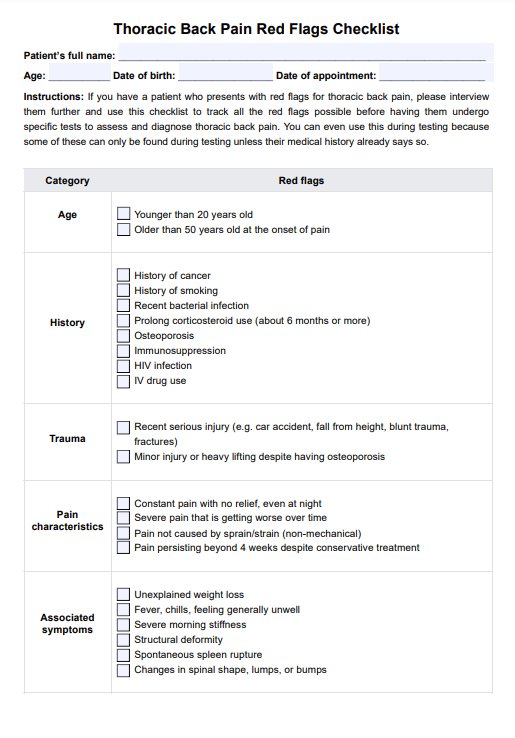
Understanding thoracic back pain: its causes, potential consequences, and red flags. Learn how to recognize symptoms with our Thoracic Back Pain Red Flags Checklist.
Thoracic Back Pain Red Flags Checklist Template
Commonly asked questions
The duration can vary widely based on the underlying cause. Acute episodes might resolve within a few weeks with proper treatment, whereas chronic conditions might result in persistent or recurring pain.
Yes, specific exercises designed to strengthen the back, improve flexibility, and enhance core stability can effectively manage and reduce thoracic back pain. It's important to consult with a physical therapist or healthcare provider to get a tailored exercise regimen that's safe and effective for your specific condition.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











