Average stereopsis results typically range from 40 to 60 seconds of arc, indicating the ability to perceive depth accurately within a specific range of vision.
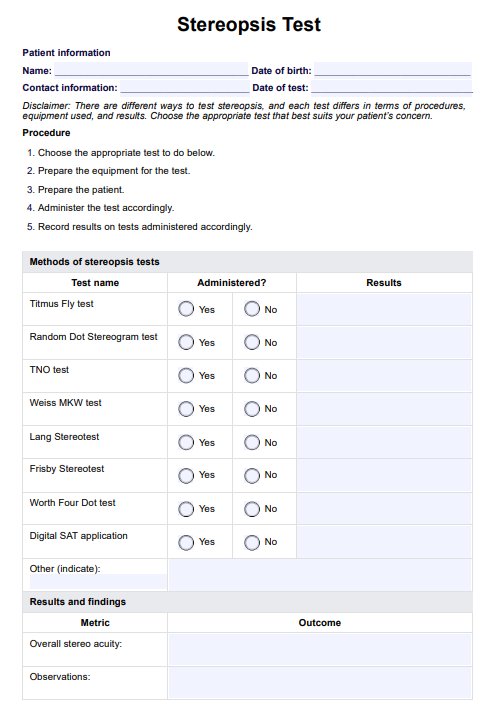
Stereopsis Test
Stereopsis Test: Assess depth perception with our innovative tool. Accurate, easy, and essential for evaluating binocular vision. Try it today!
Stereopsis Test Template
Commonly asked questions
Stereopsis is evaluated through tests that require the patient to use binocular vision to perceive depth, often involving the identification of disparities between images or objects presented in a controlled setting.
Stereopsis, or depth perception, refers to the ability of the eyes to perceive depth and three-dimensional objects by combining slightly different images from each eye, which allows the brain to interpret spatial relationships.
EHR and practice management software
Get started for free
*No credit card required
Free
$0/usd
Unlimited clients
Telehealth
1GB of storage
Client portal text
Automated billing and online payments











