Sacroiliac Distraction Test
Explore our comprehensive guide on the Sacroiliac Distraction Test, a crucial tool for diagnosing lower back pain and guiding treatment strategies.


What are sacroiliac sprains and dysfunctions?
Sacroiliac sprains and dysfunctions involve the impairment or injury of the sacroiliac joints, which link the spine to the pelvis. These conditions can result from acute trauma or chronic stress affecting these joints. Sacroiliac dysfunctions can disrupt the normal movement mechanics of the pelvis and spine, leading to pain and reduced mobility.
Common symptoms of such sprains and dysfunctions
Symptoms of sacroiliac joint (SIJ) dysfunction typically include:
- Lower back pain that can extend to the hips and legs
- Pain that worsens with standing or moving from sitting to standing
- Stiffness or a burning sensation in the pelvis
- Instability in the pelvis and lower back, feeling as if the legs might buckle
What are their causes?
The causes of a painful sacroiliac joint are varied, often involving a mix of physical stress and biological changes:
- Physical trauma: Traumatic events such as falls, vehicle accidents, or any direct impact on the lower back or pelvis can lead to sacroiliac joint dysfunction. These incidents can disrupt the normal alignment and function of the sacroiliac joints, resulting in pain and limited mobility.
- Repetitive stress: Regular engagement in activities that place continuous pressure on the sacroiliac joints—such as jogging, stair climbing, or extensive periods of standing—can precipitate sacroiliac joint dysfunction. These activities stress the joints and surrounding ligaments, potentially leading to inflammation and pain.
- Pregnancy: During pregnancy, the body undergoes significant hormonal changes that relax ligaments to prepare for childbirth. These changes and increased body weight can strain the sacroiliac joints, increasing the risk of sprains and dysfunctions.
- Arthritis: Osteoarthritis and other degenerative joint diseases can degrade the cartilage in the sacroiliac joints, leading to pain and stiffness. The bones may rub together as the protective cartilage wears down, causing further discomfort and joint damage.
Incorporating sacroiliac pain provocation tests and specific sacroiliac joint tests into a diagnostic routine can help pinpoint the exact cause of symptoms, guiding more effective treatment strategies.
Sacroiliac Distraction Test Template
Sacroiliac Distraction Test Example
What is the Sacroiliac Distraction Test?
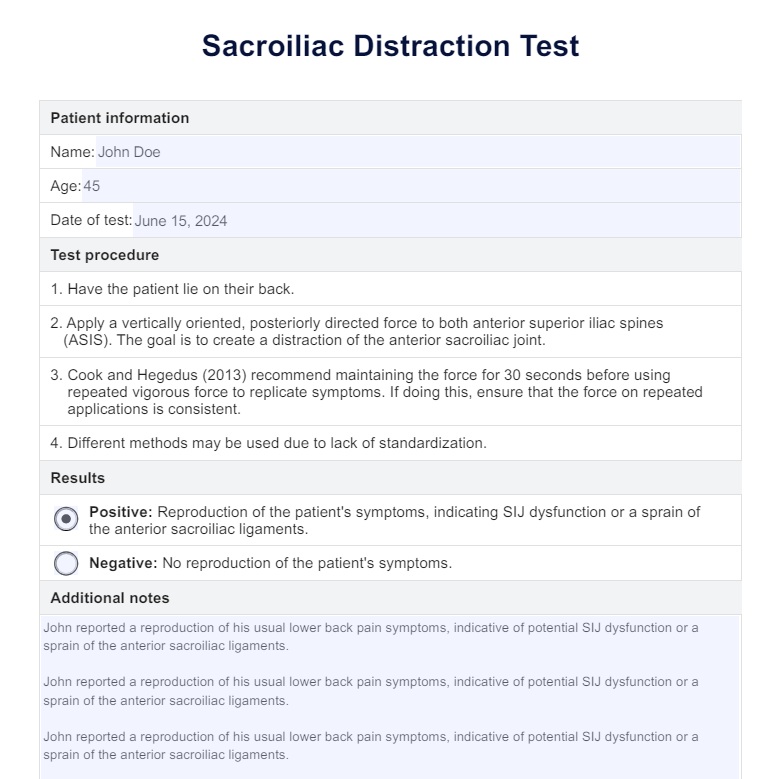
The Sacroiliac Distraction Test, or the pelvic compression test, is an orthopedic physical examination test used by healthcare professionals for diagnosing painful sacroiliac joints, particularly in individuals experiencing lower back pain. This test assesses the pain provocation and stability of the sacroiliac joints.
How is it conducted?
The patient lies on their back on an examination table. The healthcare provider stands beside the patient. The examiner places their hands on the anterior superior iliac spines (ASIS) — the prominent bones at the front of the pelvis. They then apply downward and outward pressure, effectively 'distracting' or pulling the pelvis apart. During the pressure application, the clinician observes the patient's reaction for any signs of pain or discomfort, which indicates sacroiliac joint dysfunction.
How are the results interpreted?
A positive result is indicated if the patient experiences pain in the sacroiliac joints during the test. This suggests potential sacroiliac joint dysfunction or related pathology. A negative result, where no pain is elicited, indicates that the sacroiliac joints are not the source of pain.
How to use our Sacroiliac Distraction Test template
To effectively use the Sacroiliac Distraction Test template in your clinical practice, follow these steps:
- Download the Sacroiliac Distraction Test template via the Carepatron app or from our resource library.
- Fill in the patient details and follow the procedure in the template. Apply consistent pressure across the sacroiliac joints while the patient is lying down.
- Record any signs of pain or discomfort as the patient indicates, noting the areas affected.
- Use the observations noted in the template. Pain elicitation means a positive test result, while no pain means negative.
Based on the results, decide on further diagnostic tests (like the sacroiliac joint double block) or begin treatment if necessary.
Benefits of conducting this test
Our free Sacroiliac Distraction Test is an invaluable diagnostic tool for clinicians addressing lower back pain related to sacroiliac joint dysfunction. Here’s a brief overview of its benefits:
Diagnosing the source of pain
This test helps clinicians accurately pinpoint the cause of lower back pain by assessing the sacroiliac joints. A positive test suggests that the sacroiliac joint may be the source of discomfort, enabling targeted treatment.
Guiding treatment
Based on the test outcomes, healthcare providers can devise appropriate treatment strategies. These may range from physical therapy to strengthen surrounding muscles to interventions to reduce inflammation or surgical options for severe cases. The test's results directly influence treatment decisions, ensuring patients receive the most appropriate care tailored to their needs.
The Sacroiliac Distraction Test is crucial in diagnosing and managing sacroiliac joint issues, facilitating better health outcomes through more precise and focused treatment approaches.
Treatments for sacroiliac sprains and dysfunctions
Effective management of sacroiliac sprains and dysfunctions may include:
- Physical therapy: Targeted exercises to stabilize the sacroiliac joints, improve pelvic alignment, and enhance muscular support around the spine and pelvis.
- Medication and injections: Anti-inflammatory drugs or muscle relaxants to reduce inflammation and pain. Corticosteroid injections can be used for severe cases.
- Manual therapy: Techniques such as adjustments or manipulations to decrease pain and increase function.
- Supports or bracing: Use pelvic belts or braces to stabilize the sacroiliac joints and relieve pain.
- Surgery: In cases where conservative treatments fail, surgical options such as fusion of the sacroiliac joints may be considered to stabilize the joints and relieve persistent pain.
Each component in our outline aims to equip healthcare professionals with practical tools and knowledge to assess, diagnose, and treat sacroiliac joint dysfunctions effectively, using the Sacroiliac Distraction Test as a fundamental diagnostic tool.
Is this test reliable?
The Sacroiliac Distraction Test has shown varying levels of reliability and validity across different studies. Cook and Hegedus (2013) report that the test has a reasonable specificity and inter-rater reliability, making it a useful tool in assessing SIJ dysfunction, especially in pregnant women. However, the lack of a standardized technique has led to differences in how practitioners perform the test, contributing to variability in responses and lowering inter-tester reliability. This inconsistency is a significant factor that affects the overall reliability of the test.
Further research and reviews suggest that while the Sacroiliac Distraction Test can be a valuable diagnostic tool, it is most effective when used as part of a cluster of tests rather than in isolation. Studies, including those by Laslett et al. (2005) and van der Wurff et al. (2000), indicate that the test's reliability and sensitivity improve significantly when combined with other SIJ tests. This cluster approach enhances the diagnostic accuracy and helps confirm hypotheses regarding SIJ dysfunction, making the test a reliable component of a comprehensive assessment strategy.
References
Cook, C., & Hegedus, E. J. (2014). Orthopedic physical examination tests: An evidence-based approach. Pearson Education Limited.
Laslett, M., Aprill, C. N., McDonald, B., & Young, S. B. (2005). Diagnosis of sacroiliac joint pain: Validity of individual provocation tests and composites of tests. Manual Therapy, 10(3), 207–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.math.2005.01.003
van der Wurff, P., Meyne, W., & Hagmeijer, R. H. M. (2000). Clinical tests of the sacroiliac joint. Manual Therapy, 5(2), 89–96. https://doi.org/10.1054/math.1999.0229
Commonly asked questions
Individual provocation tests, such as the Sacroiliac Distraction Test or the compression test, are critical in diagnosing sacroiliac joint pain. These tests apply specific stress to the sacroiliac joints to identify discomfort and help pinpoint the source of pain, enhancing diagnostic accuracy.
Physical therapists use sacroiliac provocation tests to assess pain response and joint functionality. These tests, including manual compression and distraction tests, help evaluate the integrity of the sacroiliac joints and guide treatment planning for patients with lower back and buttock pain.
MRI can significantly enhance the diagnosis of sacroiliac joint pathology by providing detailed images of the joint's structure. It helps detect inflammation, degeneration, or other abnormalities that might not be evident through physical examination alone.

.jpg)