Risk for Injury Care Plan
Download Carepatron's free PDF example of a risk-for-injury care plan to help assess and manage potential risks and prevent injury.


What does it mean for a person to be at risk for injury?
Being at risk for injury signifies an individual's heightened susceptibility to harm due to various factors. In clinical practice, healthcare providers conduct thorough nursing assessments to identify such risks, utilizing nursing diagnoses to categorize them effectively. These assessments encompass many safety assessments, including patient safety, environmental hazards, and fall risk factors.
Key elements in the nursing process of assessing the patient's risk of injury involve evaluating their mental status, identifying potential safety measures, and determining the patient's need for assistive devices. By understanding the patient's fall risk and implementing appropriate nursing interventions, healthcare professionals aim to mitigate potential harm and enhance patient safety.
Factors that make a person at risk for injury
Identifying factors contributing to an individual's risk for injury is crucial for effective nursing care. Below are key risk factors to have healthcare facilities consider:
- Impaired mobility: Limited mobility due to age, injury, or illness increases the risk of falls and other injuries.
- Medication side effects: Certain medications can cause dizziness, drowsiness, or impaired judgment, elevating the risk of accidents.
- Cognitive impairment: Conditions such as dementia or delirium can affect decision-making and awareness of hazards.
- Environmental hazards: Poor lighting, slippery floors, and cluttered pathways pose significant risks, especially for older adults.
- History of falls: Previous falls indicate an increased risk of future incidents and require proactive fall prevention strategies.
- Muscle weakness: Weakness in muscles, especially in the lower extremities, compromises balance and stability.
- Vision impairment: Poor eyesight or vision loss impairs depth perception and awareness of surroundings, leading to accidents.
- Chronic conditions: Conditions like diabetes or Parkinson's disease may affect coordination and increase the risk of falls.
Risk for Injury Care Plan Template
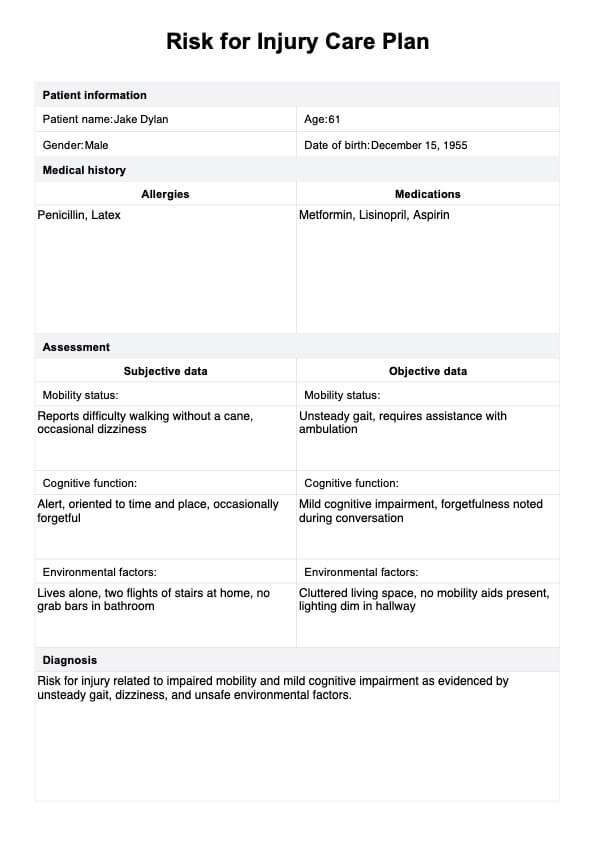
Risk for Injury Care Plan Example
What is a Risk for Injury Care Plan?
A Risk for Injury Care Plan can identify and mitigate factors that increase a patient's susceptibility to harm, ensuring their safety and promoting functional and independent living. It involves systematic assessments, nursing diagnoses, interventions and more to address specific risks such as muscle and bone injury or falls in an unfamiliar environment.
The plan should be thorough and adhere to the nursing profession’s moral and legal obligation to protect patients. By implementing tailored interventions, healthcare professionals aim to help patients remain free from injury and enhance overall safety.
Goals of a Risk for Injury Care Plan
A risk-for-injury care plan outlines the objectives and strategies to minimize the risk of injury and ensure patient safety. The goals of such a risk diagnosis and care plan include:
- Preventing falls: Implement measures to reduce the risk of falls, such as providing assistive devices and modifying the environment.
- Minimizing medication-related risks: Monitor medication use closely to prevent adverse effects that may increase the risk of injury.
- Promoting mobility and independence: Encourage activities that improve strength, balance, and coordination to enhance mobility and independence. This includes physical therapy and other forms of exercises.
- Addressing eco hazards: Identify and eliminate potential hazards in the patient's surroundings to create a safe environment.
- Educating patients and caregivers: Provide education on fall prevention strategies, medication management, and safety measures to empower patients and caregivers.
How to use our Risk for Injury Care Plan Template
Here's how to use our simple and printable template:
Comprehensive assessment
Healthcare professionals conduct thorough assessments to identify risk factors and evaluate the patient's overall condition. This includes examining aspects such as mobility, cognitive function, medication use, medical history, and environmental factors.
Formulating diagnoses
Based on clinical assessment and on the assessment findings, healthcare professionals create diagnoses to categorize the patient's injury risk. Common diagnoses related to injury risk include "risk for falls" and "risk for traumatic brain injury."
Set goals and expected outcomes
After assessment and diagnosis, healthcare professionals work with the patient to set realistic goals and outcomes for reducing their risk of injury. These goals may include improving balance and strength, increasing awareness of potential hazards in their environment, or managing medications more effectively.
Implementing interventions and rationales
Tailored interventions are developed and applied to address identified risk factors and enhance patient safety. Rationales for interventions may include reducing environmental hazards, improving medication management, providing assistive devices, or implementing exercise programs.
Ongoing monitoring and evaluation
Continuous monitoring and evaluation are crucial to assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust the care plan as needed. Healthcare professionals work closely with the patient and the interdisciplinary team to ensure appropriate measures are in place to promote safety and prevent injuries.
Benefits of having this type of care plan
Implementing a Risk for Injury Care Plan offers numerous benefits for patients and healthcare providers. Below are the key advantages of utilizing this type of care plan:
Enhanced patient safety
Risk for Injury Care Plans are specifically tailored to address patients' individual risk factors and needs, thereby with appropriate interventions, promoting patient safety and minimizing the likelihood of injury-related incidents such as falls or medication errors.
Individualized nursing care
These care plans ensure patients receive personalized nursing care tailored to their unique circumstances and requirements by identifying and addressing high-risk factors through a nursing assessment, diagnoses, and targeted interventions.
Prevention of falls and traumatic brain injury
With a focus on risk factors such as impaired mobility and medication side effects, these care plans help prevent common injury-related occurrences such as patient falls and traumatic brain injuries, ultimately improving patient outcomes and reducing healthcare costs.
Education and empowerment
Risk for Injury Care Plans provide opportunities to educate patients and their caregivers about injury prevention strategies, medication management, and environmental safety measures. This empowerment enables patients to take an active role in their care and reduces the likelihood of injury-related incidents.
Interdisciplinary collaboration
These care plans facilitate interdisciplinary collaboration by involving various healthcare professionals, such as nurses, physicians, occupational therapists, and pharmacists, in the health care team involved in patient assessment and developing and implementing interventions to promote patient safety and well-being.
Effective medication management
By incorporating medication-related risk factors into the care plan, healthcare providers can administer medications judiciously and monitor for adverse effects, reducing the likelihood of medication-related injuries and complications.
Commonly asked questions
Being at risk for injury signifies an individual's increased susceptibility to harm due to factors such as impaired mobility, cognitive impairment, environmental hazards, or other factors identified through nursing diagnosis.
Factors include impaired mobility, medication side effects, cognitive impairment, environmental hazards, a history of falls, muscle weakness, vision impairment, and chronic conditions, all of which are considered in injury nursing diagnosis.
The goals are to prevent falls, minimize medication-related risks, promote mobility and independence, address environmental hazards, and educate patients and caregivers.