High Protein Diet Plan
Download our free High Protein Diet Plan PDF to help your patients reach their health and fitness goals with ease.


What is a high-protein diet?
A high-protein diet focuses on consuming protein in greater amounts than the standard recommended dietary allowance. This type of diet is commonly used to lose weight and improve body composition by decreasing body fat while preserving muscle mass. Clinical trials, according to Moon and Koh (2020), have demonstrated that high-protein meals not only support weight loss but can also help prevent weight regain. Additionally, high-protein meal plans can be tailored to both low-calorie and standard-calorie diets, making them versatile for different nutritional goals.
The health benefits of a high-protein diet extend beyond weight management. Increasing protein intake boosts the production of certain hormones that enhance satiety, reducing hunger and food intake. Combined with a higher diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT), this mechanism means high-protein foods like grilled chicken, plant-based proteins, and brown rice help burn more calories during digestion. Individuals may also use protein powder and amino acids and include them in their high-protein meal plan. Knowing how much protein intake is crucial, as it supports the maintenance of muscle mass and keeps metabolism active.
When planning high-protein meals, it's important to consult a registered dietitian to ensure you’re getting enough protein—typically measured in grams based on your weight and goals. Proper meal prep, such as preparing meals in advance and refrigerating them overnight, can simplify the process and help maintain metabolic syndrome and overall health.
High Protein Diet Plan Template
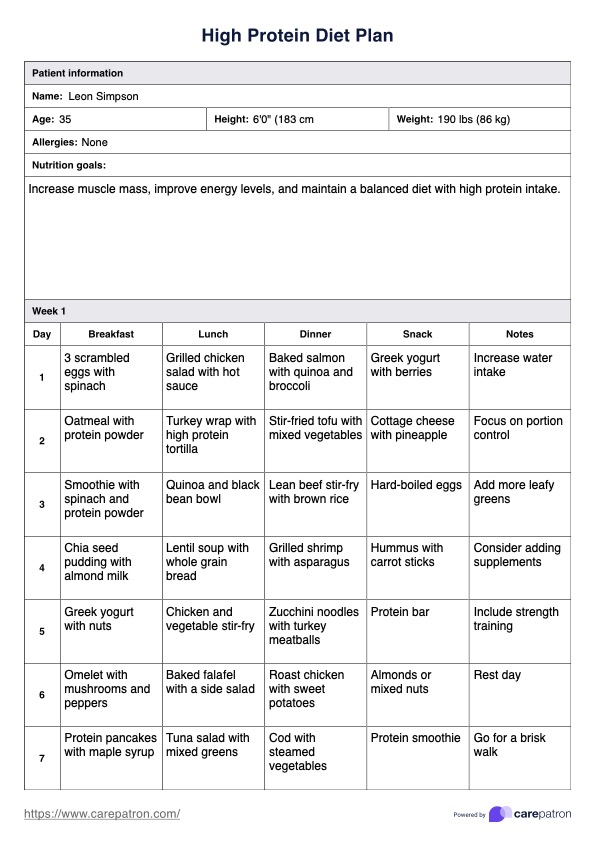
High Protein Diet Plan Example
How does it work?
Carepatron’s High-Protein Diet Plan template is an effective tool designed for healthcare practitioners to guide patients through structured, high-protein meal plans. This section will walk you through the steps of accessing, reviewing, and customizing the template and how to use it to monitor patient progress.
Access and use the template
This guide easily provides access to the High-Protein Diet Plan template. Healthcare professionals can click Download on the template preview on this page to help structure their patients' nutritional plans. Once accessed, practitioners can quickly begin personalizing the template to align with their patients' dietary needs and health goals.
Review the template content
After accessing the template, review its contents thoroughly. The template will include suggested high-protein meals, daily grams of protein, and portion sizes. Ensure that the content aligns with the patient’s health condition, fitness goals, and dietary preferences, making adjustments based on their body composition and caloric requirements.
Introduce the plan template to the patient
Once reviewed, introduce the high-protein meal plan to your patient. Explain how planning a high-protein diet can help them lose weight, reduce body fat, or manage conditions such as metabolic syndrome. Walk them through the meal plan and ensure they understand the process.
Customize the diet plan template
To ensure maximum effectiveness, customize and collaborate with the patient on the High-Protein Diet Plan according to their lifestyle. Consider their eating preferences and whether they prefer meal prep strategies like refrigerating meals overnight, and ensure the plan includes enough protein and calories based on their individual needs.
Monitor progress
As the patient follows the high-protein meal plan, regularly monitor their progress. This includes tracking weight changes, body composition, and overall health. Adjust the High-Protein Diet Plan as necessary, making sure the patient maintains healthy habits and continues to benefit from the health benefits of a high-protein diet.
When would you use this plan?
The High Protein Diet Plan is a flexible and comprehensive nutritional tool suitable for use by both individuals looking to enhance their diet and professionals assisting others in their dietary endeavors. This plan is especially applicable and beneficial for a range of groups, including:
- Athletes or active individuals: The benefits of a high protein diet are substantial for those regularly involved in physical activities, particularly strength training. This diet plays a pivotal role in muscle repair, growth, and recovery – key factors for athletic performance.
- Weight management: A high-protein diet can benefit individuals focusing on weight loss or management. Protein-rich foods enhance satiety, helping to reduce overall calorie intake while preserving lean muscle mass during weight loss.
- Post-operative recovery: After surgery, the body requires additional protein for healing and rebuilding tissues. A High Protein Diet Plan can aid in faster recovery by providing the necessary building blocks for repair.
- Injury recovery: Similar to postoperative recovery, healing from injuries, especially those involving muscles, bones, and connective tissues, can be aided with increased protein intake.
- Older adults: With age, maintaining muscle mass becomes crucial. A high-protein diet can help prevent sarcopenia (age-related muscle loss), enhancing strength and mobility in older adults.
- General health improvement: For individuals looking to improve their overall nutritional intake, incorporating more protein into their diet can lead to better health outcomes, as protein plays a critical role in various bodily functions.
Pros and cons of the High-Protein Diet Plan
A High-Protein Diet Plan has become popular for its potential benefits in weight management and overall health. One of the primary advantages is its ability to promote weight loss and maintain lean muscle mass. By consuming extra protein, individuals can experience increased satiety, which helps reduce overall calorie intake.
In addition to weight management, a High-Protein Diet Plan supports physical activity by supplying the necessary amino acids for muscle repair and growth. For individuals who exercise regularly, ensuring they meet their grams of protein target—typically around 1.6 to 2.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight—can enhance performance and recovery.
However, there are potential downsides to consider. Following a High-Protein Diet Plan may lead to nutrient imbalances if individuals neglect other food groups. It is crucial to maintain a balanced diet that includes adequate carbohydrates and fats to support energy levels and overall health. Additionally, some people may experience digestive issues, such as constipation, when increasing protein intake without sufficient fiber. It’s essential to incorporate various recipe instructions that include vegetables and whole grains to prevent such issues.
Reference
Moon, J., & Koh, G. (2020). Clinical evidence and mechanisms of high-protein diet-induced weight loss. Journal of Obesity & Metabolic Syndrome, 29(3), 166–173. https://doi.org/10.7570/jomes20028
Commonly asked questions
High-protein diets are not inherently bad. They can be highly beneficial for muscle building, weight loss, and recovery. However, like any diet, balance and moderation are key. Excessive protein intake, especially without a balanced intake of other nutrients, can strain the kidneys and liver. It's important to approach high protein diets with a balanced perspective, ensuring adequate consumption of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats alongside protein-rich foods.
High-Protein Diet Plans often improve performance by aiding muscle repair and growth. They also enhance satiety and preserve muscle mass during weight loss.
High-Protein Diet Plans are designed to help individuals meet their specific protein requirements through a balanced diet. By increasing the proportion of protein-rich foods in daily meals, these plans guide users in achieving their targeted protein intake. Essential protein sources in these diets include lean meats, poultry, fish, dairy products, eggs, and various plant-based options like beans, lentils, and tofu.
The duration of a High-Protein Diet Plan can vary depending on individual goals and needs. For specific objectives like muscle building or recovery, the plan might be followed for several weeks to months. In cases of long-term weight management or general health improvement, the diet can be integrated into a permanent lifestyle change. However, it's important to periodically reassess nutritional needs and make adjustments as necessary, potentially consulting with a healthcare or nutrition professional for personalized advice and guidance.