Hypochondria Test
Effectively assess health anxiety and manage concerns with Carepatron’s free downloadable Hypochondria Test PDF.


What is hypochondria?
Hypochondria or hypochondriasis, also known as illness anxiety disorder (IAD), is a mental health disorder where individuals experience extreme anxiety over their health status (Healthdirect Australia, 2020). They often misinterpret normal bodily sensations or physical symptoms as signs of illness, believing they have a serious medical condition despite medical reassurance. This persistent health anxiety leads to frequent medical tests, excessive self-examinations, and disruptions in daily life. A mental health professional can diagnose and treat this condition, helping patients manage their health concerns and reduce the fear of undiagnosed illnesses.
Symptoms
Individuals experiencing health anxiety frequently check their bodies for signs of illness and seek repeated medical tests despite negative results. They may research serious illnesses obsessively, avoid hospitals due to fear of bad news, or visit multiple doctors looking for validation. This somatic symptom disorder leads to an inability to trust medical reassurance, heightening mental health issues like anxiety and depression. Some develop “white coat syndrome,” where just being in a medical setting triggers extreme anxiety. Over time, these behaviors interfere with daily life, relationships, and work, making professional treatment necessary.
Risks
Untreated illness anxiety disorder significantly impacts mental well-being and daily functioning. Individuals may experience serious medical condition fears so intense that they avoid doctors altogether, paradoxically increasing health risks by neglecting real issues. Excessive stress weakens the immune system, leading to more physical symptoms. Persistent worry strains relationships, as loved ones struggle to provide constant reassurance. Many with hypochondria also suffer from mental health issues, including depression, generalized anxiety, and obsessive-compulsive tendencies.
Treatment
Managing hypochondria involves therapy, medication, and behavioral changes. Cognitive behavioral yherapy (CBT) is the most effective treatment, helping individuals challenge irrational health concerns and break compulsive checking habits. A mental health professional may also prescribe anti-anxiety or antidepressant medications to reduce extreme anxiety. Education about normal bodily sensations reassures patients that minor discomforts are not indicators of a serious illness. Encouraging mindfulness, stress management, and reducing online symptom-checking can significantly improve quality of life. With proper intervention, individuals can regain control over their thoughts and lead a balanced, worry-free life.
Hypochondria Test Template
Hypochondria Test Example
What is the Hypochondria Test?
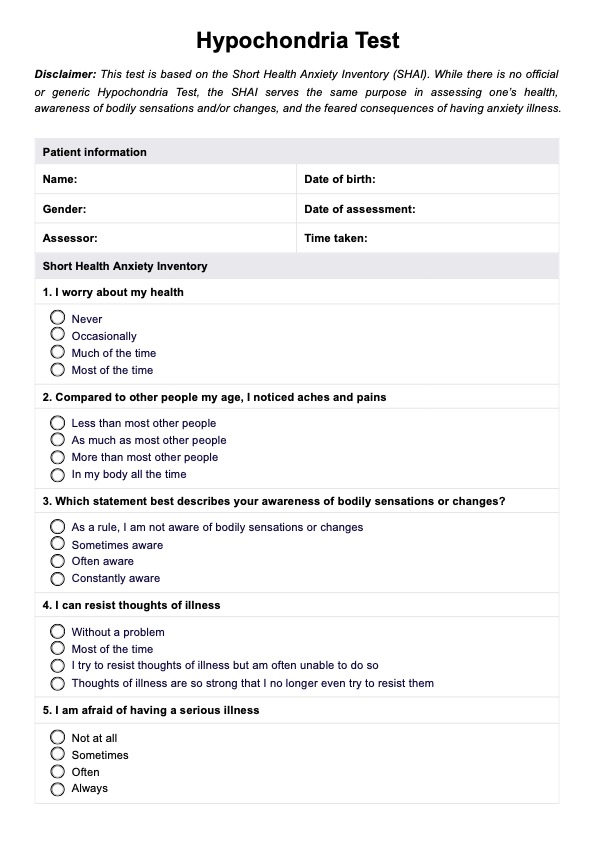
The Hypochondria Test is a screening tool used to assess health worries and anxiety about serious illness. While there is no universally recognized Hypochondria Test, Carepatron's assessment is based on the Short Health Anxiety Inventory (SHAI). This widely used tool evaluates a person’s perception of their health, sensitivity to symptoms, and fear of becoming seriously ill. The SHAI helps distinguish between normal concerns about medical care and high-risk health anxiety that may indicate a mental health condition like obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) or illness anxiety disorder.
Developed for use in both clinical and non-clinical populations, the SHAI consists of 18 items that measure fears related to specific illness, interpretation of bodily changes, and patterns of seeking reassurance from medical professionals (Salkovskis et. al., 2002). Alberts et. al. (2013) supports its effectiveness in identifying individuals with heightened health anxiety, particularly those with a history of childhood illness or excessive concern over a family member’s medical history. The test is useful for assessing early symptoms in early adulthood, where coping skills may still be developing.
How does it work?
You can use Carepatron’s Hypochondria Test to assess patients’ health worries and anxiety about serious illness. This structured process ensures accurate evaluation, clear interpretation, and effective discussion of findings. Follow these steps to integrate the test into your patient assessments and guide them toward appropriate medical care and interventions.
Step 1: Access the test template
Click "Use template" to access Carepatron’s Hypochondria Test instantly. This will direct you to Carepatron’s app download, where you can seamlessly integrate the test into your workflow. Once downloaded, you can begin using the template to evaluate health anxiety, interpret results efficiently, and track patient progress over time.
Step 2: Use the test template in patient assessment
Incorporate the test as part of a comprehensive mental health evaluation. This tool helps identify high-risk individuals experiencing extreme anxiety about their health status. The Hypochondria Test is particularly effective in differentiating normal bodily concerns from excessive fear of serious medical conditions, allowing for informed clinical decisions.
Step 3: Conduct the test
Guide the patient through each test item, ensuring they understand the questions. The Short Health Anxiety Inventory format assesses their response to symptoms, reactions to medical care, and patterns of seeking reassurance. Encourage honest responses to obtain an accurate representation of their health anxiety and psychological state.
Step 4: Gather and interpret results
Analyze responses to identify patterns of obsessive health concerns. Compare findings to standardized criteria to determine whether the patient exhibits illness anxiety disorder symptoms. Consider other mental health conditions, such as obsessive-compulsive disorder, that may contribute to their health worries and guide appropriate treatment recommendations.
Step 5: Discuss results with patient
Present findings in a clear and reassuring manner. Validate the patient’s health concerns while emphasizing the difference between serious illness and anxiety-driven symptoms. Avoid reinforcing unnecessary fears, and instead, focus on guiding the discussion toward effective coping skills and possible therapeutic interventions.
Step 6: Provide patient education and next steps
Educate the patient about health anxiety, its impact, and self-help strategies to manage excessive worry. If needed, refer them to a mental health professional for further evaluation. Encourage behavioral techniques, such as limiting medical tests, reducing symptom checking, and practicing mindfulness to regain control over health concerns.
Scoring and interpretation
Carepatron's Hypochondria Test, based on the Short Health Anxiety Inventory, has a total score (0-54) along with two subscale scores. The health anxiety subscale (0-42) measures anxiety about health status, while the negative consequences subscale (0-12) assesses fear of severe outcomes from serious illness.
Higher scores indicate heightened health concerns, with percentiles comparing results to community and clinical samples. A Normative Percentile of 50 reflects average health awareness, while illness anxiety disorder cases typically exceed 99, meaning they score higher than 99% of the population.
Benefits of using this test
The Hypochondria Test is a valuable tool for medical professionals assessing patients who are easily alarmed by minor symptoms and have excessive fear of severe illness. This structured assessment helps differentiate between rational health concerns and health anxiety, improving diagnostic accuracy and treatment planning.
By systematically evaluating a patient’s family history, symptom interpretation, and anxiety levels, the test aids in identifying those who may need targeted interventions. Since the exact cause of illness anxiety disorder varies, this test provides objective data to guide diagnosis and inform clinical decisions. It also helps professionals in providing reassurance to patients, reducing unnecessary medical tests and excessive healthcare visits.
Additionally, tracking patient scores over time allows for monitoring treatment efficacy, whether through cognitive-behavioral therapy, relaxation techniques, or medication. With early intervention, patients can manage their fears effectively, experience less distress over pain or common bodily sensations, and ultimately regain the ability to enjoy life without constant worry about disease.
References
Alberts, N. M., Hadjistavropoulos, H. D., Jones, S. L., & Sharpe, D. (2013). The Short Health Anxiety Inventory: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Anxiety Disorders, 27(1), 68–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.janxdis.2012.10.009
Healthdirect Australia. (2020, April 14). Hypochondria. Healthdirect. https://www.healthdirect.gov.au/hypochondria
Salkovskis, P. M., Rimes, K. A., Warwick, H. M. C., & Clark, D. M. (2002). The Health Anxiety Inventory: Development and validation of scales for the measurement of health anxiety and hypochondriasis. Psychological Medicine, 32(5), [Article number or page range]. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0033291702005822
Commonly asked questions
Testing for hypochondria, now known as illness anxiety disorder (IAD), involves a clinical assessment by a mental health professional. This includes structured interviews, psychological questionnaires, and ruling out actual medical conditions through physical exams and tests.
A person may be considered a hypochondriac if they exhibit persistent and excessive fear of serious illness, often misinterpreting normal bodily sensations as signs of disease. This anxiety leads to frequent doctor visits, excessive health-related research, or avoidance of medical care due to fear of bad news. Their distress continues despite medical reassurance and negatively impacts their daily life.
The two types of hypochondria, as categorized in the DSM-5, are illness anxiety disorder and somatic symptom disorder (SSD). IAD involves excessive worry about illness with few or no physical symptoms, while SSD includes significant distress over actual physical symptoms, even if they have no clear medical explanation. Both conditions involve health-related anxiety, but SSD is more focused on physical discomfort.