Hawkins Classification Chart
Use our free Hawkins Classification Chart template to classify talar neck fractures. Incorporate this into your physical therapy practice for free.


What are talar neck fractures?
Talar neck fractures are breaks or disruptions in the narrow portion of the talus bone, which sits between the ankle joint and the talus body. This type of talus fracture often involves the lateral process, a bony projection on the outside of the talus. They can occur due to various causes, such as impact to the medial malleolus, trauma from ankle injuries, falls, or accidents.
The talus bone transmits weight and forces from the leg to the foot. Fractures in the neck region can have significant consequences, as they may affect the stability and function of the ankle joint. In severe cases, talar neck fractures can lead to impairment of blood supply from the posterior tibial artery. This problem leads to complications like avascular necrosis (AVN), where the blood supply to the bone is compromised, resulting in bone tissue death (Jordan et al., 2017).
Talus fractures, particularly those affecting the talar neck, can extend to the talar body, impacting adjacent structures such as the talar dome or the subtalar joint. This is part of the foot's complex joint network. These fractures may also involve the articular surface, lateral process, medial surface, and posterior process, affecting both the bone integrity and the associated soft tissues.
Symptoms of talar neck fractures include pain, swelling, bruising, and difficulty weight-bearing on the affected foot. In some cases, the ankle joint may be deformed or unstable.
Hawkins Classification Chart Template
Hawkins Classification Chart Example
What is the Hawkins Classification Chart?
The Hawkins Classification Chart is a system for categorizing talar neck fractures based on the degree of displacement and associated dislocations. It was initially described by Leland G. Hawkins in 1970 and has since been widely used in diagnosing and treating these fractures.
Orthopedic surgeons use the Hawkins Classification Chart to assess the risk of AVN of the talus bone. The classification system helps determine the appropriate treatment approach and predict the likelihood of successful healing.
How does it work?
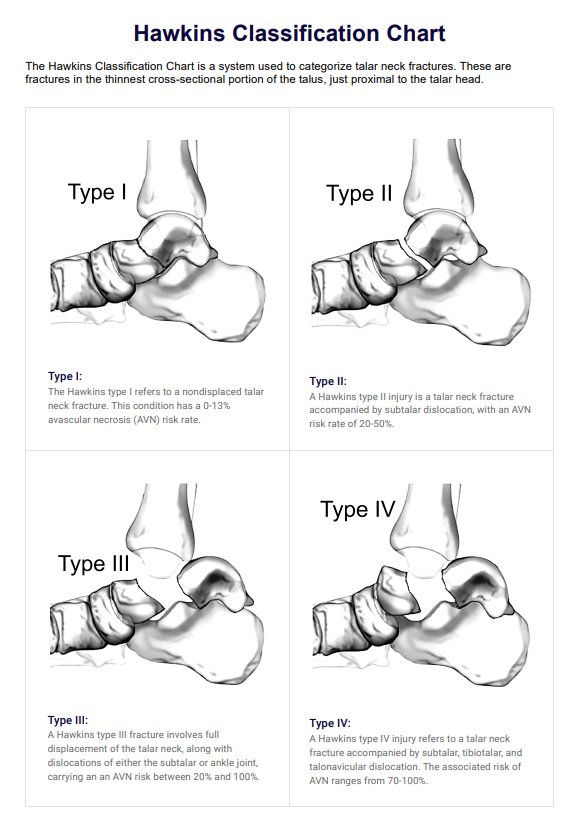
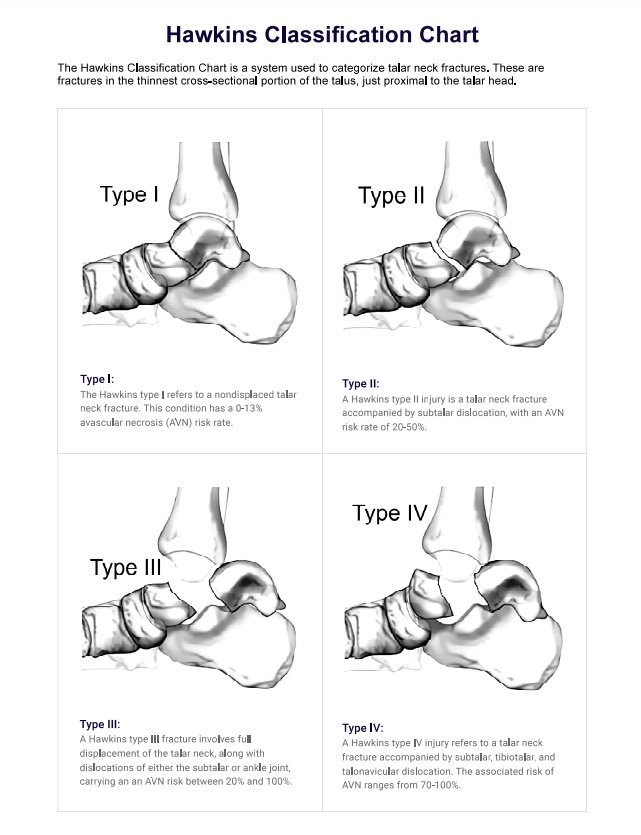
The Hawkins Classification Chart categorizes talar neck fractures into four types based on the degree of displacement and associated dislocations (Hawkins, 1970; Canale & Kelly, 1978; Haverkort et al, 2015):
- Type I: Non-displaced fractures without dislocations, presenting an AVN risk of 0-13%.
- Type II: Fractures featuring partial displacement of the talar neck, without dislocations, carrying an AVN risk of 20-50%.
- Type III: Fractures with a complete displacement of the talar neck, accompanied by dislocations of the subtalar or ankle joint, with an AVN risk ranging from 20-100%.
- Type IV: Fractures involving complete displacement of the talar neck and dislocations of the subtalar, tibiotalar, and talonavicular joints are associated with an AVN risk of 70-100%.
What is Hawkins sign?
You can use the Hawkins Classification Chart with the Hawkins sign to determine the severity of a talar neck fracture. The Hawkins sign is a radiographic finding that indicates sufficient vascularity of the talus following a talar neck fracture. It appears as subchondral lucency (radiolucent band) in the talar dome on an anteroposterior (AP) radiograph of the ankle, typically seen 6-8 weeks after the injury.
This sign is a positive indication that the bone is healing properly and has a good blood supply, which can help predict a successful outcome. The absence of the Hawkins sign may suggest a higher risk for avascular necrosis, non-union, or other complications.
How does our Hawkins Classification Chart work?
Carepatron's free Hawkins Classification Chart contains talus fracture patterns, which can help you classify talar neck fractures more easily. Follow these steps to get started:
Step 1: Access the template
Open a copy of the template by clicking the "Use template" button on this page. This button opens the template in the Carepatron app, where you can customize it before printing or sharing it. You can also get a ready-to-print copy by clicking "Download."
Step 2: Print or use the digital copy
Our free handout chart is available in both printable and digital formats. You can either print it out or use the digital copy on your computer, tablet, or smartphone.
Step 4: Use the Hawkins sign to determine severity
Carefully examine your patient's X-ray for the presence or absence of the Hawkins sign. This will help you determine the degree of vascularity and potential for healing in the injured area.
Step 5: Classify the fracture
Based on your assessment of the X-ray and use of the Hawkins sign, classify the talar neck fracture according to the Hawkins classification system. Use the chart as a reference to determine the appropriate classification.
Benefits of using Carepatron's chart for talar fractures
Carepatron's free Hawkins Classification Chart offers many benefits for your clinical practice. Some of these advantages are:
Fully digital
You can access and use our chart on any device with internet access, including your computer, tablet, or smartphone. There is no need to print out multiple copies or worry about losing the physical copy.
Easy to use
Our chart provides a simple and intuitive way to classify talar fractures using the Hawkins classification system. It's easy to understand and use, saving you time and effort in your clinical practice.
Complete reference
Our Hawkins Classification Chart includes all four types of talar fractures and their descriptions, giving you a comprehensive reference for classification. You can also use it to educate patients about their specific fracture type and potential treatment options.
Treatment options for talar neck fractures
Depending on the severity and type of talar neck fracture, treatment can vary. Non-surgical options may include immobilization with a cast or boot for several weeks, followed by physical therapy to regain strength and range of motion.
Surgical options may involve open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) to properly align and stabilize the bones and vascularized bone grafts to help promote healing and prevent AVN.
References
Canale, S. T., & Kelly, F. B. (1978). Fractures of the neck of the talus. Long-term evaluation of seventy-one cases. The Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery (J Bone Joint Surg Am). American Volume, 60(2), 143–156. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/417084/
Haverkort, J. J. M., Leenen, L. P. H., & Wessem, K. J. P. van. (2015). Diagnosis and treatment of talar dislocation fractures illustrated by 3 case reports and review of literature. International Journal of Surgery Case Reports, 16, 106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijscr.2015.09.025
Hawkins, L. G. (1970). Fractures of the neck of the talus. The Journal of Bone & Joint Surgery (J Bone Joint Surg Am), 52(5), 991–1002. https://journals.lww.com/jbjsjournal/Abstract/1970/52050/Fractures_of_the_Neck_of_the_Talus.13.aspx
Jordan, R. K., Bafna, K. R., Liu, J., & Ebraheim, N. A. (2017). Complications of talar neck fractures by Hawkins classification: A systematic review. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery (J Foot Ankle Surg), 56(4), 817–821. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.jfas.2017.04.013
Commonly asked questions
Talar neck fractures specifically involve a break in the neck region of the talus. This area is crucial for blood supply to the bone, making these fractures more susceptible to complications such as avascular necrosis (AVN). Other types of talar fractures, like talar body fractures or lateral process fractures, affect different parts of the talus and may have different implications for foot movement and stability.
The treatment for fractures of the talus, including talar neck and body fractures, depends on the fracture's severity and location. Non-surgical options may include immobilization with a cast or walking boot. Surgical options often involve open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) to realign and stabilize the fracture fragments. In some cases, especially with significant bone damage or disruption of the blood supply, additional procedures like bone grafts or may be necessary.
The Hawkins classification is a system used to classify talar neck fractures based on the risk of developing avascular necrosis (AVN) or bone death. The higher the grade on the classification chart, the greater the risk of AVN. Type I and II fractures have a lower risk, while type III and IV fractures have a higher risk.