Hemoglobin Level
Have a hemoglobin level chart on hand when analyzing and interpreting your patient’s hemoglobin level test results. Click here to download a free template.


What are normal hemoglobin levels?
Hemoglobin is a complex protein molecule found in red blood cells that plays a crucial role in oxygen and carbon dioxide transport throughout the body. It carries oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and helps remove carbon dioxide, making it essential for overall health and well-being (Ahmed et al., 2020).
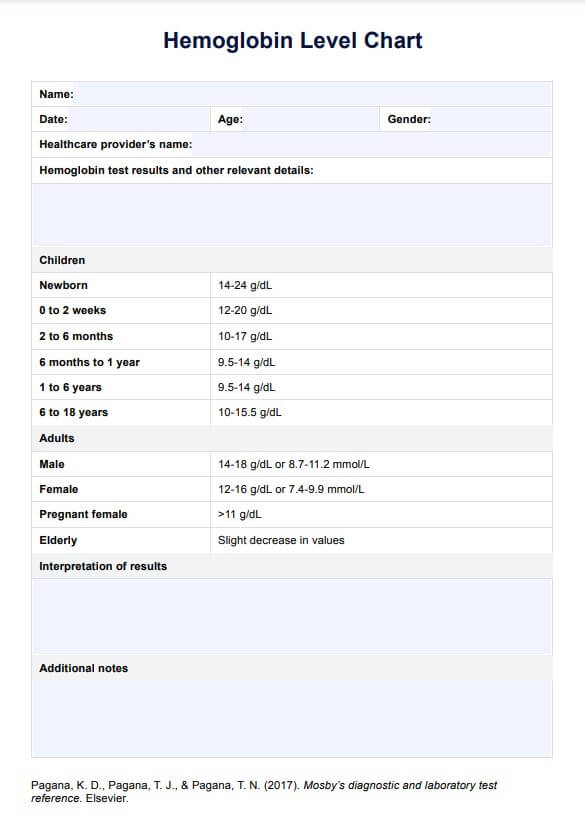
A hemoglobin test measures the amount of hemoglobin in the blood, but this is also typically measured as part of a complete blood count (CBC). The normal range can vary slightly depending on factors such as age, sex, and pregnancy status. Generally, normal hemoglobin levels are:
- Adult men: 14 to 18 g/dL
- Adult women: 12 to 16 g/dL
- Children: 9.5 to 24 g/dL (varies by age)
- Pregnant women: 11.0 to 14.0 g/dL
What affects hemoglobin levels?
When hemoglobin levels fall below the normal range, it may indicate anemia. Common causes of low hemoglobin count and fewer healthy red blood cells being produced in the body include:
- Iron deficiency anemia, sickle cell anemia
- Chronic diseases (e.g., chronic kidney disease, cancer)
- Vitamin deficiencies (B12, folate)
- Blood loss
- Bone marrow disorders
On the other hand, elevated hemoglobin levels can be caused by:
- Dehydration
- Lung diseases
- Congenital heart disease
- Polycythemia vera
- Living at high altitudes
High hemoglobin levels may increase the risk of blood clots and related complications. These irregular levels can also cause issues that lead to fewer red blood cells.
Hemoglobin Level Template
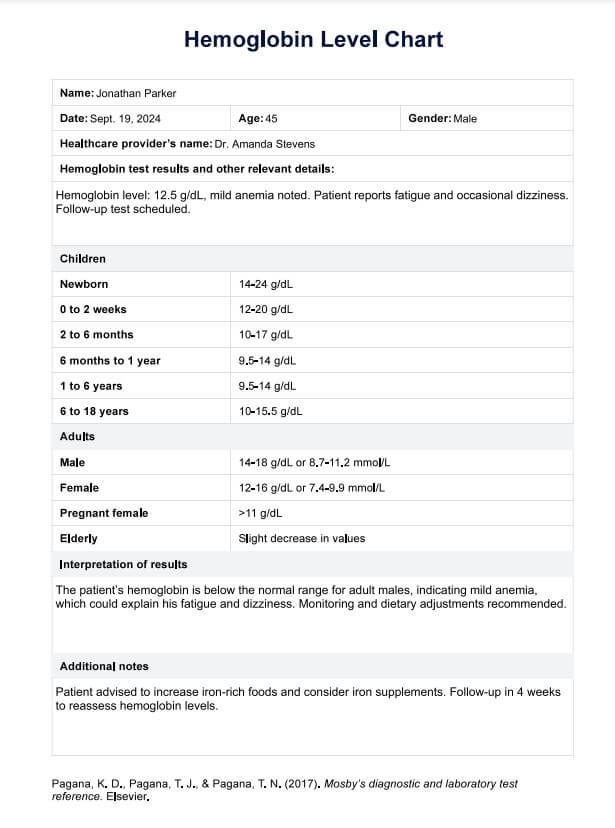
Hemoglobin Level Example
What is a Hemoglobin Level Chart?
A Hemoglobin Level Chart is valuable for healthcare practitioners to assess and monitor a patient's blood health. It visually represents the normal ranges of hemoglobin concentrations in the blood, typically measured in grams per deciliter (g/dL) or grams per liter (g/L). These charts are essential for quickly identifying whether a patient's hemoglobin levels fall within the expected range or if they indicate potential health issues.
How to use our Hemoglobin Level Chart
The following steps can be followed to make the most out of this hemoglobin levels chart in your practice:
Step 1: Obtain a copy of the template
Hemoglobin Level Charts are a valuable resource that's best to keep handy. First, click "Use template” to open it in the Carepatron app, where you can customize it before filling it out or printing it. You can also download a fillable, non-customizable PDF by clicking "Download."
Step 2: Input essential information
If you plan on using it as more than a visual aid when educating patients on normal hemoglobin levels, it's best if you fill out essential patient details, including the test results of their hemoglobin test.
Step 3: Compare and contrast
After the hemoglobin test, use the chart provided to compare and contrast normal levels with those found on your patient's test results document. Don't forget to consider their age and gender when analyzing.
Step 4: Write down interpretation
On our template, you may write your observations and/or findings in the space dedicated to interpreting results. You may also utilize the space for additional notes or information to write down medical interventions you need to perform or further examinations you must conduct.
How to measure hemoglobin levels
Measuring hemoglobin levels is crucial for assessing a patient's overall health and detecting various blood disorders that affect red blood cell production. This process typically involves different blood tests, which can be performed differently depending on the clinical setting and the specific information needed (Karakochuk et al., 2019).
Complete blood count test
The most common method for measuring hemoglobin levels is through a complete blood count (CBC). This comprehensive test provides information about various blood components, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Hemoglobin concentration is a key part of the CBC results. The CBC provides hemoglobin concentration in grams per deciliter (g/dL) or grams per liter (g/L).
Point-of-care testing
Point-of-care hemoglobin testing devices are used in some clinical settings for rapid results. These portable devices can measure hemoglobin levels from a small blood sample, often obtained through a finger prick. While convenient, it's important to note that these devices may be slightly less accurate than laboratory-based tests and are typically used for screening purposes or in situations where immediate results are necessary.
Hemoglobin electrophoresis
Hemoglobin electrophoresis may be performed for more detailed analysis, particularly when investigating hemoglobin disorders like sickle cell disease or thalassemia. This test separates different types of hemoglobin and normal red blood cells based on their electrical charge, allowing for the identification of a defective hemoglobin gene.
Hemoglobin A1c test
Hemoglobin A1C, or glycated hemoglobin, is a valuable marker for long-term blood sugar control in diabetes management. This test measures the percentage of hemoglobin molecules with glucose attached to them, providing an average blood glucose level over the past 2-3 months.
References
Ahmed, M. H., Ghatge, M. S., & Safo, M. K. (2020). Hemoglobin: Structure, function and allostery. In Vertebrate and Invertebrate Respiratory Proteins, Lipoproteins and Other Body Fluid Proteins. Springer. https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-3-030-41769-7_14
Karakochuk, C. D., Hess, S. Y., Moorthy, D., Namaste, S., Parker, M. E., Rappaport, A. I., Wegmüller, R., & Dary, O. (2019). Measurement and interpretation of hemoglobin concentration in clinical and field settings: A narrative review. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1450(1), 126–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/nyas.14003
Commonly asked questions
Hemoglobin levels that fall significantly below the normal range are considered concerning and may indicate anemia. Generally, hemoglobin levels below 12 g/dL in adult women and below 14 g/dL in adult men are considered low and warrant further investigation and potential treatment.
The lowest acceptable hemoglobin level can vary depending on the individual's age, sex, and overall health status. However, as a general guideline, hemoglobin levels below 10 g/dL are typically considered low and may require medical intervention. Levels below 7 g/dL are considered severe anemia and require prompt treatment.
The normal range for hemoglobin levels in babies can vary based on their age. A hemoglobin level between 14-24 g/dL in newborns is considered normal. By 6 months of age, the normal range is typically 9.5 to 14 g/dL. Healthcare providers monitor infant hemoglobin levels closely to ensure proper red blood cell production and oxygen delivery during this critical stage of development.