Flexitarian Diet Plan
Use Carepatron's Flexitarian Diet Plan to support patient nutrition goals. Learn its benefits and structure for balanced dietary management.


What is a flexitarian diet?
The flexitarian diet is a semi-vegetarian diet that focuses on plant-based foods while allowing occasional meat consumption (Derbyshire, 2017). Unlike vegetarian and vegan diets, it does not require individuals to eliminate animal products entirely but encourages them to reduce meat intake for improved healthy eating habits. This dietary approach emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and plant protein sources such as nuts, seeds, and beans. While flexitarians may eat meat, they typically prioritize meal prep with plant foods and minimally processed ingredients.
Unlike other plant-based diets, the flexitarian approach lacks strict rules regarding calorie or macronutrient targets, making it adaptable to various meal prep preferences. According to Hemler & Hu (2019), a plant-based diet pattern can offer significant health benefits, including better weight management, lower blood pressure, and reduced risk of chronic diseases compared to a regular meat-eater diet. Meanwhile, the flexitarian diet's flexibility also appeals to individuals transitioning from meat-eater habits toward plant-based foods without fully committing to vegan diets.
Flexitarian Diet Plan Template
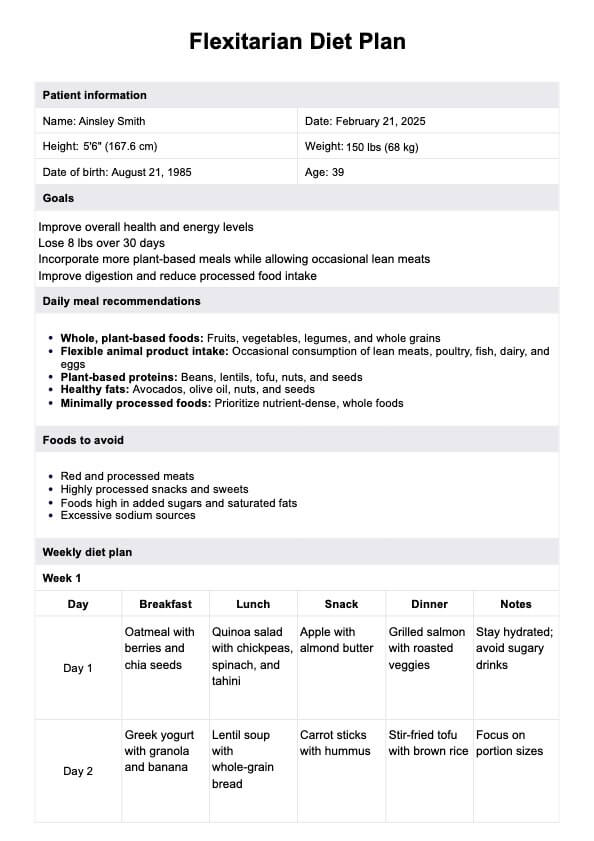
Flexitarian Diet Plan Example
What is a Flexitarian Diet Plan?
A Flexitarian Diet Plan is a structured approach to plant-based eating that encourages consuming more plant foods while allowing moderate animal product intake. It focuses on creating plant-based meals with fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes while reducing red meat and processed meats. The plan guides balancing plant-based recipes and occasional animal products like grilled salmon or eggs, helping clients maintain a healthy diet without fully committing to vegetarianism. Healthcare professionals and registered dietitians use this plan to promote reducing meat consumption and achieving a balanced diet through intentional meal prep and food choices.
Foods to include
A Flexitarian Diet Plan emphasizes more plant-based foods to support a healthy diet while allowing limited animal products. Key inclusions are whole grains like quinoa, brown rice, and oatmeal, which form the base of many plant-based meals. Fresh fruits, leafy greens, and colorful vegetables increase fiber and nutrient intake. Legumes, beans, lentils, and meat substitutes such as veggie burgers offer valuable plant protein sources.
Incorporating healthy fats from avocados, olive oil, nuts, and seeds supports heart health. Moderate consumption of grilled salmon, eggs, and dairy can complement plant-based eating when clients inquire about how much meat to include. Using plant-based recipes promotes a flexitarian lifestyle focused on more plant foods and less reliance on animal products.
Foods to avoid
A well-balanced Flexitarian Diet Plan advises limiting foods that hinder a healthy diet. Clients should reduce red meat intake, focusing on less frequent consumption. Processed meats like bacon, sausage, and deli meats should be minimized due to their link to chronic diseases. High consumption of highly processed foods, including chips and packaged snacks, should be avoided to reduce unhealthy fats and added sugars.
Refined grains, such as white bread and pasta, lack nutrients compared to whole grains. Clients should also limit fast food and sugary drinks that disrupt balanced eating. When advising patients, emphasize the importance of avoiding processed meats and making informed food choices to support a sustainable flexitarian lifestyle and overall wellness.
How does it work?
Medical professionals can seamlessly incorporate this Flexitarian Diet Plan template into their workflow to streamline patient dietary planning. The process is straightforward, enabling practitioners to develop tailored, balanced diet strategies while saving time on administrative tasks. Follow the steps below to use the template effectively.
Step 1: Access the diet plan template
Click the "Use template" button to access the Flexitarian Diet Plan template instantly. You will be directed to Carepatron’s platform, where you can create customized diet plans immediately. This quick action eliminates setup time, allowing you to focus on patient-centered dietary planning. You can also click on "Download" to get a fillable PDF copy.
Step 2: Introduce the diet plan to the patient
Explain the Flexitarian Diet Plan to the patient, highlighting how it supports a healthy diet by increasing plant-based meals and reducing red meat and processed meat consumption. Emphasize the flexitarian lifestyle benefits, ensuring patients understand the plan’s balance between plant-based eating and occasional animal products.
Step 3: Use the template for diet planning
Utilize the template’s fillable fields to create a tailored plan based on patient goals, dietary preferences, and health needs. Include details like whole grains, plant protein options, and guidance on how much meat is appropriate. The template ensures comprehensive, patient-specific dietary recommendations.
Step 4: Provide further patient education
Enhance patient understanding by offering practical advice on meal prep, choosing more plant foods, and integrating plant-based recipes into daily routines. Encourage discussions on limiting highly processed foods and making healthier choices, reinforcing the long-term benefits of the flexitarian lifestyle.
Step 5: Save and implement
Easily save the completed Flexitarian Diet Plan directly within Carepatron’s platform. This integration allows seamless storage, quick retrieval, and efficient patient sharing. Implementing the template into your practice helps maintain consistent, effective dietary guidance while simplifying your overall workflow.
Benefits of using this diet plan
Using the Flexitarian Diet Plan offers several advantages for medical professionals aiming to improve patient outcomes and streamline dietary planning. The template provides a structured approach to flexitarian eating, making it easy to follow while ensuring patients receive essential nutrients from diverse food groups. By incorporating a weekly meal plan, practitioners can help patients consume less meat while obtaining adequate animal proteins when needed. This reduces saturated fat intake, supports overall health, and lowers the risk of chronic conditions.
The plan also simplifies the identification of potential nutrient deficiencies and allows healthcare providers to recommend certain foods to address them. With a foundation rooted in food science, the template ensures balanced nutrition while accommodating patient preferences. This structured approach improves consultation efficiency, saves time on manual planning, and enables consistent, evidence-based dietary recommendations tailored to individual health needs.
References
Derbyshire, E. J. (2017). Flexitarian diets and health: A review of the evidence-based literature. Frontiers in Nutrition, 3, Article 55. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnut.2016.00055
Hemler, E. C., & Hu, F. B. (2019). Plant-based diets for personal, population, and planetary health. Advances in Nutrition, 10(Suppl. 4), S275–S283. https://doi.org/10.1093/advances/nmy117
Commonly asked questions
A flexitarian meal plan focuses on plant-based meals with occasional inclusion of animal proteins like fish, poultry, or dairy. It emphasizes whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and legumes to promote balanced nutrition while reducing meat consumption.
Flexitarians limit processed meats, saturated fat sources, and highly refined foods while avoiding excessive red meat intake. The diet discourages certain foods like sugary snacks, fried items, and low-nutrient processed options.
Pros include improved overall health, a lower risk of chronic diseases, and easier access to essential nutrients through diverse food groups. Cons may involve potential nutrient deficiencies if animal proteins are inadequately replaced with plant-based alternatives.
Yes, the flexitarian diet can support weight loss by reducing saturated fat and promoting high-fiber, plant-based foods that increase satiety. Its easy-to-follow structure encourages healthier choices without strict restrictions.