Estrogen Blood Test
Discover the role of estrogen testing in healthcare with our guide. Learn how Carepatron streamlines hormonal testing for better patient care.


What is an Estrogen Test?
Navigating the world of healthcare can often feel like solving a complex puzzle, and the Estrogen Blood Test is one of the critical pieces. This test is a straightforward yet powerful tool in the hands of healthcare professionals, offering essential insights into a patient's health with a simple blood or urine sample.
An Estrogen Blood Test measures the levels of estrogen, a hormone that plays a crucial role in reproductive health and overall well-being. It's like a health detective helping to uncover the story behind various symptoms. Whether it's irregular periods, fertility concerns, or changes during menopause, this test provides the answers to make informed decisions.
But it's not just about women's health. Estrogen levels are essential for everyone, influencing everything from bone density to mood. This test is a staple in healthcare, guiding professionals in diagnosing and managing various conditions.
Integrating the Estrogen Blood Test into your practice is a breeze with practice management software from Carepatron. This software makes managing test results easy, ensuring you have more time to care for your patients and less time to deal with paperwork.
The Estrogen Blood Test is a vital tool, simple in its execution but profound in its impact. It's about bringing clarity to health concerns and guiding better health.
Estrogen Blood Test Template
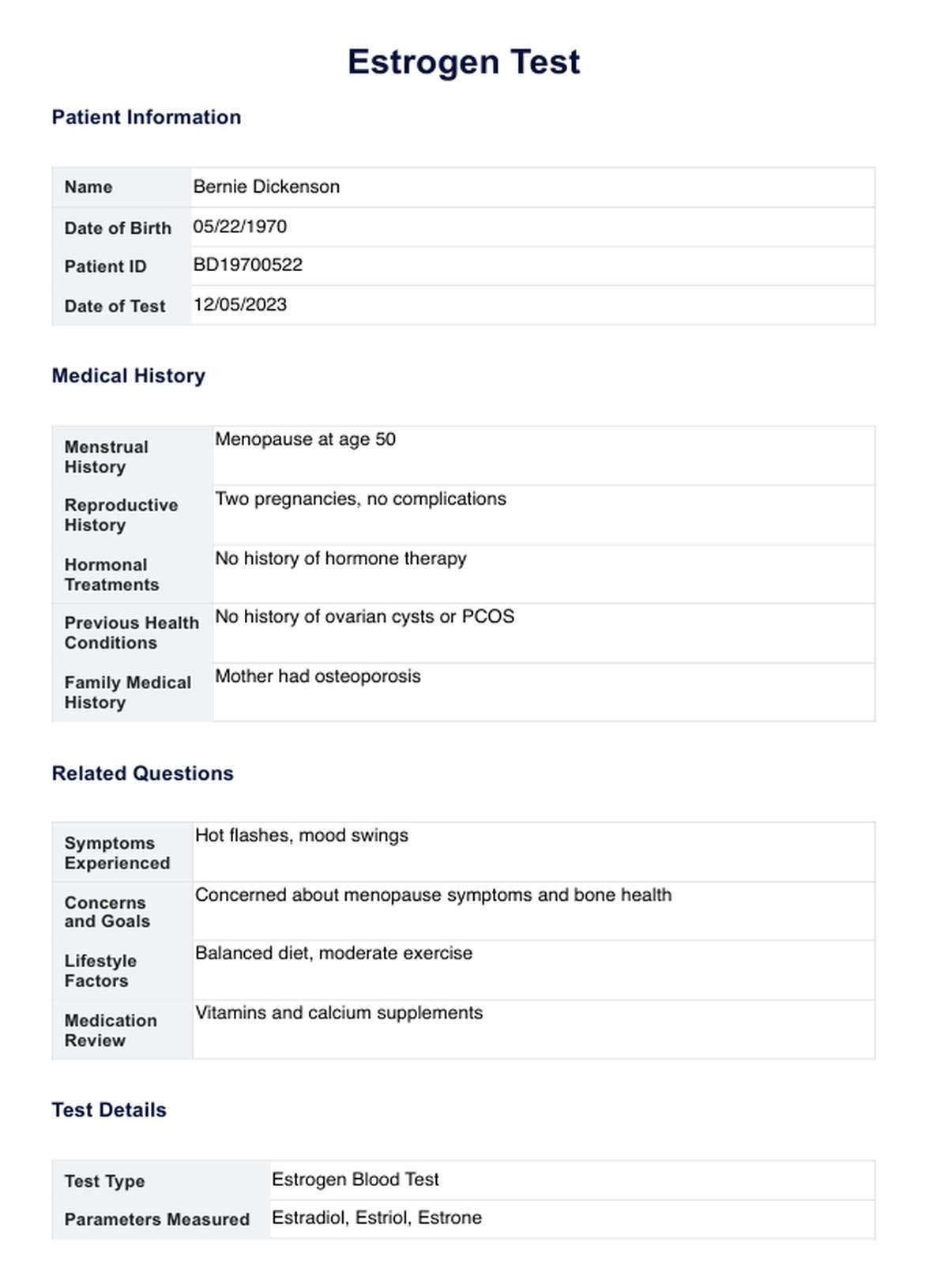
Estrogen Blood Test Example
What does the test measure?
At the heart of the Estrogen Blood Test is its ability to measure estrogen levels in the blood, but what does this mean for patient care? Estrogen, a hormone synonymous with reproductive health, plays a multifaceted role in the body, and understanding its levels is critical to unlocking a wealth of health information.
- Estrogen types: The test primarily measures three types of estrogen: estradiol, estriol, and estrone. Estradiol is the most common form in women of childbearing age; estriol levels are significant during pregnancy, and estrone becomes prominent after menopause.
- Reproductive health: In women, the test is crucial for assessing conditions like irregular menstrual cycles, symptoms of menopause, and overall fertility health. It helps in diagnosing conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) and ovarian insufficiency.
- Pregnancy monitoring: During pregnancy, estrogen levels indicate the health of the placenta and the developing fetus. Abnormal levels can signal potential complications.
- Bone health: Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining bone density. Low levels can indicate an increased risk of osteoporosis, especially in postmenopausal women.
- Hormone therapy monitoring: For patients undergoing hormone replacement therapy, either as part of menopause treatment or gender transition, this test helps in monitoring and adjusting hormone levels.
The Estrogen Blood Test is a window into the body's hormonal balance. It's a critical tool that aids healthcare professionals in diagnosing, monitoring, and managing various health conditions, ensuring personalized and effective patient care.
Test overview
The Estrogen Blood Test is a critical diagnostic tool in healthcare, offering valuable insights into a patient's hormonal balance. This test measures the levels of estrogen hormones in the blood, which play a vital role in both reproductive and overall health. Here's a brief overview of what this test entails:
- Purpose of the test: The primary goal of the Estrogen Blood Test is to assess the levels of estrogen hormones, including estradiol, estriol, and estrone. These measurements are crucial in evaluating various health conditions, from reproductive health issues to bone density concerns.
- Who needs the test: This test is commonly recommended for individuals experiencing symptoms related to hormonal imbalances, such as irregular menstrual cycles, fertility issues, or menopausal symptoms. It's also used in monitoring hormone replacement therapy and assessing the health of the ovaries and placenta during pregnancy.
- What it measures: The test precisely measures:
- Estradiol: The primary form of estrogen in women of childbearing age.
- Estriol: An estrogen that increases significantly during pregnancy.
- Estrone: An estrogen that becomes prominent after menopause.
- Procedure: The test involves a simple blood draw, typically from a vein in the arm. The procedure is quick and usually takes just a few minutes.
- Interpreting results: The results are measured in picograms per milliliter (pg/mL) and are analyzed based on the patient's age, sex, and physiological conditions. Abnormal levels can indicate various health issues requiring further investigation and management.
The Estrogen Blood Test is a straightforward yet essential procedure in healthcare, providing key information for diagnosing and managing a range of health conditions related to estrogen levels.
What do the results mean?
Interpreting the results of an Estrogen Blood Test is a crucial step in understanding a patient's hormonal health. The estrogen levels measured in the blood provide significant insights into various physiological and health conditions. Here's what these estrogen test results typically indicate:
- Estradiol levels: This is the primary form of estrogen in women of childbearing age. High levels can indicate conditions like ovarian tumors or early puberty, while low levels might suggest menopause, ovarian failure, or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). In men, elevated estradiol levels can be associated with gynecomastia.
- Estriol levels: Predominantly measured during pregnancy, high estriol levels can indicate a healthy pregnancy and fetal development. Abnormally low levels may suggest potential complications with the pregnancy, such as Down syndrome or other chromosomal abnormalities.
- Estrone levels: This form of estrogen becomes more prominent after menopause. Elevated levels in postmenopausal women can be expected, but they can also indicate an increased risk for conditions like breast or endometrial cancer.
- Overall hormonal balance: The balance between different types of estrogen is essential. Discrepancies can indicate various health issues, from hormonal imbalances to more severe conditions like estrogen-producing tumors.
- Contextual interpretation: It's crucial to interpret these results regarding the patient's overall health, symptoms, age, and specific circumstances like pregnancy or menopause.
In summary, the results from an Estrogen Blood Test are not just numbers; they are indicators of a patient's hormonal health and can guide healthcare professionals in diagnosing and managing a range of conditions related to estrogen levels.
The difference between estrogen and estradiol
Understanding the distinction between estrogen and estradiol is crucial in hormonal health. While often used interchangeably in casual conversation, they have specific roles and implications in medical diagnostics.
Estrogen
This term refers to a group of hormones that play a vital role in sexual and reproductive development, primarily in women. Estrogen is not a single hormone but a class of related hormones, including estradiol, estriol, and estrone. Each type of estrogen has unique functions and varies in concentration depending on factors like age, sex, and physiological conditions.
Estradiol
Estradiol is the most potent and prevalent form of estrogen, especially in women of childbearing age. It is primarily responsible for developing and maintaining female reproductive tissues, including the breasts, ovaries, and uterus. Estradiol levels fluctuate during the menstrual cycle and are a crucial focus in fertility treatments and assessing menstrual irregularities.
Key differences
- Role and potency: While all estrogens contribute to reproductive health, estradiol is the most active in terms of influencing sexual and reproductive functions.
- Concentration variations: Estradiol levels are significantly higher in premenopausal women, whereas estrone becomes more dominant post-menopause. Estriol levels are significant during pregnancy.
- Clinical implications: The specific estrogen measured can provide different insights. For example, estradiol levels are crucial in evaluating menstrual and fertility issues, while estriol is monitored during pregnancy, and estrone levels are observed in postmenopausal health assessments.
When should you test for hormonal imbalance?
Identifying the right time to test for hormonal imbalance is vital in providing timely and effective healthcare. Hormonal imbalances can affect various bodily functions and manifest in multiple symptoms. Here are some scenarios when testing for hormonal imbalance, particularly estrogen levels, is advisable:
- Irregular menstrual cycles: Women experiencing irregularities in their menstrual cycle, such as missed periods, excessively heavy or light bleeding, or unpredictable cycle lengths, should consider hormonal testing.
- Symptoms of menopause: Common menopausal symptoms, including hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness, can indicate changes in estrogen levels.
- Fertility concerns: Couples facing challenges in conceiving may opt for hormonal testing to assess factors affecting fertility, as estrogen levels play a crucial role in ovulation and reproductive health.
- Pregnancy monitoring: During pregnancy, hormonal testing can help monitor the health of the placenta and the developing fetus, as certain estrogen levels indicate fetal well-being.
- Postmenopausal health: Postmenopausal women may undergo hormonal testing to evaluate risks associated with decreased estrogen levels, such as osteoporosis or cardiovascular issues.
- Symptoms in men: Men experiencing symptoms like gynecomastia (enlarged breasts), erectile dysfunction, or loss of libido may also benefit from hormonal testing, as estrogen plays a role in male health, too.
Testing for hormonal imbalance is crucial in diagnosing and managing various health conditions. It helps healthcare professionals tailor treatment plans to address specific hormonal issues, ensuring better patient outcomes.
Next steps: if estrogen levels are too low
Discovering that estrogen levels in pregnant women are too low can be a turning point in a patient's healthcare journey. It's a signal that the body needs a bit of extra help. Here's what to do next:
- Consult with your doctor: The first step is a conversation with your healthcare provider. They can help you understand what low estrogen levels mean for your specific health situation and discuss potential causes like menopause, ovarian issues, or other hormonal imbalances.
- Consider hormone replacement therapy (HRT): For many, especially those going through menopause, Hormone Replacement Therapy can be a game-changer. It helps replenish estrogen levels, easing symptoms like hot flashes and protecting against bone loss.
- Lifestyle adjustments: Sometimes, small changes make a big difference. Incorporating a balanced diet rich in calcium and vitamin D, regular exercise, and stress reduction techniques can improve overall well-being and help manage low estrogen symptoms.
- Regular monitoring: Keep in touch with your doctor and schedule regular check-ups. Monitoring estrogen levels over time ensures that treatment or lifestyle changes work effectively.
- Stay informed: Knowledge is power. Understanding the role of estrogen and staying aware of how its levels affect your body empowers you to make informed health decisions.
Remember, low estrogen levels are a common experience for many, and you can effectively manage the situation with the right approach. It's all about taking those next steps with confidence and care.
Commonly asked questions
Common symptoms include hot flashes, night sweats, mood swings, and vaginal dryness. These symptoms are often seen in menopause or other conditions affecting estrogen production.
Yes, men can experience estrogen imbalances, which may lead to symptoms like enlarged breasts (gynecomastia), erectile dysfunction, or reduced libido.
Hormone replacement therapy can be safe and effective but requires careful consideration of individual risks and benefits. It's important to discuss with your healthcare provider to determine the best approach.