Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout
Download our Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout to empower patients in their recovery journey and give them information about treating elbow dislocations.


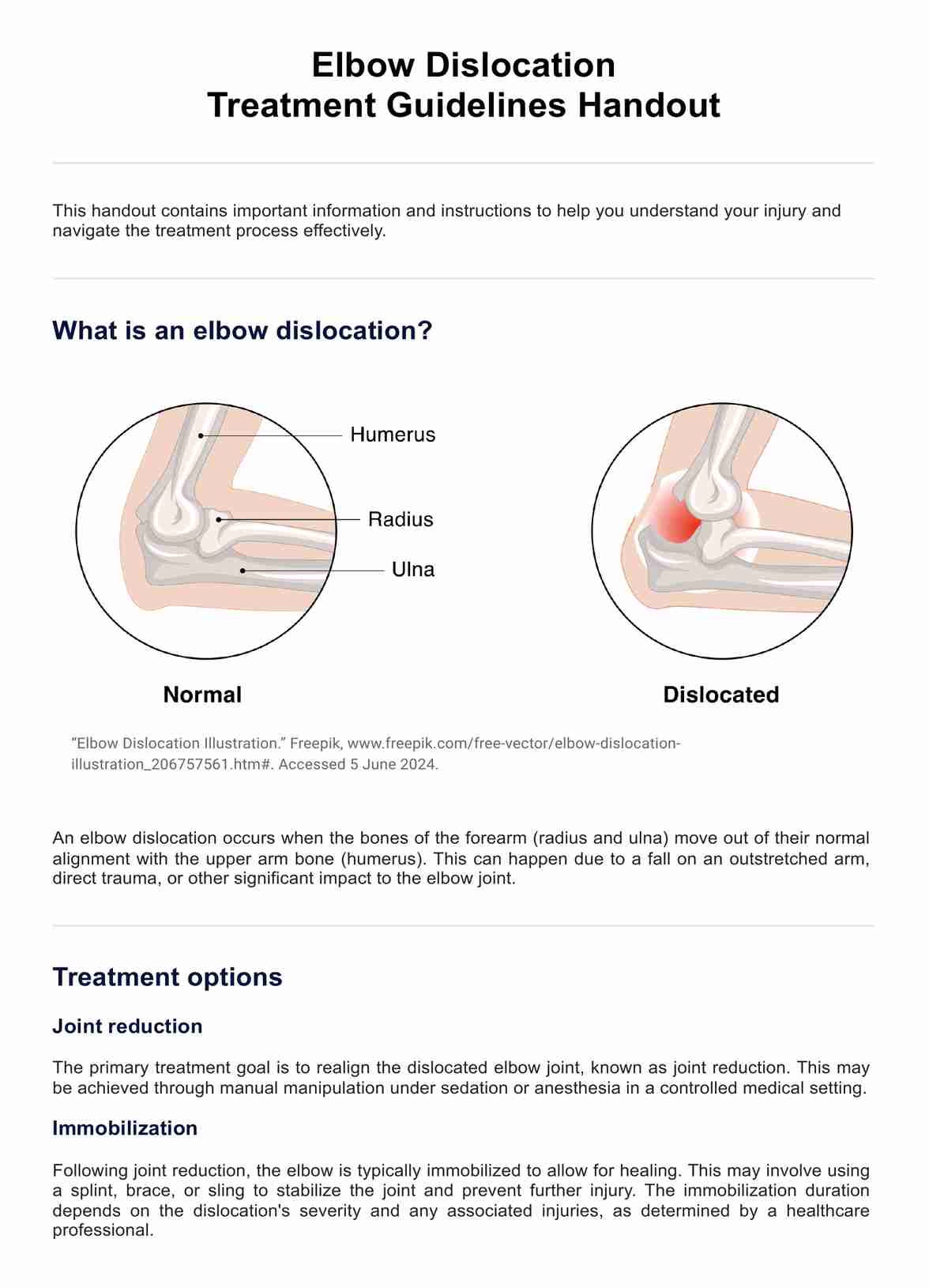
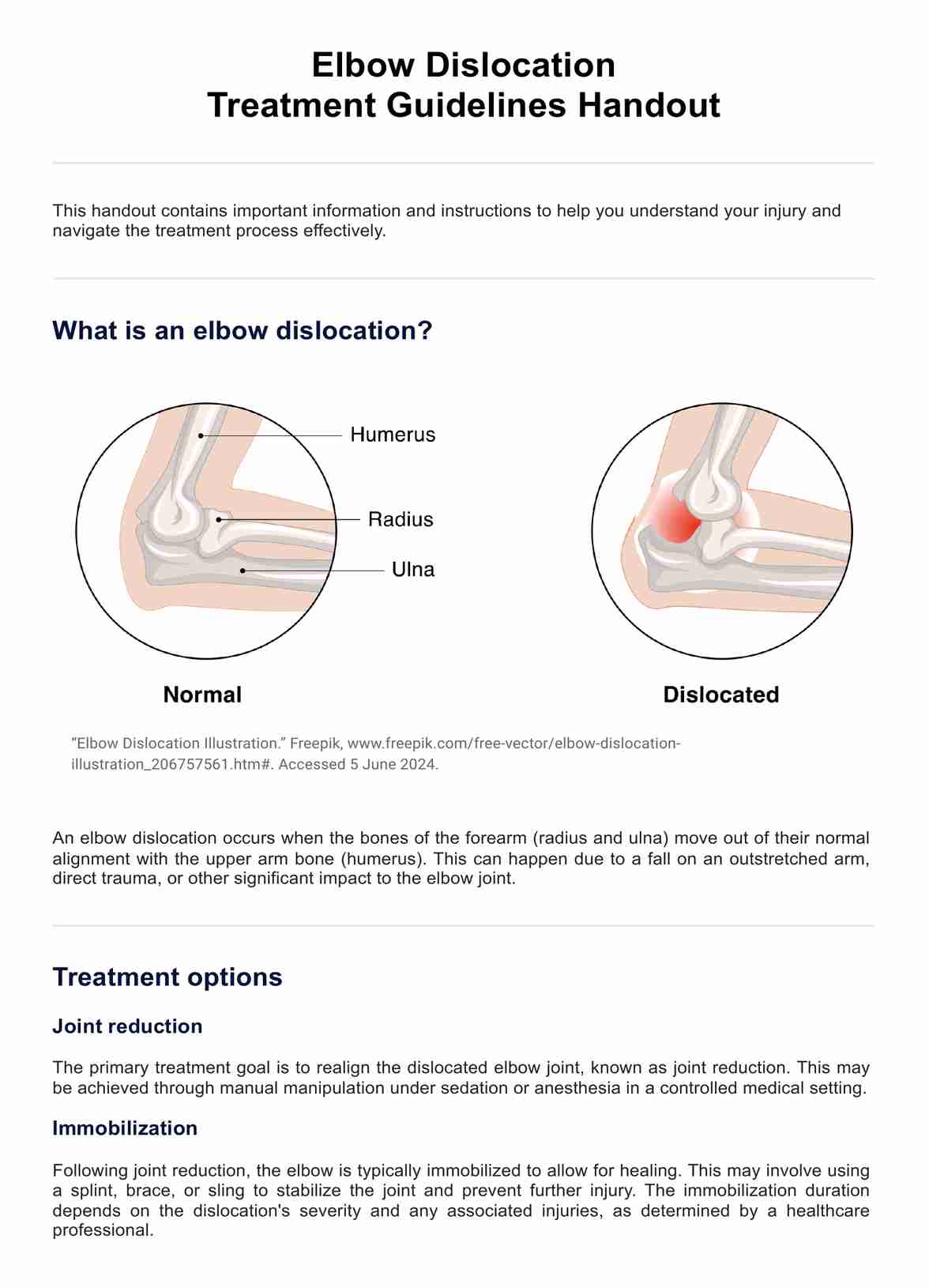
What does it mean to have a dislocated elbow joint?
A dislocated elbow joint results from the misalignment of the forearm bones (radius and ulna) with the upper arm bone (humerus) at the elbow joint, typically caused by a fall on an outstretched arm or direct trauma like a motor vehicle accident. This dislocation can be partial (subluxation) or complete, and it is categorized into simple, without major fractures, or complex, involving associated fractures.
Posterior dislocations, where the forearm is displaced behind the humerus, constitute the majority of cases. Symptoms of most elbow dislocations include intense pain, visible deformity, swelling, and restricted elbow movement, often accompanied by nerve or artery damage manifesting as numbness and poor hand circulation. Urgent medical intervention is crucial to realign the joint, followed by immobilization and rehabilitation.
While simple dislocations typically respond well to non-surgical methods, complex cases often necessitate surgery to repair fractures and ligament tears.
Common causes of elbow dislocation
Risk factors for elbow dislocation include participation in activities with a high risk of falls or direct trauma, such as contact sports or occupations involving manual labor. Common causes of elbow dislocation include acute events like a fall on an outstretched arm or a forceful impact to the elbow, leading to a simple elbow dislocation or complex dislocation. In simple elbow dislocations, there may be soft tissue injury without major fractures.
In contrast, complex dislocations often involve fractures and ligament tears, resulting in recurrent elbow instability and restricted range of motion. Posterior dislocations, where the forearm is displaced behind the humerus, are the most common, but anterior dislocations can also occur, particularly involving the radial head. Acute elbow dislocations require prompt medical attention to prevent further damage and restore joint alignment.
Problems elbow dislocation may cause
Elbow dislocation can lead to a range of problems, both immediate and long-term. Immediately following the dislocation, there can be severe pain, swelling, and deformity of the elbow joint. Nerve or artery damage may occur, resulting in numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hand and forearm due to impaired circulation or nerve compression.
Long-term complications may include chronic instability of the elbow joint, leading to recurrent dislocations or subluxations, which can significantly impair function and quality of life. There may be joint stiffness and limited range of motion, especially if the injury is not promptly treated or if there are associated fractures or soft tissue injuries. In some cases, arthritis may develop over time, further contributing to pain and decreased mobility in the affected elbow.
Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout Template
Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout Example
How are elbow dislocations treated?
After assessing the injury, possibly through X-rays or other imaging tests, determine the extent of the dislocation and any associated fractures or soft tissue injuries. Here are possible treatments that can be offered:
Joint reduction
The primary treatment for an elbow dislocation is to realign the dislocated joint, known as joint reduction. This procedure is typically performed through manual manipulation under sedation or anesthesia to ensure patient comfort and safety in a controlled medical environment. Elbow dislocations occur during a fall onto an outstretched hand as a combination of axial-compressive and rotational-shear forces are conducted across the elbow joint (McCabe & Savoie, 2012).
Immobilization
Post-reduction, the elbow is often immobilized to allow the joint and surrounding tissues to heal. This involves using a splint, brace, or sling to stabilize the elbow and prevent further injury. The duration of immobilization varies depending on the severity of the dislocation and any associated injuries, as determined by a healthcare professional (McCabe & Savoie, 2012).
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation is crucial to restore the affected elbow's strength, flexibility, and range of motion. Physical therapy exercises and techniques are prescribed to gradually strengthen the muscles around the elbow and improve joint mobility. Treatment advances are helping to improve results, and early movement helps minimize scar tissue and improve overall elbow motion (Gregory et al., 2023).
Surgical intervention (for complex dislocations)
Complex elbow dislocations or those accompanied by significant fractures or ligament injuries may require surgical intervention. Surgery aims to repair fractured bones, reconstruct damaged ligaments, or address other structural issues to restore stability and function to the elbow joint. Complex dislocations may require additional surgeries to repair blood vessels, nerves, and bone and ligament injuries (National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases., 2021).
What is an Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout?
An Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout is a document designed to provide comprehensive information and instructions to patients who have experienced an elbow dislocation. Typically created by healthcare professionals, such as orthopedic surgeons or physical therapists, the handout is a valuable resource to educate patients about their injuries and guide them through treatment and rehabilitation.
The handout conveys the following information:
- Treatment options: It outlines the various treatment options available for elbow dislocations, including joint reduction, immobilization, rehabilitation, and surgical intervention.
- Post-reduction care: It offers instructions on how to care for the elbow after joint reduction, including recommendations for immobilization with splints, braces, or slings and the importance of adhering to healthcare provider recommendations.
- Rehabilitation exercises: This section outlines specific exercises and techniques to help patients regain strength, flexibility, and range of motion in the affected elbow joint. These may include both in-clinic physical therapy sessions and at-home exercises.
- Pain management strategies: It provides information on pain management techniques, such as using ice packs, over-the-counter pain medications, or prescribed medications as directed by healthcare providers.
Benefits of using this handout
Using this Elbow Dislocation Treatment Guidelines Handout offers several benefits for both healthcare practitioners and their patients:
Consistency
Distributing a standardized handout ensures that all patients receive consistent information about elbow dislocation management, regardless of the healthcare practitioner they see.
Enhanced compliance
Patients are more likely to adhere to treatment recommendations when they have access to written instructions and guidance, leading to better outcomes and faster recovery.
Resource for reference
The handout is a valuable resource that patients can refer to throughout their recovery journey. It reinforces key concepts and provides reassurance as they progress.
Improved patient satisfaction
Providing patients with educational materials demonstrates a commitment to their care and enhances their overall satisfaction with the healthcare experience.
References
Gregory, J., Aibinder, W., & Athwal, G. (2023). Elbow dislocation. OrthoInfo. https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/diseases--conditions/elbow-dislocation
McCabe, M. P., & Savoie, F. H. (2012). Simple elbow dislocations: Evaluation, management, and outcomes. The Physician and Sportsmedicine, 40(1), 62–71. https://doi.org/10.3810/psm.2012.02.1952
National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases. (2021, September). Sports Injuries. https://www.niams.nih.gov/health-topics/sports-injuries
Commonly asked questions
Elbow dislocations typically occur due to a forceful impact on the elbow joint, such as a fall onto an outstretched hand or a direct blow to the elbow.
Clinical assessment involves evaluating the patient's history, conducting a thorough physical examination, assessing neurovascular status, and ordering appropriate imaging studies such as X-rays to confirm the diagnosis and assess for associated injuries.
Depending on associated fractures or soft tissue injuries, elbow dislocations can be classified as simple or complex. Posterior dislocations are most common, but anterior dislocations can also occur.