Bone Marrow
Discover the importance of Bone Marrow Tests in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Learn about the procedures, results, and reliability.


What is a Bone Marrow Test?
A bone marrow test, also known as a bone marrow biopsy or aspiration, is an essential medical procedure that provides crucial insights into the health of your bone marrow. Bone marrow, the soft, spongy tissue found within your bones, is the primary production center for blood cells. Your body depends on this vital tissue to produce red blood cells (to carry oxygen), white blood cells (to fight infections), and platelets (to help your blood clot).
This critical test plays a significant role in diagnosing various health conditions. It identifies and monitors diseases such as anemia, cancer like leukemia and lymphoma, infections, and other blood disorders. It can also provide invaluable insights into unexplained fevers, uncontrolled bleeding, and abnormalities in your blood count, such as a low platelet count.
Furthermore, a bone marrow test is often performed to check the treatment progress for these conditions or to determine if a previously diagnosed disease has progressed. It is also used to check for compatibility for bone marrow transplants. The procedure involves extracting a small sample of bone marrow, usually from the hip bone, using a long, thin needle. Although it may cause discomfort, it is generally safe, and complications are rare.
For more comprehensive information, please visit our resources, where you'll find detailed clinical documentation associated with bone marrow tests. This knowledge will empower you to approach this test confidently.
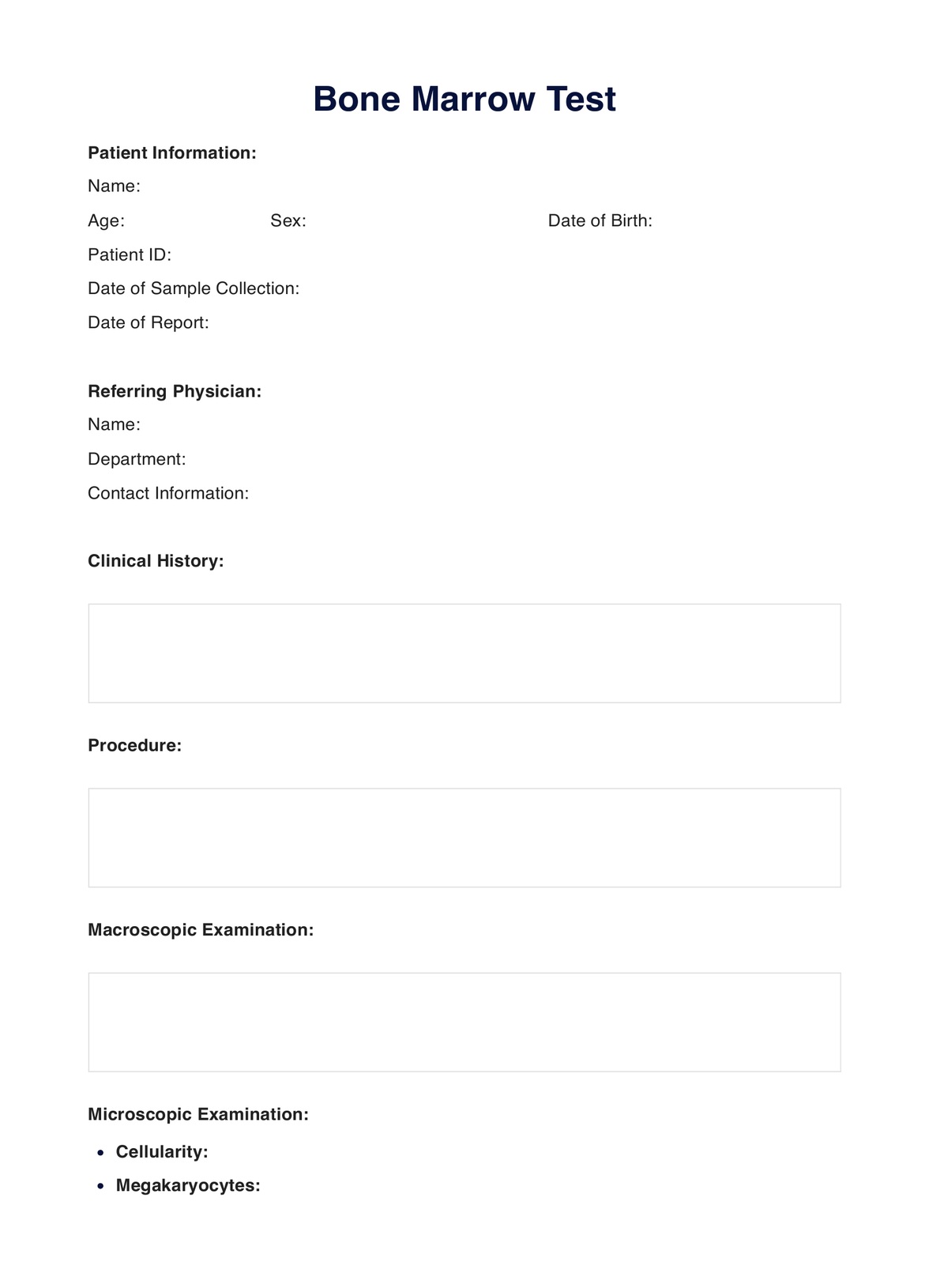
Bone Marrow Template
Bone Marrow Example
How Does it Work?
A bone marrow test is a highly specialized procedure that requires careful preparation, precise execution, and meticulous analysis. Here is a detailed walk-through of the process:
Step 1: Preparation
The first step in a bone marrow test involves preparing the patient for the procedure. The doctor will begin by cleaning the needle's insertion area, typically the hipbone or sternum. This is done to minimize the risk of infection.
To ensure comfort throughout the procedure, you may receive local anesthesia. This numbing medication is applied to the skin and underlying tissue, reducing any discomfort you might experience during needle insertion.
Step 2: Insertion
Once the area is cleaned and numbed, the doctor will proceed with the insertion phase. A special hollow needle, a biopsy needle, is gently but firmly inserted into the bone. The needle has a mechanism to retrieve a small sample of bone marrow tissue. This part of the procedure requires skill and precision to obtain a sufficient sample while minimizing discomfort.
Step 3: Sample Collection
After the bone marrow tissue is extracted, it's carefully placed in a sterile container. The sample is then sent to a laboratory for a comprehensive analysis. Medical technologists and pathologists will examine the sample under a microscope, looking for abnormalities in the blood cells and bone marrow tissue.
The results of the bone marrow test can provide valuable insights into your health, aiding in the diagnosis of various conditions and guiding treatment decisions.
We've created a printable Bone Marrow Test Procedure to provide a step-by-step overview of what to expect during your bone marrow test.
When Would you use This Test?
A bone marrow test provides in-depth information about the state of your bone marrow and the blood cells it produces, which can be instrumental in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Here are some scenarios where a bone marrow test could be instrumental:
Diagnosing Blood Disorders
A bone marrow test is often used when other tests, such as blood tests, fail to provide conclusive results or need more detailed information. This test can help diagnose different types of blood disorders, including anemia, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), and neutropenia (low count of a type of white blood cell).
Detecting Cancers
The test is critical in diagnosing cancers that affect the blood and bone marrow, such as leukemia and lymphoma. Doctors can identify cancerous cells by examining the bone marrow sample, determine the cancer stage, and plan appropriate treatment strategies.
Investigating Unexplained Anemia or Low Platelets
If you have unexplained anemia (a condition characterized by a lack of sufficient red blood cells) or low platelets, a bone marrow test can help uncover the underlying cause. It can reveal whether the bone marrow is producing enough of these cells or if there's an issue with their lifespan or distribution.
Monitoring Treatment Progress
A bone marrow test is also helpful for monitoring the treatment progress for diseases like cancer. It can show whether the treatment is working to reduce or eliminate cancerous cells in the bone marrow.
Checking for Bone Marrow Transplant Compatibility
Before a bone marrow transplant, a donor's and recipient's tissues must be matched to increase the chances of a successful transplant. A bone marrow test can provide this crucial information.
A bone marrow test is a valuable resource for healthcare providers. It provides critical insights that can aid in diagnosing, treating, and managing various health conditions. If you're a practitioner considering this procedure, remember that the benefits should always outweigh the risks for the patient.
What do the Results Mean?
Interpreting the results of a bone marrow test can be complex, as they provide a detailed overview of the various cell types in your bone marrow. The findings can point to different health conditions based on the count and characteristics of these cells.
For instance, if the test shows increased white blood cells, it might indicate an ongoing infection in your body. The bone marrow test results reflect the immune system producing more white blood cells to combat infections. In some cases, a high white blood cell count could also suggest a more severe condition like leukemia, a cancer affecting the blood and bone marrow.
Conversely, if your bone marrow test reveals a low platelet count, it could indicate a bleeding disorder or thrombocytopenia. Platelets are essential for blood clotting; a deficiency can lead to excessive bleeding or bruising. A low platelet count might also indicate anemia, in which your body lacks enough healthy red blood cells to carry adequate oxygen to your tissues.
It's important to remember that a healthcare professional should always interpret these results. They will consider your overall health, medical history, and other test results while analyzing the bone marrow test findings. This comprehensive evaluation ensures an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan. We have a free bone marrow test to help you understand what a bone marrow test report looks like.
Research & Evidence
Tracing back the history of bone marrow tests, these diagnostic tools have been used for over a century. The first attempts to acquire a bone marrow sample for diagnostic purposes were undertaken by an Italian physician named Pianese in 1903, marking the inception of this valuable medical procedure.
The technique used was trepanning or trephining, which involves drilling into the bone to obtain a marrow sample. Trepanning is one of the oldest known surgical procedures carried out by humans, dating back to the Neolithic period. However, in the last 100 years, this technique was adapted and refined for bone marrow biopsies.
These early efforts laid the foundation for modern bone marrow tests, which have become integral in diagnosing and monitoring various health conditions. Over the years, research has consistently demonstrated the reliability and effectiveness of bone marrow tests.
For instance, bone marrow aspiration, a method of extracting liquid marrow, is considered reliable and rapid for evaluating bone marrow pathology. It is especially preferred in clinically urgent situations.
Furthermore, the detailed analysis that a bone marrow examination provides??evaluating the morphology of the cells present and the percentages of specific cells in the marrow??is crucial in diagnosing severe health conditions.
Decades of use and extensive research have established the bone marrow test as a reliable diagnostic tool. Its application in the medical field has proven invaluable, from diagnosing blood disorders and cancers to monitoring treatment progress and checking for bone marrow transplant compatibility. This testing method's ongoing development and refinement continue to enhance its precision and applicability in various clinical settings.
References
- (N.d.). Retrieved from https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06749.x
- Parapia, L. A. (2007, October 1). Trepanning or trephines: a history of bone marrow biopsy. British Journal of Haematology; Wiley-Blackwell. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2007.06749.x
- The Importance of Trephine Biopsy and Aspirate in Bone Marrow. September 28, 2023. https://health.ucdavis.edu/blog/lab-best-practice/the-importance-of-trephine-biopsy-and-aspirate-in-bone-marrow-analysis/2021/02
- The Importance of Trephine Biopsy and Aspirate in Bone Marrow. September 28, 2023. https://health.ucdavis.edu/blog/lab-best-practice/the-importance-of-trephine-biopsy-and-aspirate-in-bone-marrow-analysis/2021/02
Commonly asked questions
Usually, hematologists, oncologists, or internal medicine specialists.
They're used when a blood test can't provide enough info about a suspected condition.
They diagnose and monitor various health conditions, including cancers and blood disorders.
The procedure usually takes about 10 to 20 minutes, but the entire process can take about an hour.

.jpg)