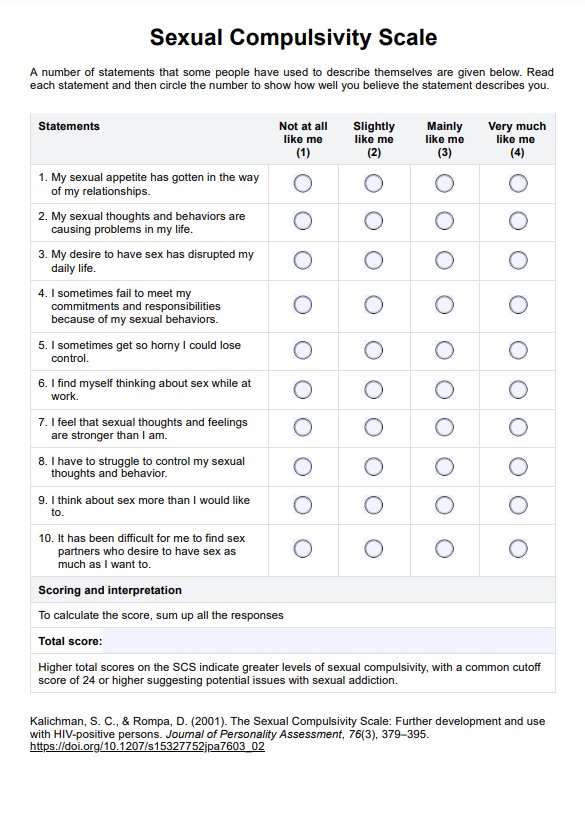
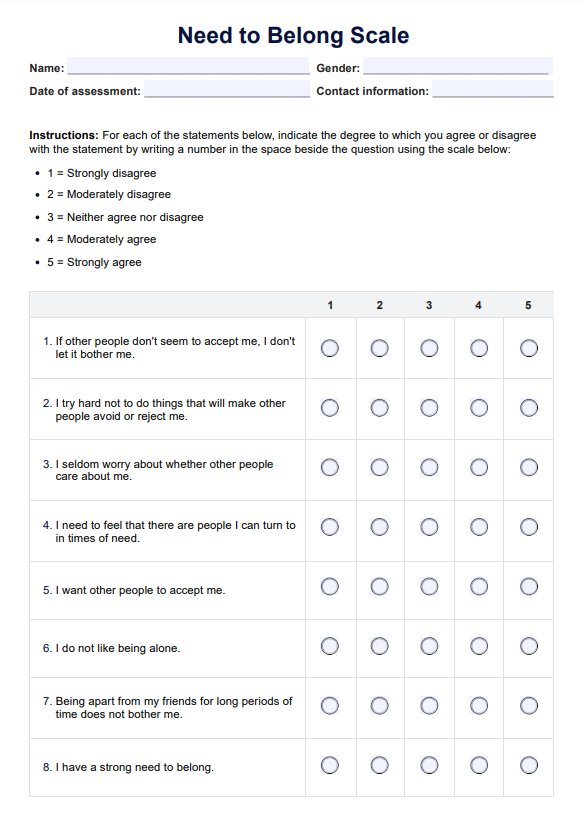
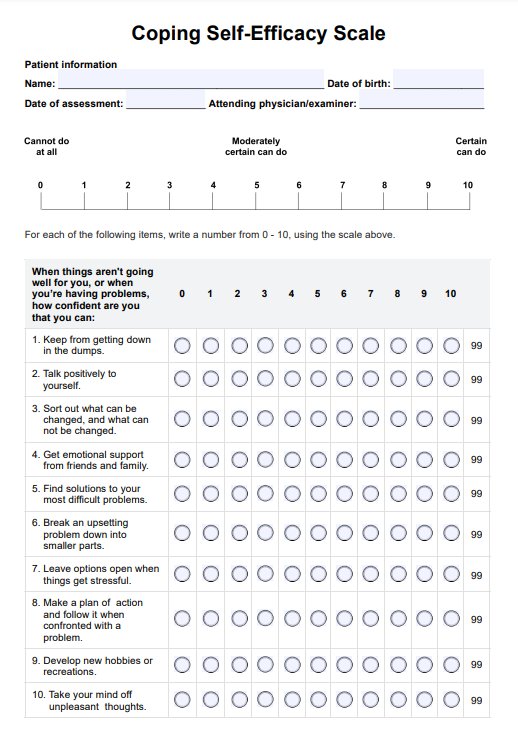
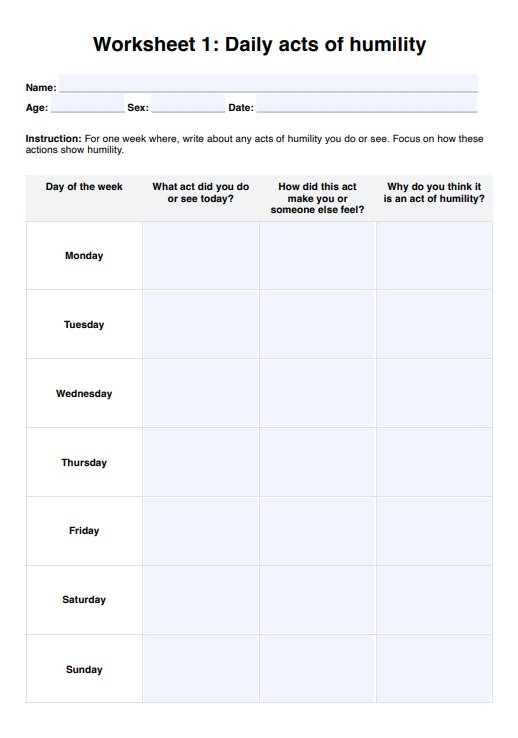
At Home STD Test
This guide for healthcare practitioners provides insights into At Home STD Tests, including sample collection, result interpretation, and patient counseling.


What is an At Home STD Test?
According to the Centers For Disease Control And Prevention, in 2020, the CDC's most recent report reveals that the United States recorded 2.4 million new cases of chlamydia, gonorrhea, and syphilis. This is amidst the COVID-19 pandemic with enforced social distancing measures. This figure is likely a conservative estimate, as individuals were less inclined to pursue testing from healthcare providers during the pandemic. This trend is expected to persist for several more years.
At Home STD Tests are a valuable addition to the toolkit of healthcare practitioners, offering patients a convenient and confidential means of assessing their sexual health. This guide is tailored to healthcare professionals and aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of At Home STD Tests and how to assist patients in their use
It is a discreet and accessible method for patients to screen for sexually transmitted infections without visiting a healthcare facility. As healthcare practitioners, it's essential to be well-informed about these tests and be prepared to guide patients effectively.
At Home STD Test Template
At Home STD Test Example
How Does it Work?
As healthcare practitioners, it's essential to be well-informed about these tests and be prepared to guide patients effectively.
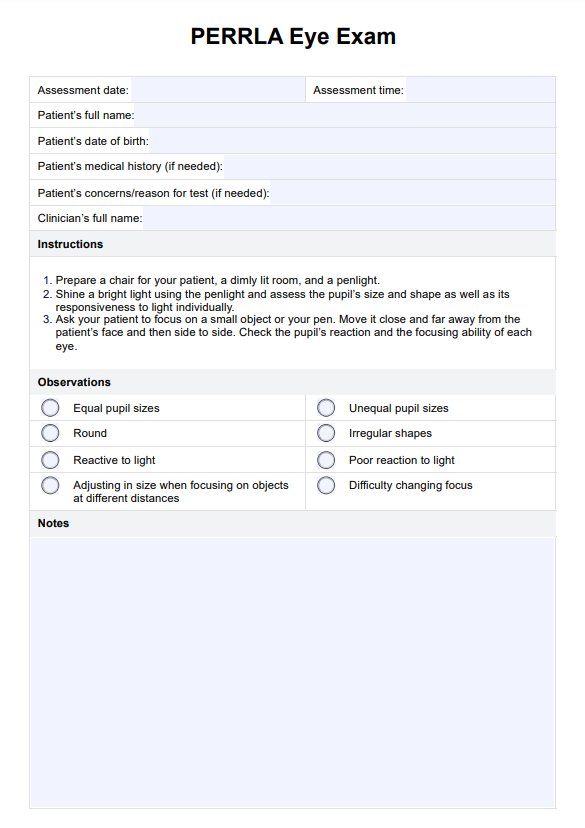
Step 1: Choose the Right Test
Understand the Printable At Home STD Test kits and their compatibility with different STIs. Be prepared to recommend specific tests based on a patient's sexual history and risk factors.
Step 2: Sample Collection
Educate patients on proper sample collection techniques, including blood, urine, and swabs. Address any concerns patients may have regarding the process.
Step 3: Sending Samples
Guide the shipping process and ensure patients understand the importance of following shipping instructions to maintain sample integrity.
Step 4: Receiving and Understanding Results
Assist patients in interpreting their results and explaining what negative and positive results mean for various STIs. Be prepared to address any questions or concerns regarding result accuracy.
Step 5: Next Steps
Outline the necessary actions for patients based on their test results. For negative results, emphasize the importance of continued safe practices and regular testing. For positive results, guide patients on seeking medical care and notifying sexual partners.
Step 6: Privacy and Support
Reinforce the privacy and confidentiality aspects of At Home STD Tests. Provide resources and counseling options for patients needing additional support or information.
When Would You Use This Test?
The At Home STD Test is a versatile and invaluable tool for a wide spectrum of healthcare practitioners, providing crucial diagnostic insights and assistance in managing patients, particularly those at risk of or diagnosed with sexually transmitted infections (STIs).
Primary care physicians rely on At Home STD Tests when patients present with symptoms or concerns about potential STIs, enabling timely diagnosis and treatment. Sexual health clinics find them indispensable for helping patients take control of their sexual well-being, especially when physical visits may be less confidential or challenging.
Community health workers incorporate these tests into outreach and prevention programs, making STI testing more accessible to underserved populations. For researchers, At Home STD Tests serve as a valuable resource for gathering data and contributing to a better understanding of the prevalence and distribution of these infections, furthering public health initiatives and enhancing patient care.
What do the Results Mean?
The results of a Free At Home STD Test are paramount in diagnosing and managing sexually transmitted infections (STIs). These results provide vital insights into a patient's sexual health and enable healthcare practitioners to make well-informed decisions.
If the test results indicate that all tested STIs are negative, it generally suggests that the patient is not infected with the evaluated STIs. However, it's crucial to emphasize that typical results do not entirely rule out the possibility of an STI, as some infections may not be detectable during the initial stages.
On the other hand, positive results for specific STIs typically indicate the presence of an infection. The severity of the elevation often corresponds with the seriousness of the infection. Higher levels may indicate more advanced stages of the STI.
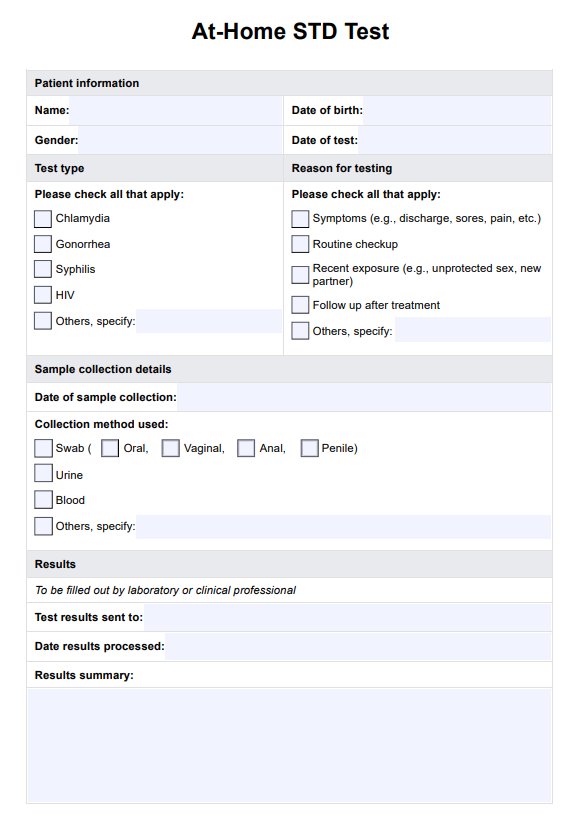
In the United States, chlamydia and gonorrhea are screened through nucleic acid amplification tests (NAAT) that allow individuals to collect their specimens at home and send them to a laboratory for analysis, with results provided via email or a secure portal. At-home testing for chlamydia and gonorrhea includes swabs for women (vaginal) and men (urethral) or a urine sample, all with clear instructions.
Syphilis testing requires a blood sample collected using a sterile needle or lancet in the kit, which individuals use for a fingerprick and then transfer the blood to a specialized card before sending it to the laboratory. The laboratory processes the samples and communicates the results promptly.
Commonly asked questions
Anyone concerned about their sexual health can request these tests.
�?�
Collect a sample per instructions, send it to a lab, and get results electronically.
Sample collection takes a few minutes, and results are usually available within a few days. Refer to the kit's instructions for specific timing.















-template.jpg)