Schatzker Classification Worksheet
Explore the Schatzker Classification system to effectively categorize and manage tibial plateau fractures, enhancing treatment accuracy.


What is the Schatzker Classification?
The Schatzker Classification system is a method used by medical professionals to categorize fractures of the tibial plateau. This is essential because it helps guide the treatment approach for these injuries. The tibial plateau, part of the top of the tibia or shinbone, is critical for knee joint stability and motion. Injuries to this area can significantly affect knee alignment and functionality.
Dr. Joseph Schatzker developed this classification system to provide a clear framework for describing the different types of tibial plateau fractures based on the fracture's characteristics and location. The system uses radiographic imaging to assess the extent and nature of the fracture, which in turn influences decisions about surgical or non-surgical treatments.
What are the classification of tibial plateau fractures?
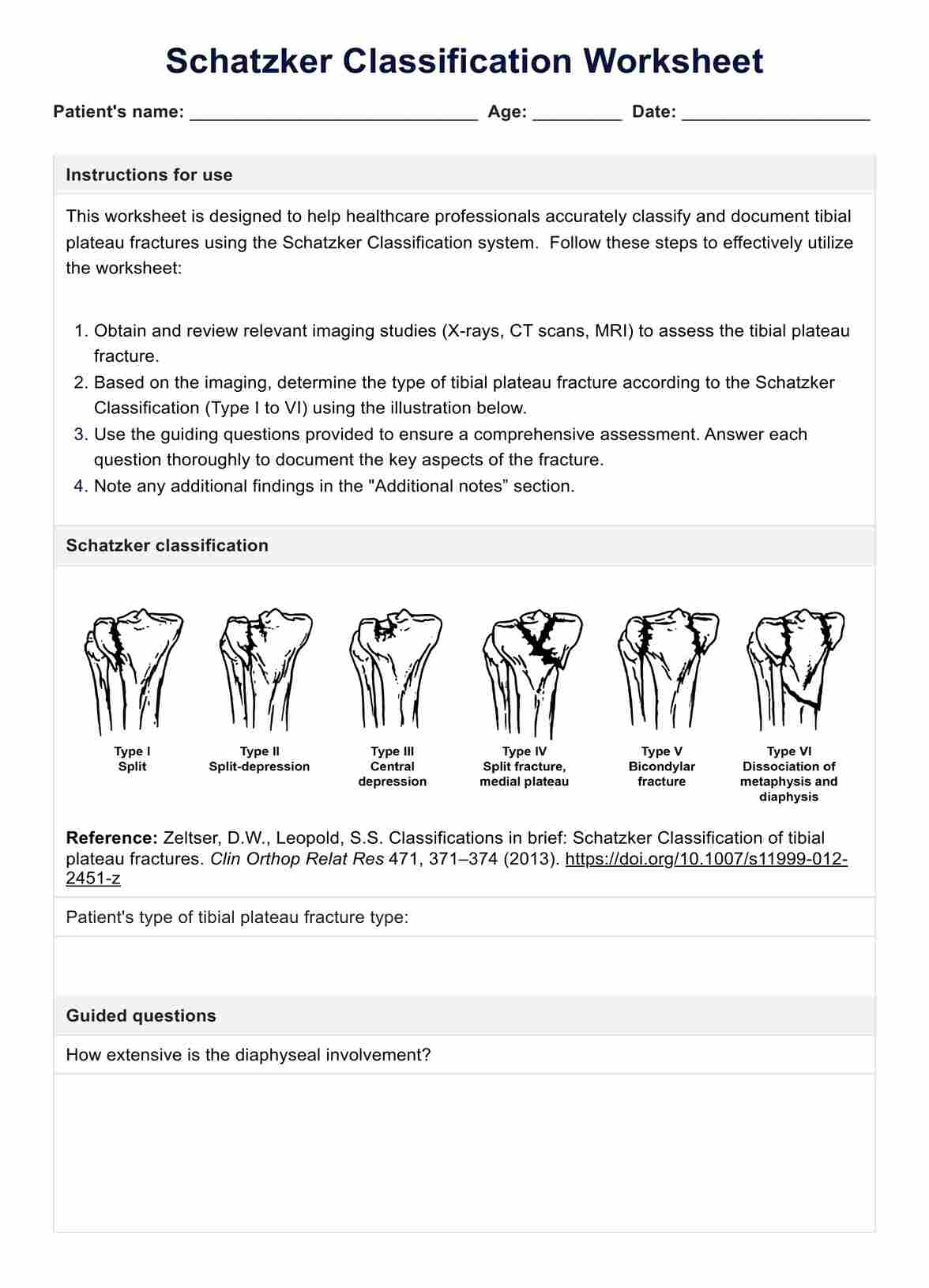
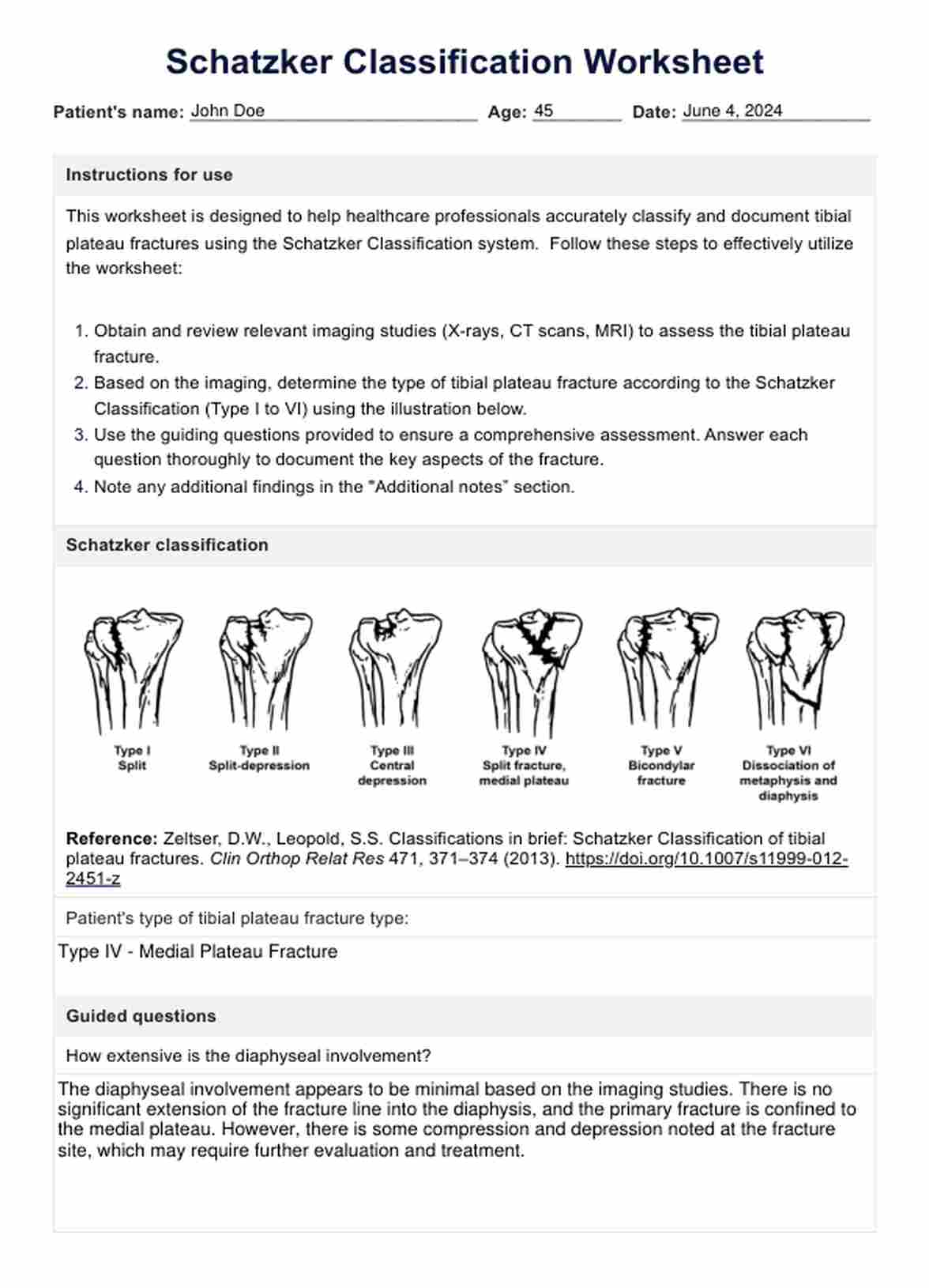
The Schatzker classification divides tibial plateau fractures into six types, each with distinct features:
- Type I: Lateral plateau fracture without depression. This type involves a cleavage fracture of the lateral tibial plateau without any significant depression of the bone.
- Type II: Lateral plateau fracture with depression. This type is similar to Type I, but it includes a depression of the fracture, where part of the bone is displaced downwards.
- Type III: Two subtypes fall under this classification, and these are:some text
- Type IIIA: Compression fracture of the lateral plateau. This subtype involves a pure depression of the lateral plateau without a cleavage component.
- Type IIIB: Compression fracture of the central plateau. This subtype involves a central depression and may significantly affect the knee's stability.
- Type IV: Medial plateau fracture. This type involves a fracture of the medial tibial plateau and is less common but more severe due to the higher forces typically required to cause a fracture in this thicker, stronger part of the bone.
- Type V: Bicondylar plateau fracture. This type involves fractures of both the medial and lateral tibial plateaus, usually indicating severe trauma and a complex injury pattern.
- Type VI: Plateau fracture with diaphyseal discontinuity. This type extends from the plateau into the shaft of the tibia, disrupting the alignment and integrity of both the plateau and the diaphyseal area.
Each type of fracture in the Schatzker Classification can suggest different treatment options and have different prognoses. Therefore, accurate fracture classification is crucial for achieving the best possible outcomes for patients with tibial plateau fractures.
Schatzker Classification Worksheet Template
Schatzker Classification Worksheet Example
Is a tibial plateau fracture a serious bone and soft tissue injury?
A tibial plateau fracture is considered a serious injury involving the bone and soft tissue around the bone joint surrounding it. This type of fracture occurs at the top of the shinbone (tibia) and affects the knee joint. Here's a closer look at why it's taken seriously:
Bone injury
The tibial plateau is critical for weight-bearing and stability in the knee joint. A fracture in operative tibial plateau fractures in this area can vary in severity from simple cracks in the bone to more complex fractures that involve the bone shattering into multiple pieces. The severity of the fracture often depends on the force of the impact, such as a fall from a significant height or a direct blow to the knee, like in a car accident. Complex fractures can lead to knee instability, alignment changes, and long-term issues such as arthritis if not properly treated.
Soft tissue injury
In addition to the bone, the soft tissues surrounding the tibia can also be affected. This includes muscles, ligaments, tendons, and the meniscus. Damage to these components can complicate the healing process, as they play a crucial role in the knee's movement and stability. Soft tissue injuries can lead to prolonged swelling, pain, and reduced mobility. Furthermore, there can be complications from soft tissue swelling, like compartment syndrome, where swelling leads to increased pressure in a closed muscle compartment, which is a medical emergency.
Treatment and recovery
Treatment for a tibial plateau fracture typically involves a combination of surgery to fix the bone fragments (if the fracture is displaced) and rehabilitation to restore function and strength to the knee. The recovery time can be extensive, often taking several months, and may include physical therapy to aid in regaining full knee function. In severe cases, even with proper treatment, individuals might experience long-term complications such as decreased range of motion, chronic pain, or arthritis.
Because of the complexities involved in both the treatment and the recovery process and the significant impact on mobility and quality of life, tibial plateau fractures are considered very serious injuries. Proper medical evaluation and treatment are crucial to minimize long-term effects and help individuals return to their normal activities.
Treatments for tibial plateau fracture
Treatment for a tibial plateau fracture depends on the severity and specifics of the fracture, such as its location, the degree of bone displacement, and associated soft tissue injuries. Here’s an overview of the common treatment options:
Non-surgical treatment
Non-surgical methods may be sufficient for less severe tibial plateau fractures, particularly those where the bone fragments have not moved out of their original position (non-displaced). These treatments protect the bone while it heals and maintain mobility to prevent stiffness and muscle loss.
Immobilization
Immobilizing the knee with a cast or brace helps keep the joint stable, ensuring the bones heal correctly. Patients are typically advised to avoid bearing weight on the affected leg and use crutches or a walker to support mobility.
Weight-bearing restrictions
Patients are advised to avoid placing weight on the injured leg for a specified period, depending on the severity of the fracture and healing progress. This is monitored through regular follow-ups and imaging tests.
Physical therapy
Initiating physical therapy after trauma surgery as the bone begins to heal is crucial for restoring strength and mobility to the knee. This phase helps regain muscle strength, improve joint function, and facilitate a gradual return to daily activities.
Surgical treatment
In cases where the tibial plateau fracture involves displaced bone fragments or significant damage to the knee joint, surgical intervention is often required. Surgery aims to realign the bone fragments, stabilize the joint, and repair any associated soft tissue injuries, thus ensuring proper healing and reducing the risk of long-term complications.
Reduction and fixation
This procedure involves realigning the displaced bone fragments and securing them with metal hardware such as plates, screws, or nails to stabilize the fracture.
Arthroscopy
A minimally invasive technique used primarily to evaluate and repair internal joint damage. Surgeons make small incisions and use specialized instruments to view and repair the joint without needing large incisions.
Reconstructive surgery
For extensive injuries, reconstructive surgery may be necessary to rebuild the joint surfaces or correct deformities caused by the fracture. This involves more complex procedures that can significantly improve the functional outcome of the knee.
Rehabilitation
After surgical treatment, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is essential. This program includes physical therapy to reduce swelling, enhance joint mobility, and strengthen the muscles around the knee. The primary goal is to ensure a gradual return to normal activities after joint surgery while managing pain and preventing joint stiffness.
How to use this Schatzker Classification Worksheet
The Schatzker Classification Worksheet is an invaluable resource for orthopedic surgeons treating tibial plateau fractures. This guide helps systematically identify, classify, and manage various types of fractures based on their complexity and specific characteristics. Follow these steps to utilize the worksheet in clinical practice effectively:
Step 1: Identify the fracture pattern
Begin by examining the X-ray images of the tibial plateau fracture. Compare the observed fracture pattern with the images in the worksheet. Each type, from I to VI, corresponds to a distinct pattern, ranging from simple splits to complex dissociations involving the metaphysis and diaphysis.
Step 2: Categorize the fracture type
Based on your comparison, categorize the fracture into one of the six types shown in the worksheet. Consider the location of the fracture (lateral, medial, or central), the presence of depression, and whether the fracture extends through the metaphysis or diaphysis.
Step 3: Consider associated injuries
Evaluate for any associated injuries such as soft tissue damage, meniscal tears, or ligament injuries. These associated injuries can influence the treatment plan and should be considered alongside the bone fracture classification.
Step 4: Plan the treatment strategy
Use the identified fracture type to plan the appropriate treatment strategy. The worksheet provides insights into the typical treatment approaches for each type of fracture, ranging from conservative management with immobilization to surgical intervention.
Step 5: Document and monitor
Record the classification and treatment plan in the patient's medical records. Use the worksheet as a guide to monitor the patient’s progress and recovery, adjusting the treatment plan as necessary based on healing and any complications that may arise.
Benefits of using this worksheet
The Schatzker Classification Worksheet is a crucial tool in managing tibial plateau fractures, allowing medical professionals to systematically assess and categorize these injuries. By employing this classification system, clinicians are better equipped to understand the fracture's extent, directly influencing treatment strategies and anticipated recovery outcomes. Below are the key benefits of utilizing the Schatzker Classification Worksheet in clinical practice:
Enhanced accuracy in diagnosis
The worksheet helps clinicians accurately classify the type of tibial plateau fracture based on detailed criteria. This precision is crucial for effective treatment planning and outcomes.
Improved communication
It facilitates clear and consistent communication among healthcare providers. By using a standardized classification, all members of the medical team, including surgeons, radiologists, and physical therapists, can have a common understanding of the injury's severity and complexity.
Streamlined treatment planning
The Schatzker Classification Worksheet aids in streamlining treatment planning by providing a clear framework for deciding on the best course of action based on the fracture type. This can lead to more targeted and effective interventions, potentially improving patient outcomes and reducing recovery times.
Commonly asked questions
The Schatzker Classification system categorizes tibial plateau fractures based on the fracture pattern and severity, helping guide treatment options and prognosis. It comprises six types, ranging from Type I (simple cleavage of the lateral plateau) to Type V and VI (severe comminuted fracture extending into the metaphysis).
The Schatzker lassification helps determine the appropriate treatment by indicating the complexity and stability of the fracture. Lower types VI fractures (I-III) are often treated non-surgically or with minimal fixation, while higher types (IV-VI) typically require more complex surgical interventions.
Yes, the Schatzker Classification can help predict long-term outcomes, as higher types are often associated with more severe injuries, longer recovery times, and a higher likelihood of complications such as arthritis or chronic pain.