Olecranon Fracture Classification Table
Explore the major classification systems for olecranon fractures—Mayo, Schatzker, and AO/OTA—to understand how these guide treatment strategies and predict outcomes in elbow injuries.


What is an olecranon fracture?
An olecranon fracture is a break in the bony tip of the elbow, known as the olecranon, which forms part of the ulna—one of the three bones comprising the elbow joint. Such fractures are frequently the result of a direct impact to the elbow or a fall onto an outstretched hand, which places significant stress on the elbow joint. These fractures can vary widely in their presentation, ranging from simple cracks that do not affect joint stability to more complex intra-articular fractures where the fracture extends into the elbow joint.
Key variations include displaced fractures, where the bone pieces shift out of alignment, and non-displaced fractures, where the bones maintain normal alignment. The fracture pattern can be simple, with a clean break, or complex, involving comminuted (multiple fragments) or oblique (angled) breaks. A transverse impacted fracture type features a horizontal fracture line across the bone, further complicating the injury if the fragments are driven into each other.
In some cases, the fracture may involve the radial head or occur distally, affecting the stability of the entire upper extremity. Each type of olecranon fracture requires careful assessment to determine the most appropriate treatment to ensure proper healing and restoration of arm function.
Symptoms of an olecranon fracture
The symptoms of an olecranon fracture typically include:
- Pain and tenderness at the elbow
- Swelling and bruising around the elbow
- Difficulty in bending and straightening the arm
- A noticeable deformity if the bone pieces are displaced
Causes of an olecranon fracture
Olecranon fractures can occur due to various reasons, such as:
- A direct impact to the elbow from a fall or blow
- Indirect trauma, such as landing on an extended arm during a fall
- Repetitive stress injuries in athletes or manual laborers
Diagnosing an olecranon fracture
The diagnosis of an olecranon fracture begins with a comprehensive physical examination. During this examination, a healthcare provider assesses the elbow for pain, swelling, and limited range of motion, which indicate a possible fracture. The visual and physical signs provide initial clues about the nature of the injury.
Following the physical exam, imaging tests play a crucial role. X-rays are typically the first step in imaging, as they clearly show bone breaks and alignments. They help confirm the presence of a fracture and provide detailed information about its location and severity.
In cases where more detail is needed, especially to assess any associated injuries to ligaments, tendons, or cartilage, a CT scan may be performed. CT scans offer a more detailed view of the bone and surrounding structures, aiding in a comprehensive assessment.
Occasionally, an MRI might be recommended if there's a suspicion of significant soft tissue damage or to get a clearer view of complex fractures. MRIs are particularly useful for visualizing bone and soft tissue injuries, providing a complete picture informing the treatment plan.
Together, these diagnostic tools enable a precise understanding of the fracture, which is crucial for developing an effective treatment strategy.
Olecranon Fracture Classification Table Template
Olecranon Fracture Classification Table Example
Classification systems of olecranon fractures
Classification systems for olecranon fractures are pivotal in guiding the therapeutic approach and forecasting patient outcomes. These systems categorize fractures based on specific criteria, such as displacement, joint involvement, and the nature of the fracture.
Mayo Classification
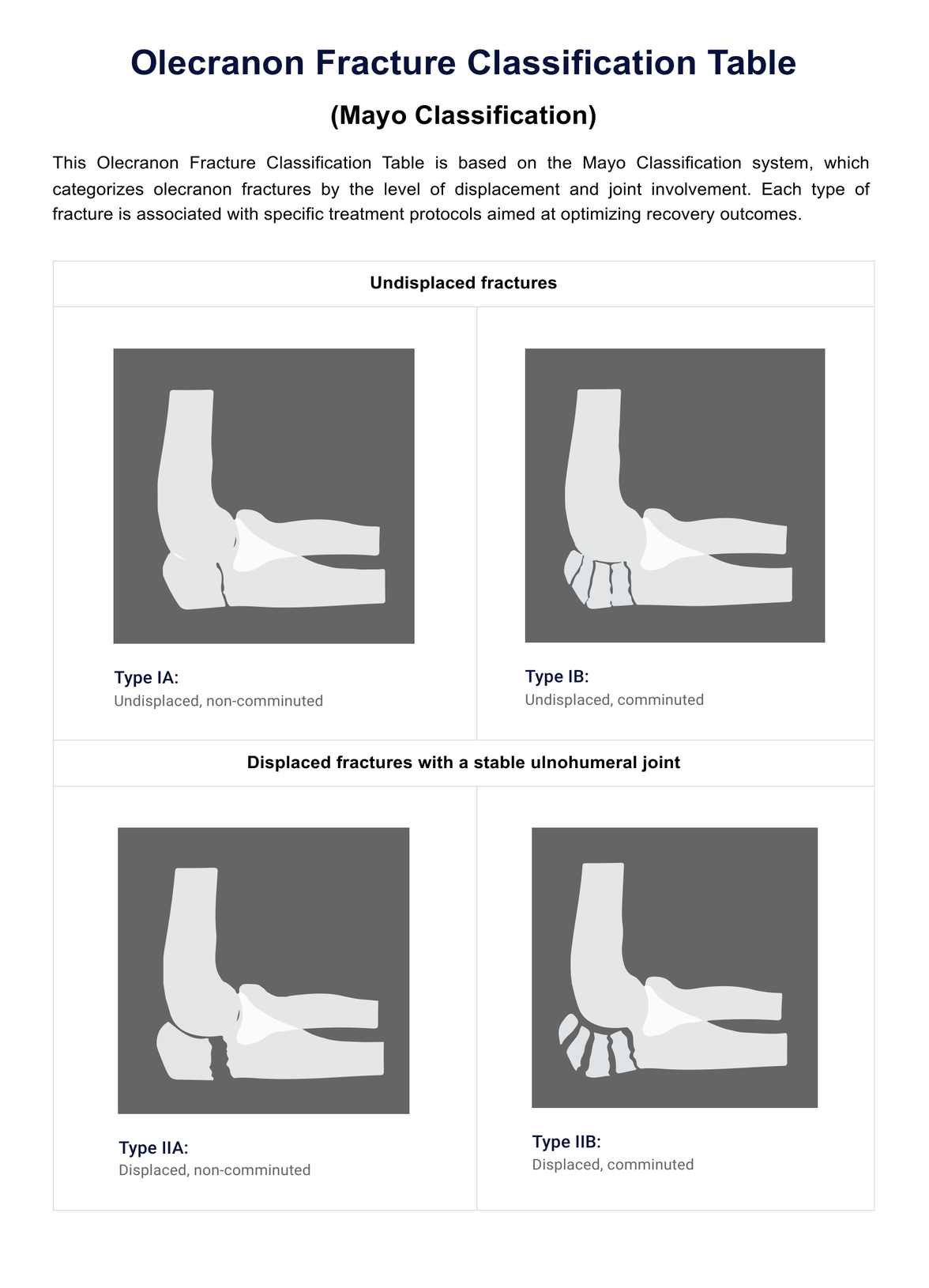
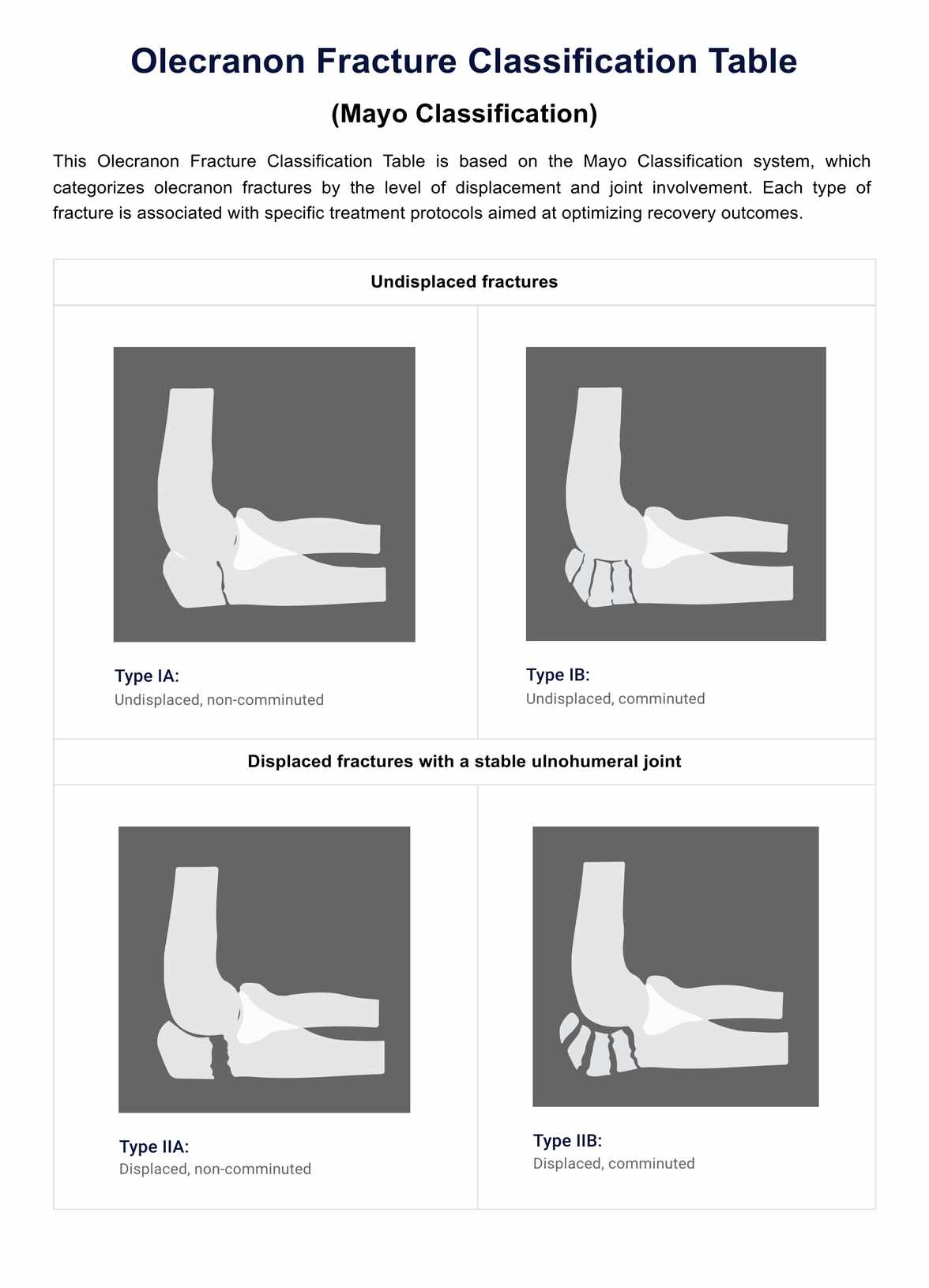
The Mayo Classification system stratifies olecranon fractures into three types based on the displacement and the stability of the fracture:
- Type I: Undisplaced fracturessome text
- Type IA: Undisplaced, non-comminuted
- Type IB: Undisplaced, comminuted
- Type II: Displaced fractures with a stable ulnohumeral jointsome text
- Type IIA: Displaced, non-comminuted
- Type IIB: Displaced, comminuted
- Type III: Displaced fractures with an unstable ulnohumeral jointsome text
- Type IIIA: Unstable, non-comminuted
- Type IIIB: Unstable, comminuted
Schatzker Classification
The Schatzker classification system focuses on the fracture morphology to categorize olecranon fractures:
- Type A: Simple transverse fracture
- Type B: Transverse impacted fracture
- Type C: Oblique fracture
- Type D: Comminuted fracture
- Type E: Oblique fracture distal to the midpoint of the trochlea
- Type F: Associated with radial head fracture
AO/OTA Classification
The AO/OTA classification system provides a detailed framework based on the location of the fracture and the extent of bone fragmentation:
- Type A: Extra-articular unifocal or 2-part proximal humeral end segment fracturessome text
- A1: Unifocal tuberosity fracture
- A2: Surgical neck fracture
- A3: Unifocal vertical metaphyseal extra-articular fracture
- Type B: Extra-articular bifocal or 3-part proximal humeral end segment fracturessome text
- B1: Extra-articular surgical neck with greater tuberosity fracture
- B1.2: Surgical neck with lesser tuberosity fracture
- Type C: Multifocal fracturessome text
- C1: Anatomical neck fracture
- C3: Anatomical neck with metaphyseal fracture
These classification systems are essential for accurately diagnosing the type of olecranon fracture, which helps in planning the appropriate treatment. They consider various important factors such as intra-articular involvement, displaced or fragmented bones, and the overall impact on the elbow’s structural integrity. This structured approach ensures tailored and effective treatment plans for individuals suffering from upper extremity fractures.
How to use our Olecranon Fracture Classification Table template?
To effectively utilize our Olecranon Fracture Classification Table template, follow these step-by-step instructions:
- Download the template: Start by downloading our user-friendly template from our website. This is your essential first step to access a well-structured tool that facilitates the classification of olecranon fractures.
- Identify the fracture type: Using the Mayo Classification system within the template, identify the specific type of olecranon fracture. The template is designed to help you accurately categorize the fracture based on characteristics like displacement, joint involvement, and fragmentation.
- Guide treatment and documentation: Then, you can use this classification template to guide your treatment plan, as different types of olecranon fractures require specific surgical techniques.
By following these steps, the Olecranon Fracture Classification Table template simplifies the classification process and enhances the effectiveness of patient treatment and care documentation.
Treatments for olecranon fractures
The treatment of olecranon fractures varies significantly depending on the type and severity of the fracture. For less severe, non-displaced fractures, non-surgical treatment is typically recommended. This approach involves immobilizing the elbow using a cast or splint, which helps maintain the alignment of the bone while it heals naturally. This method is often accompanied by physical therapy to restore strength and mobility as the healing progresses.
In cases where the fracture is displaced or involves the elbow joint, surgical intervention may be required. Surgical techniques can include internal fixation, where screws, plates, or rods are used to secure the bone fragments into their correct position. Another method is tension band wiring, which uses wires or cables to stabilize the bone. In more complex or severe fractures, particularly those involving extensive damage to the joint, joint replacement surgery might be necessary.
These surgical treatments aim to restore the elbow's alignment and function, prevent complications, and expedite the return to normal activity. Rehabilitation, including physical therapy, is typically required following surgery to ensure full joint function and strength recovery.
Commonly asked questions
An olecranon fracture is a break in the elbow's olecranon process, impacting elbow motion and stability.
Fractures are classified based on displacement, involvement of the elbow joint, and the fracture's morphology, using systems like Mayo, Schatzker, and AO/OTA.
Treatment can range from conservative methods like casting to surgical interventions such as internal fixation or joint replacement, depending on the fracture's classification.

.jpg)